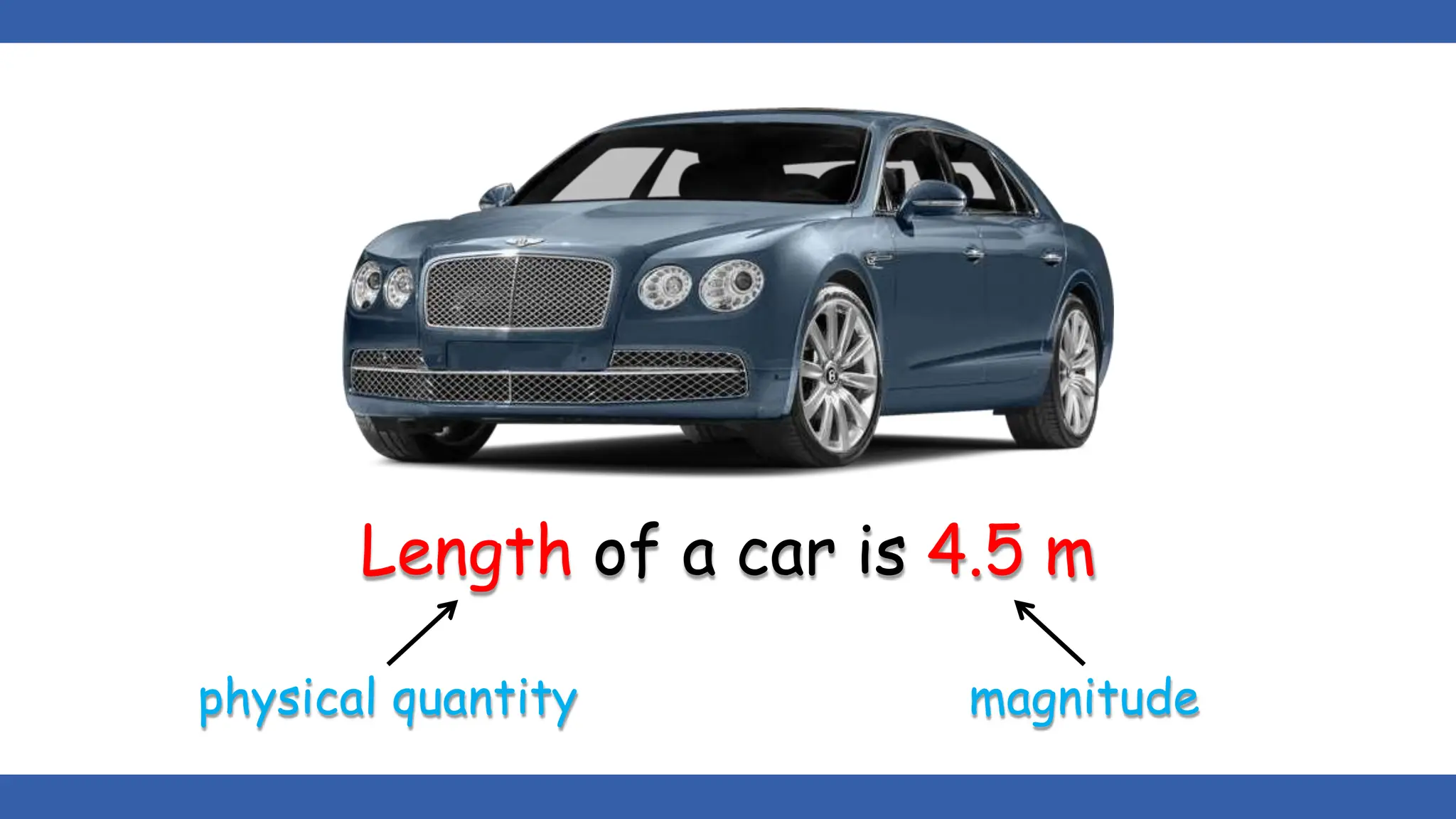
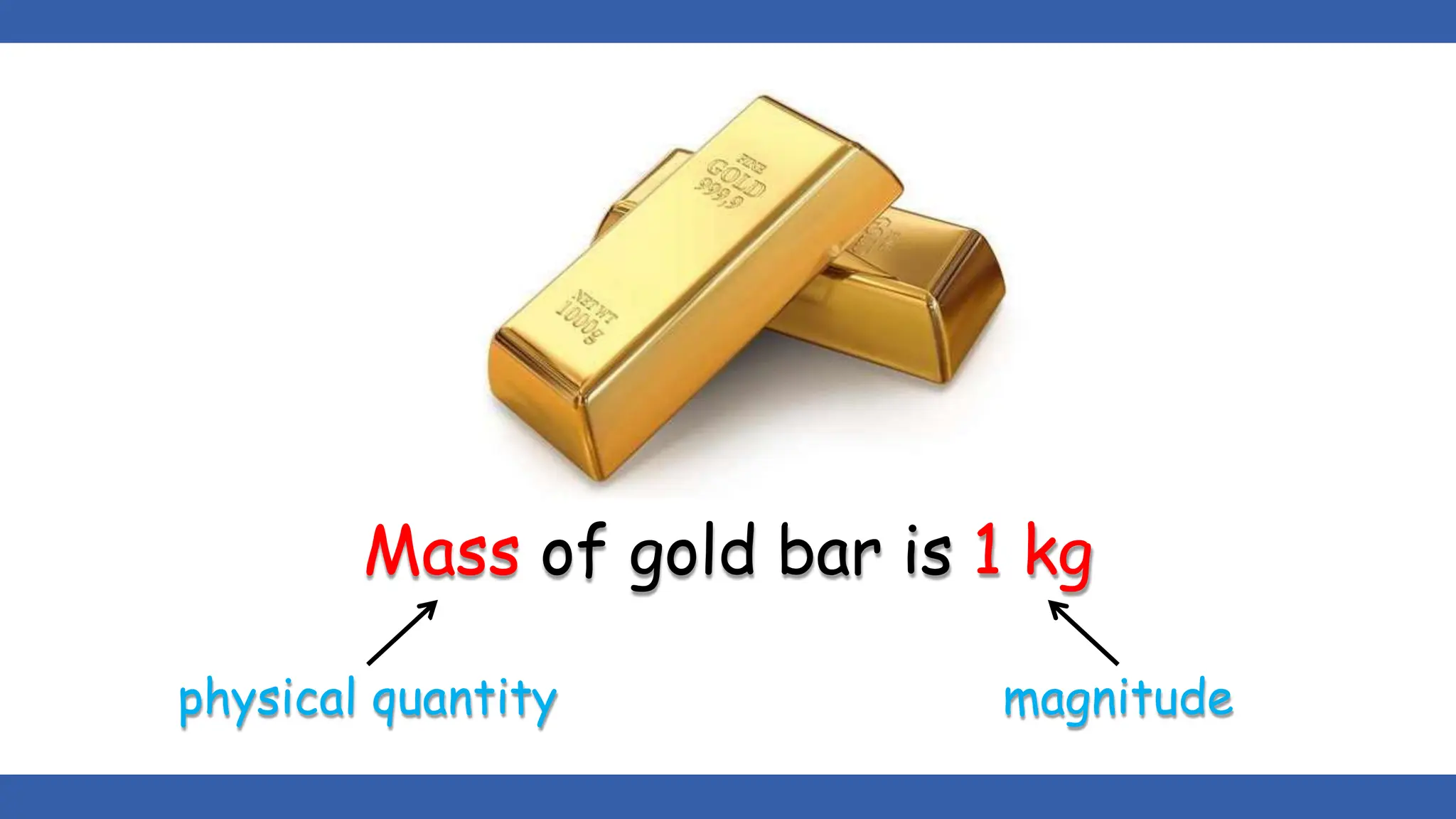
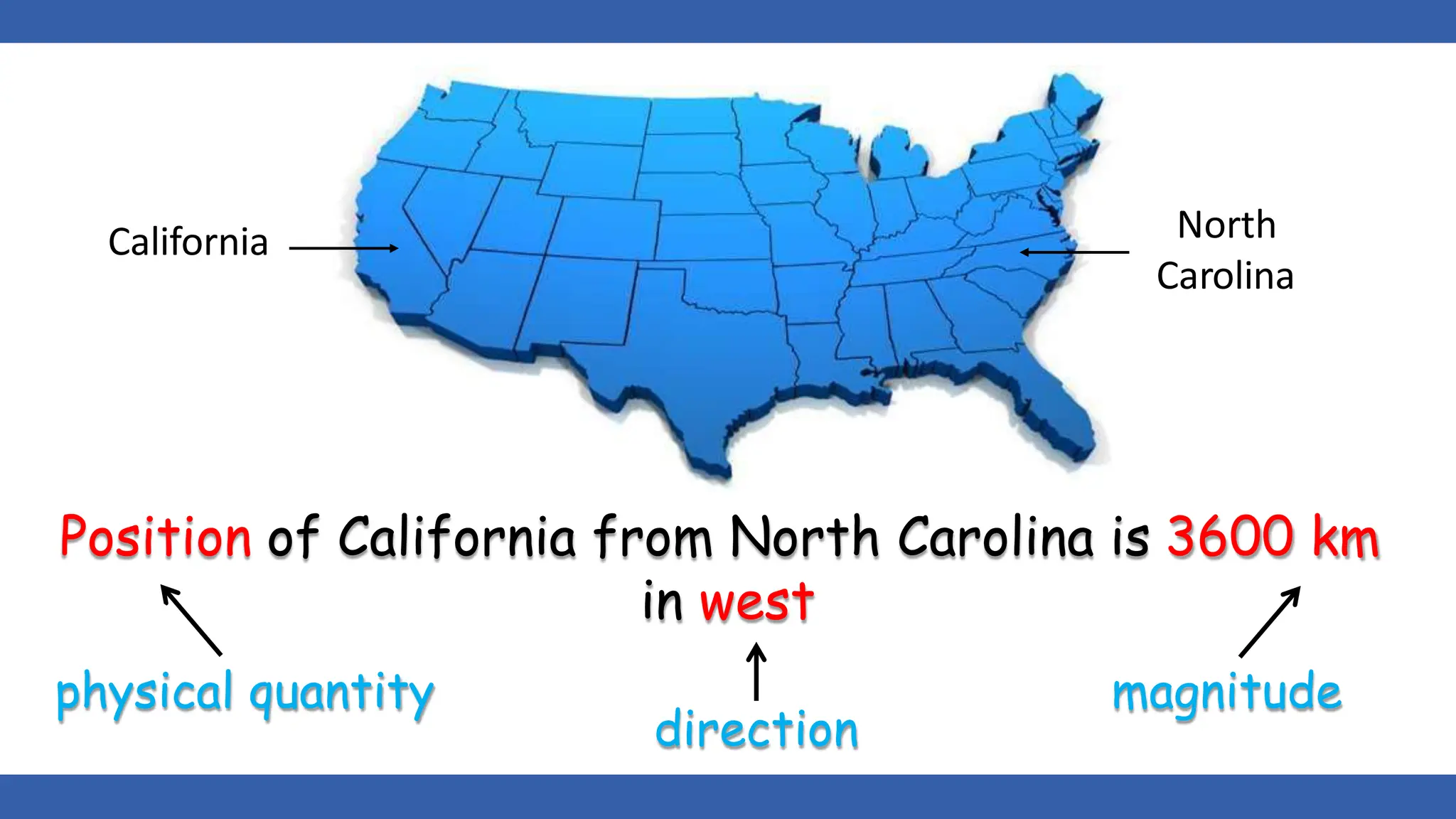
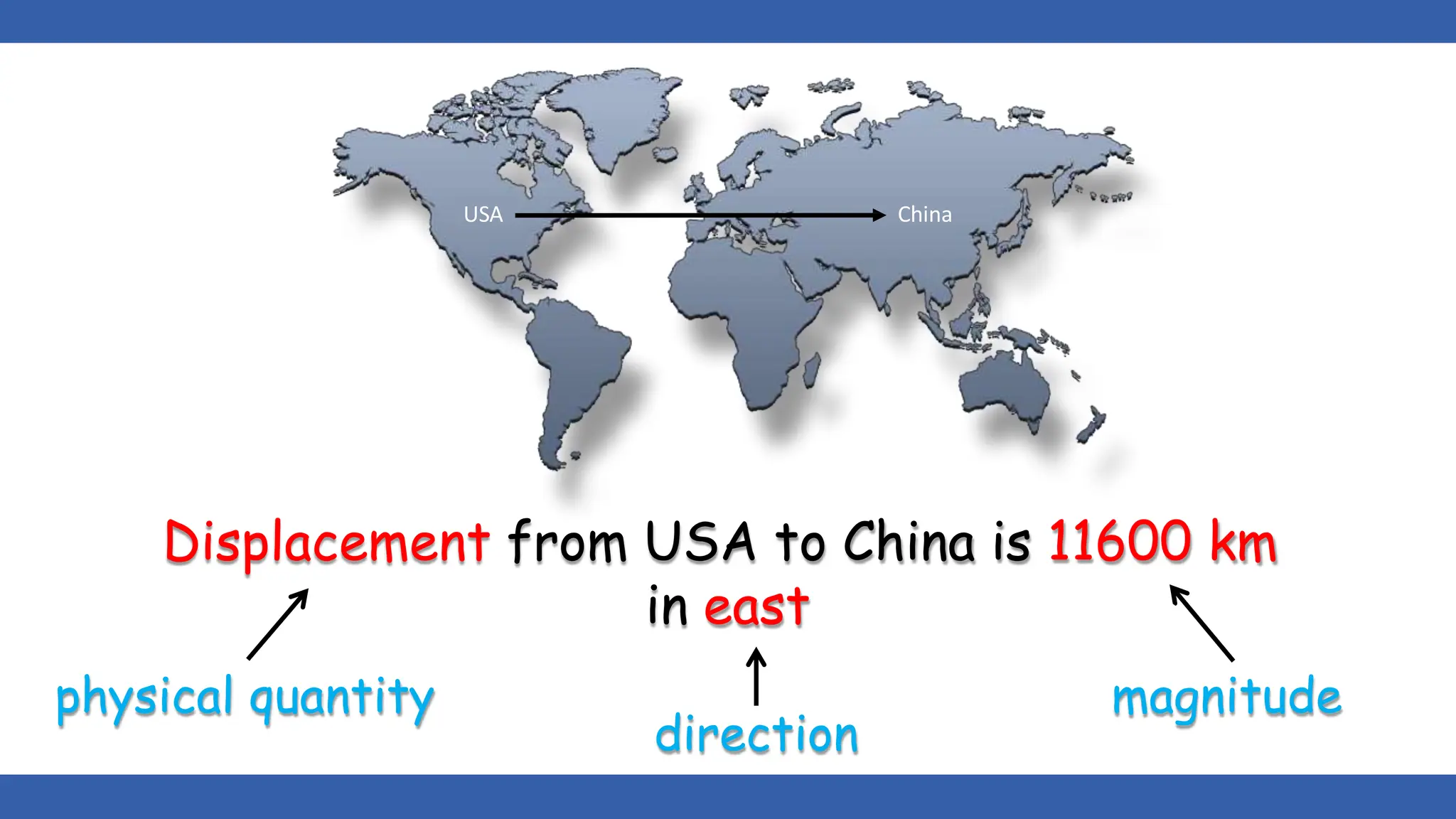
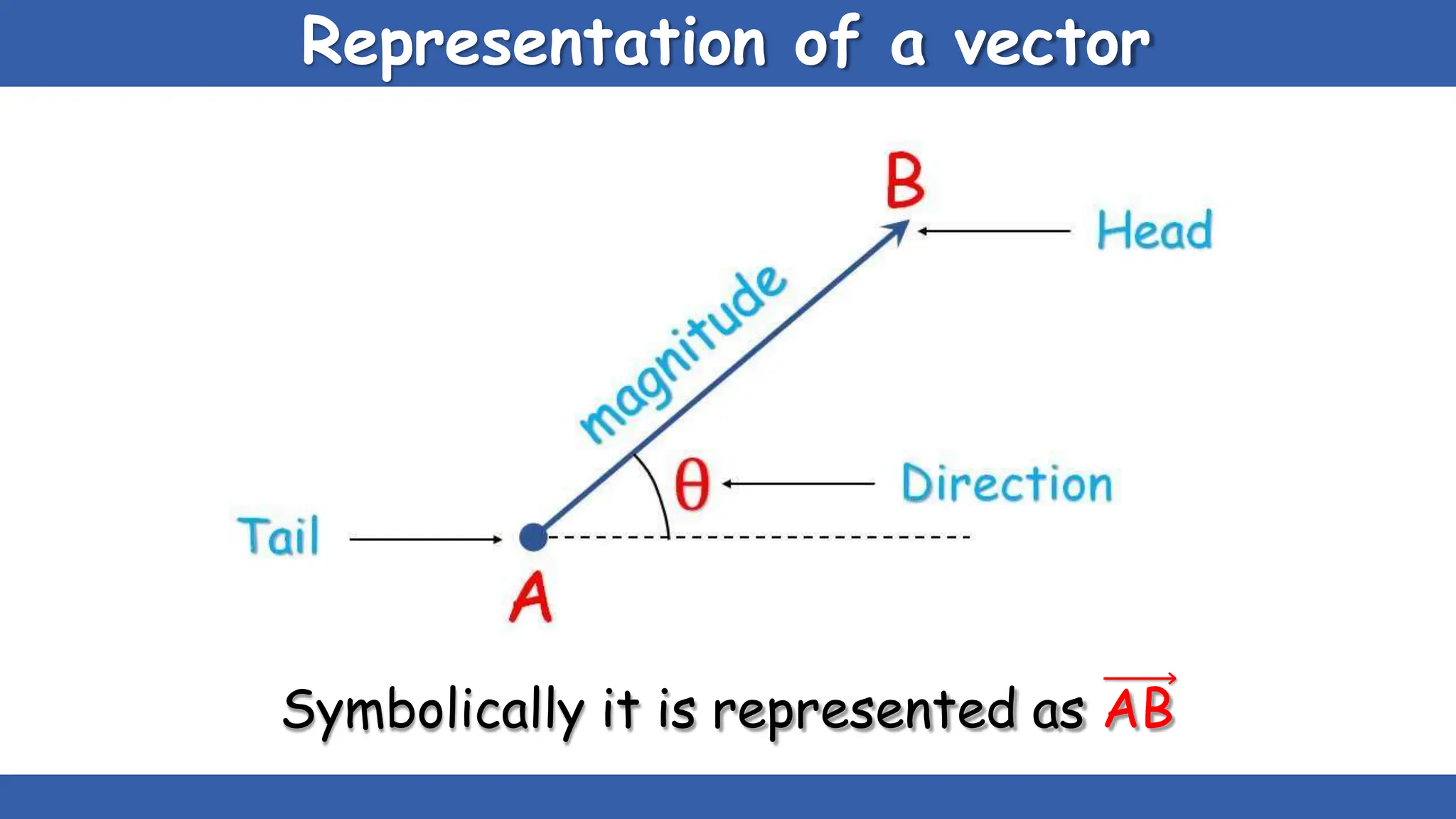
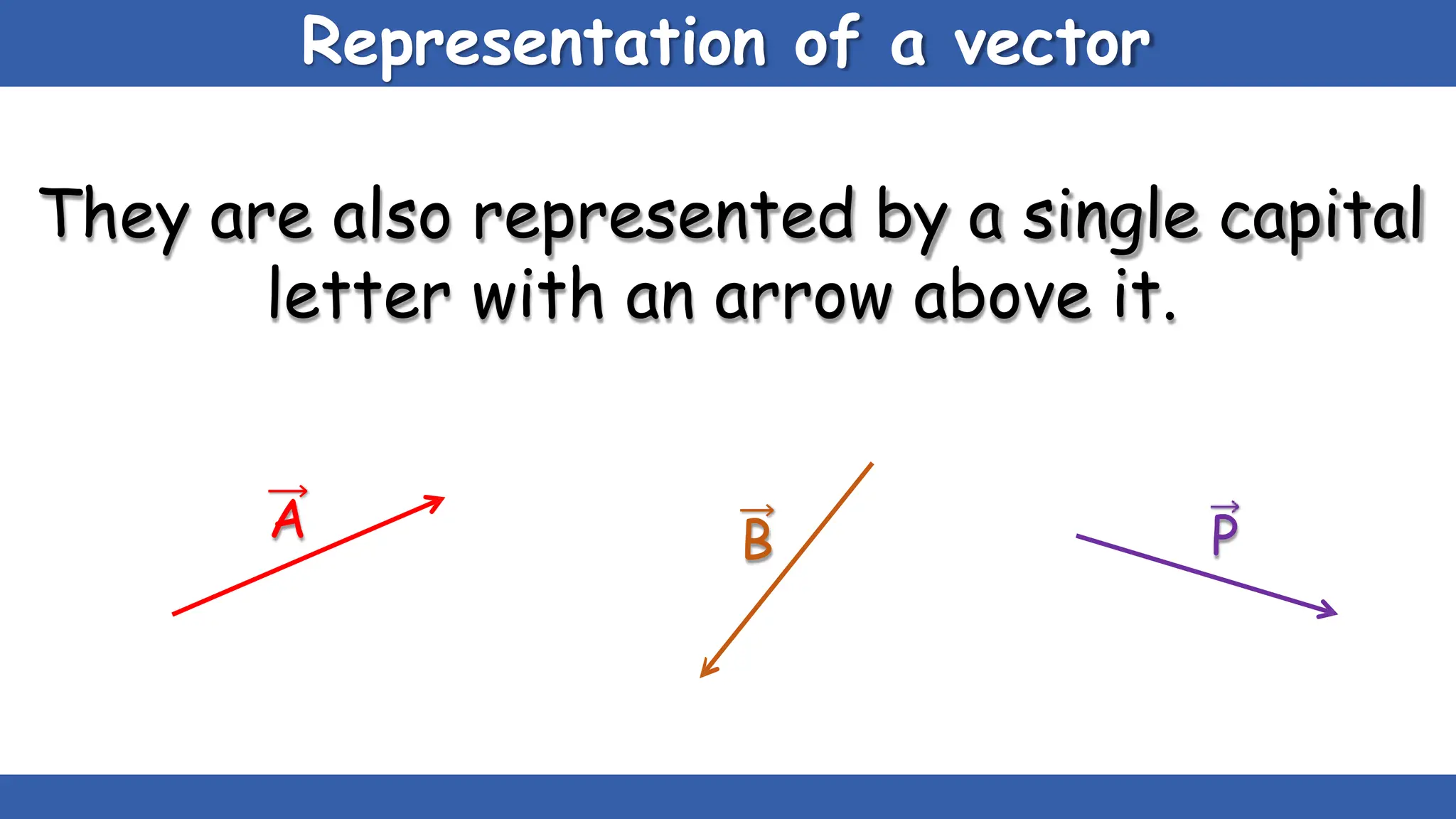
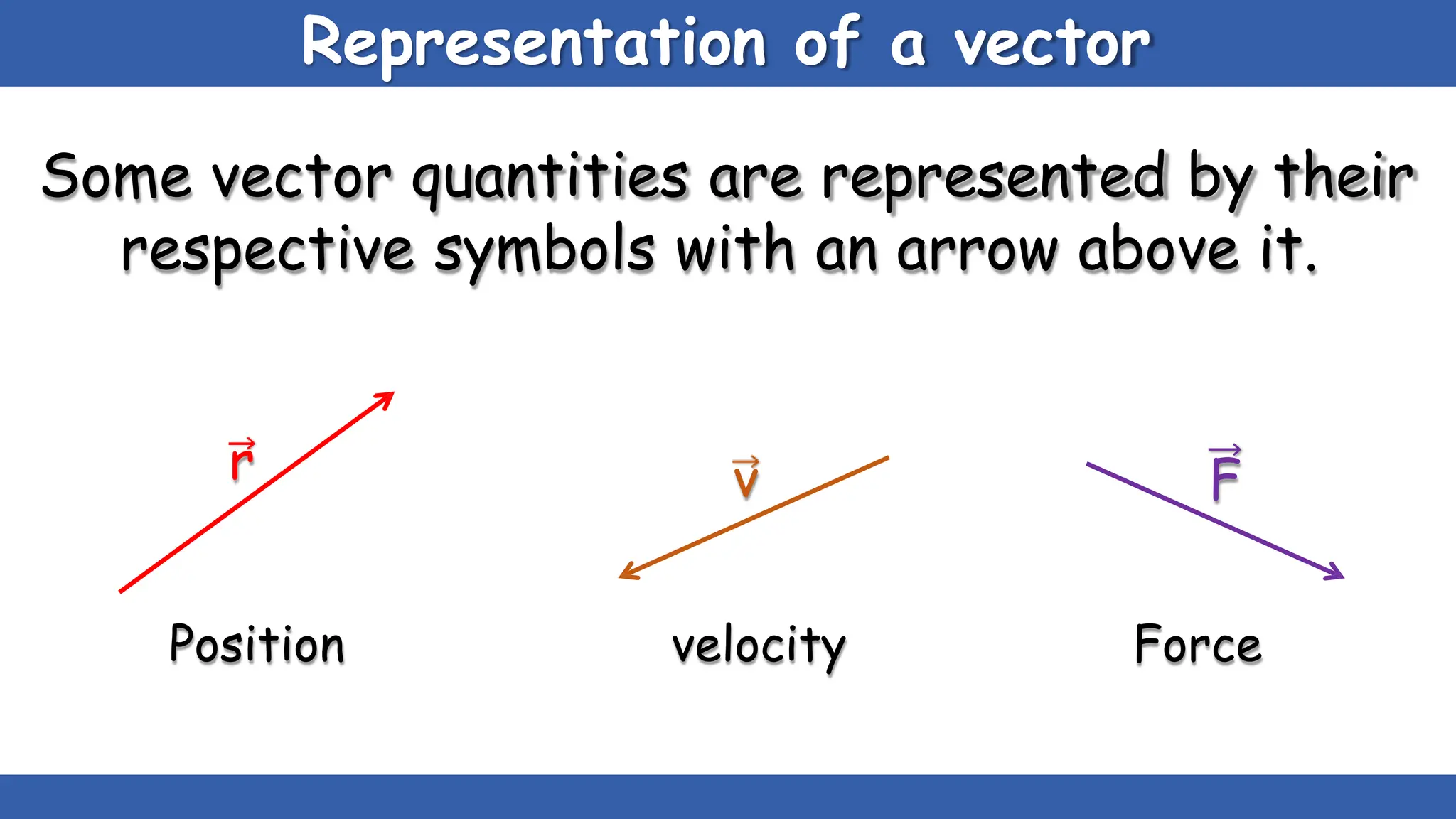
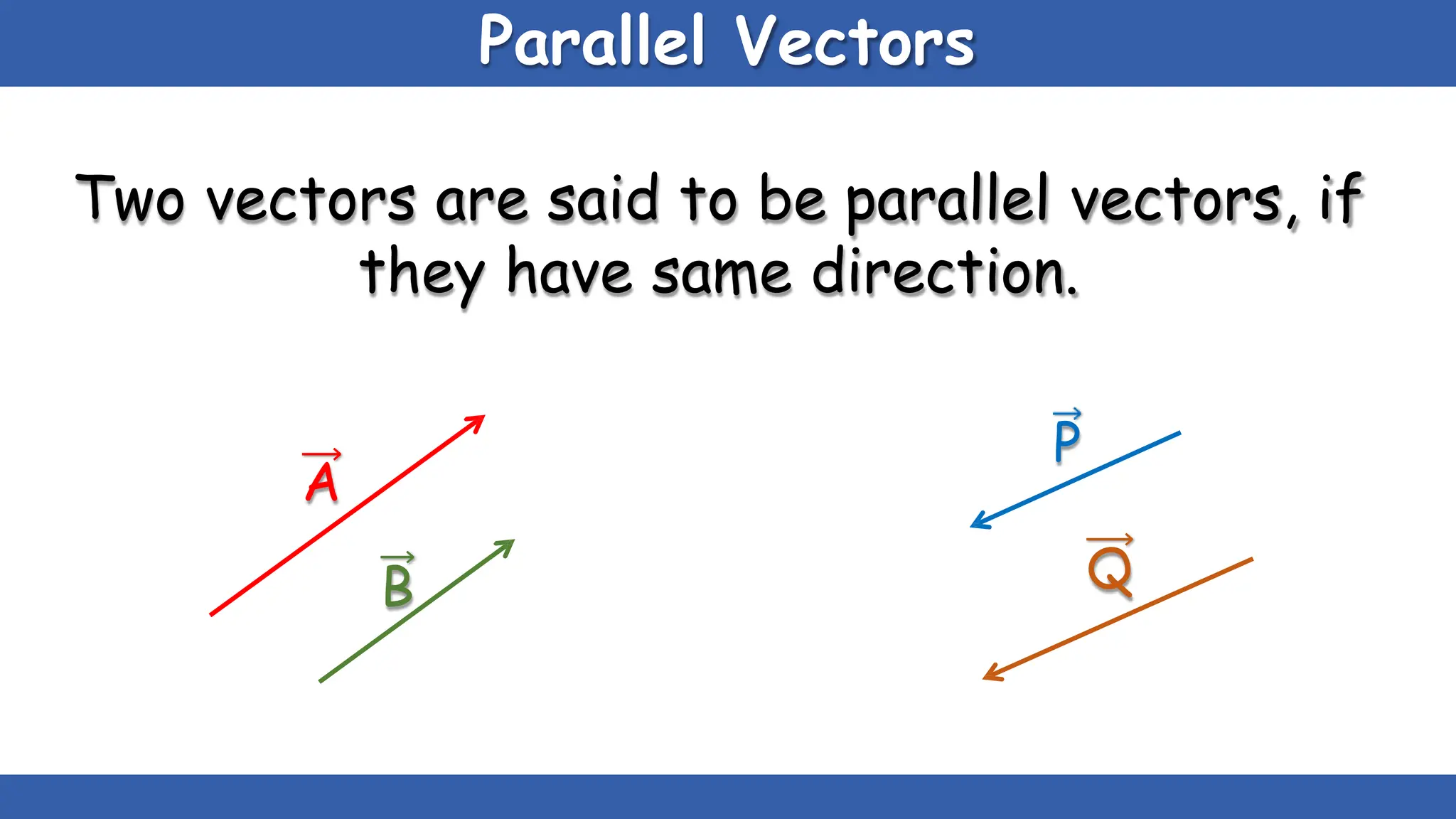
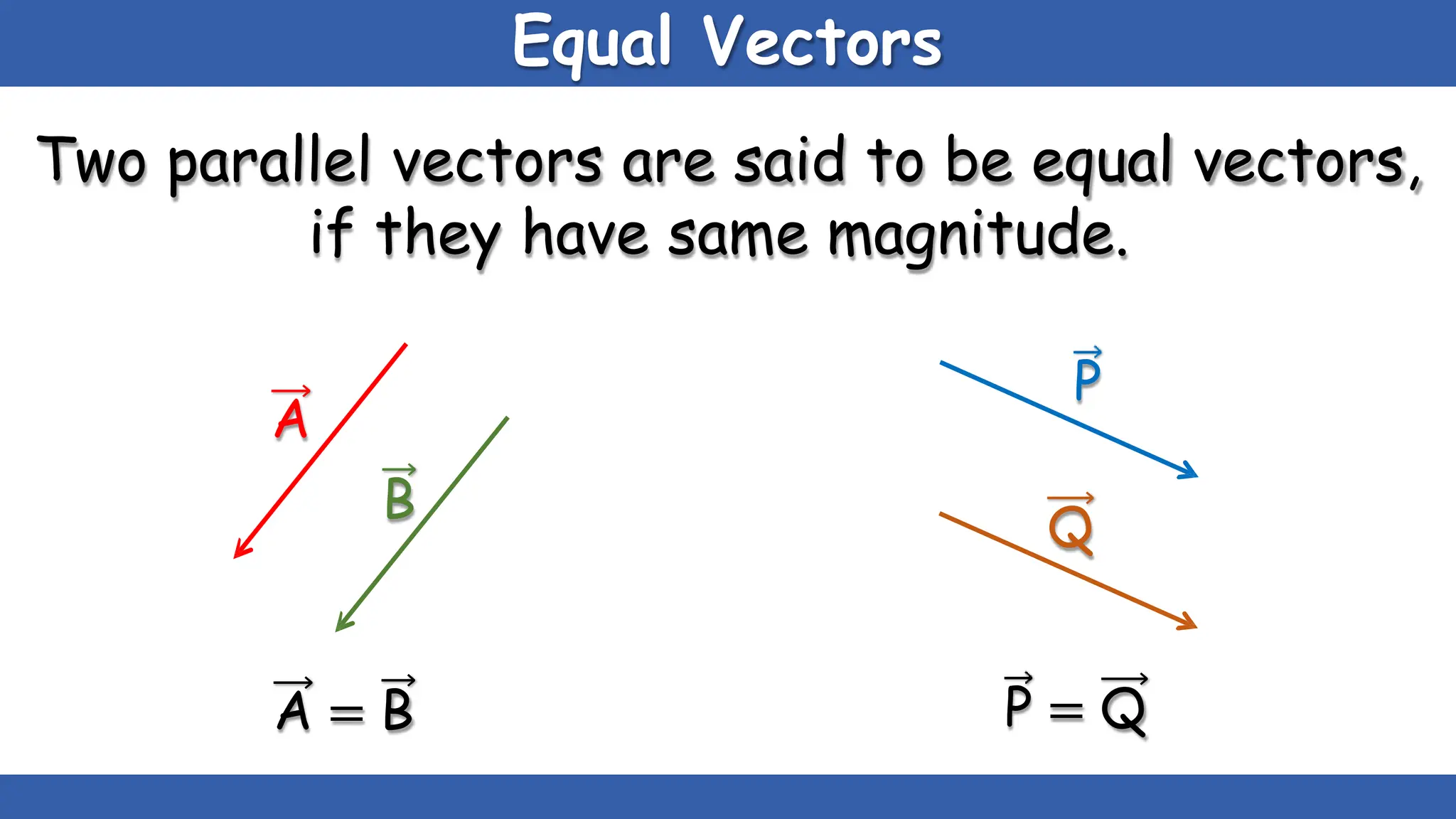
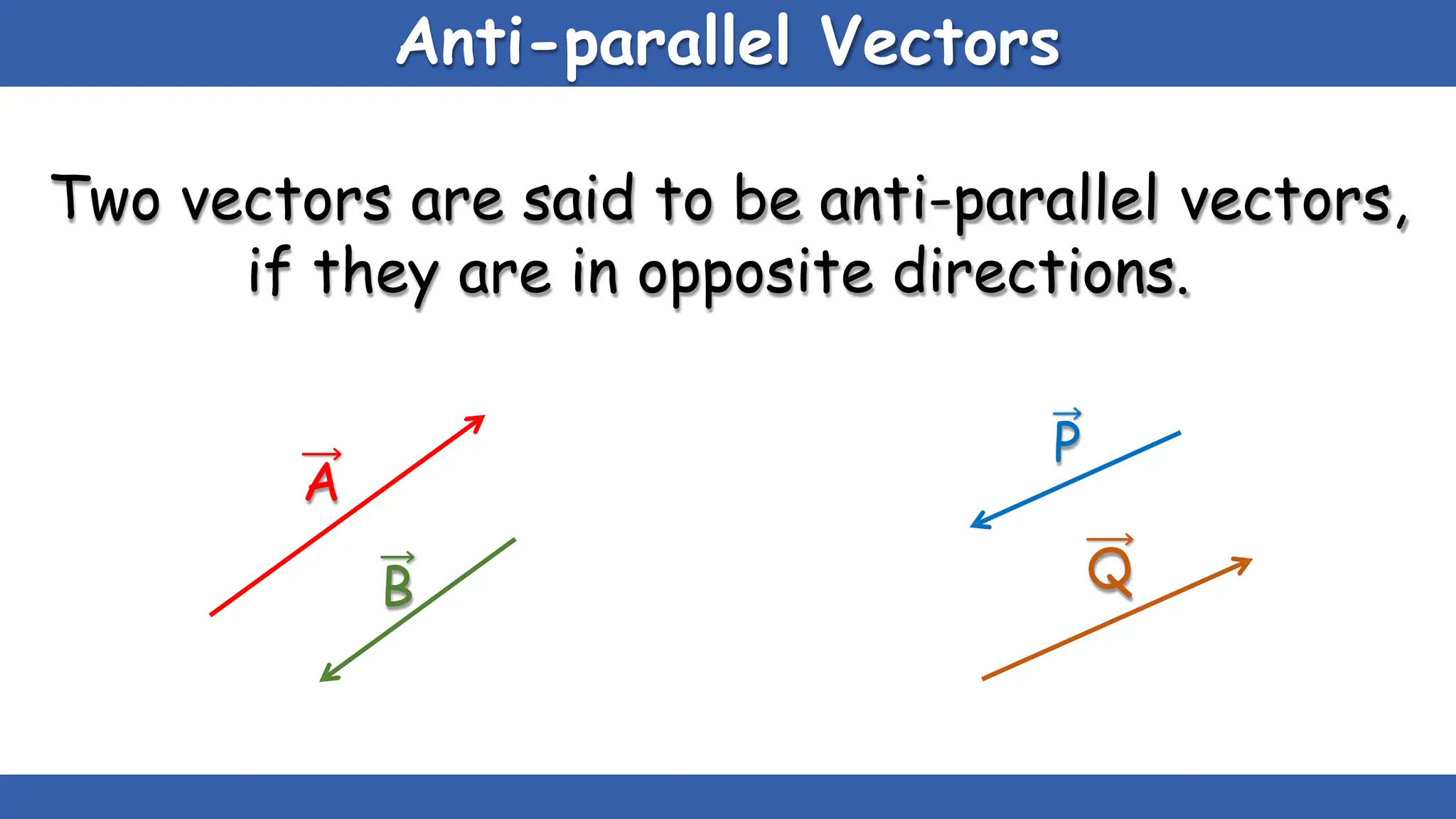
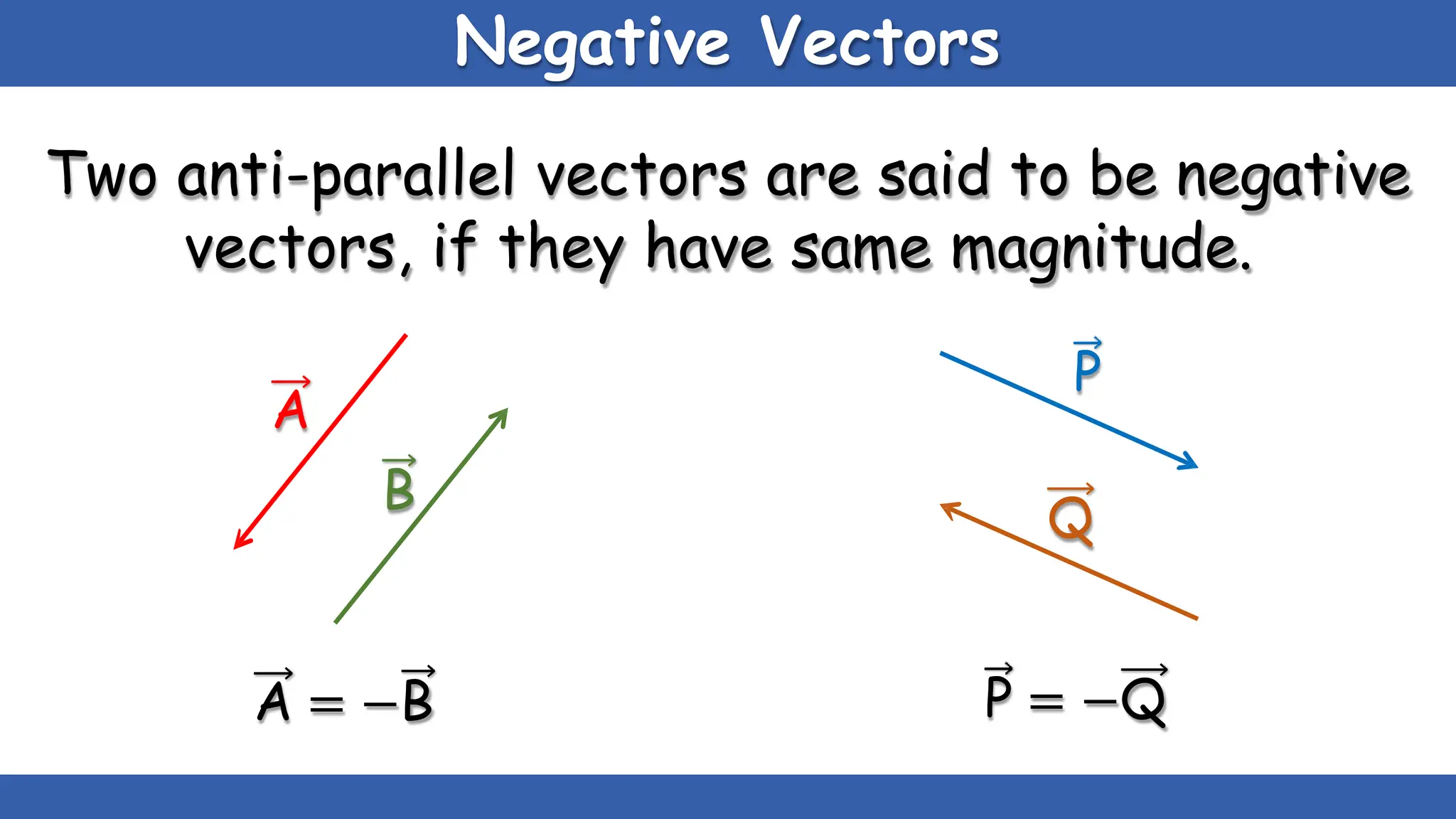
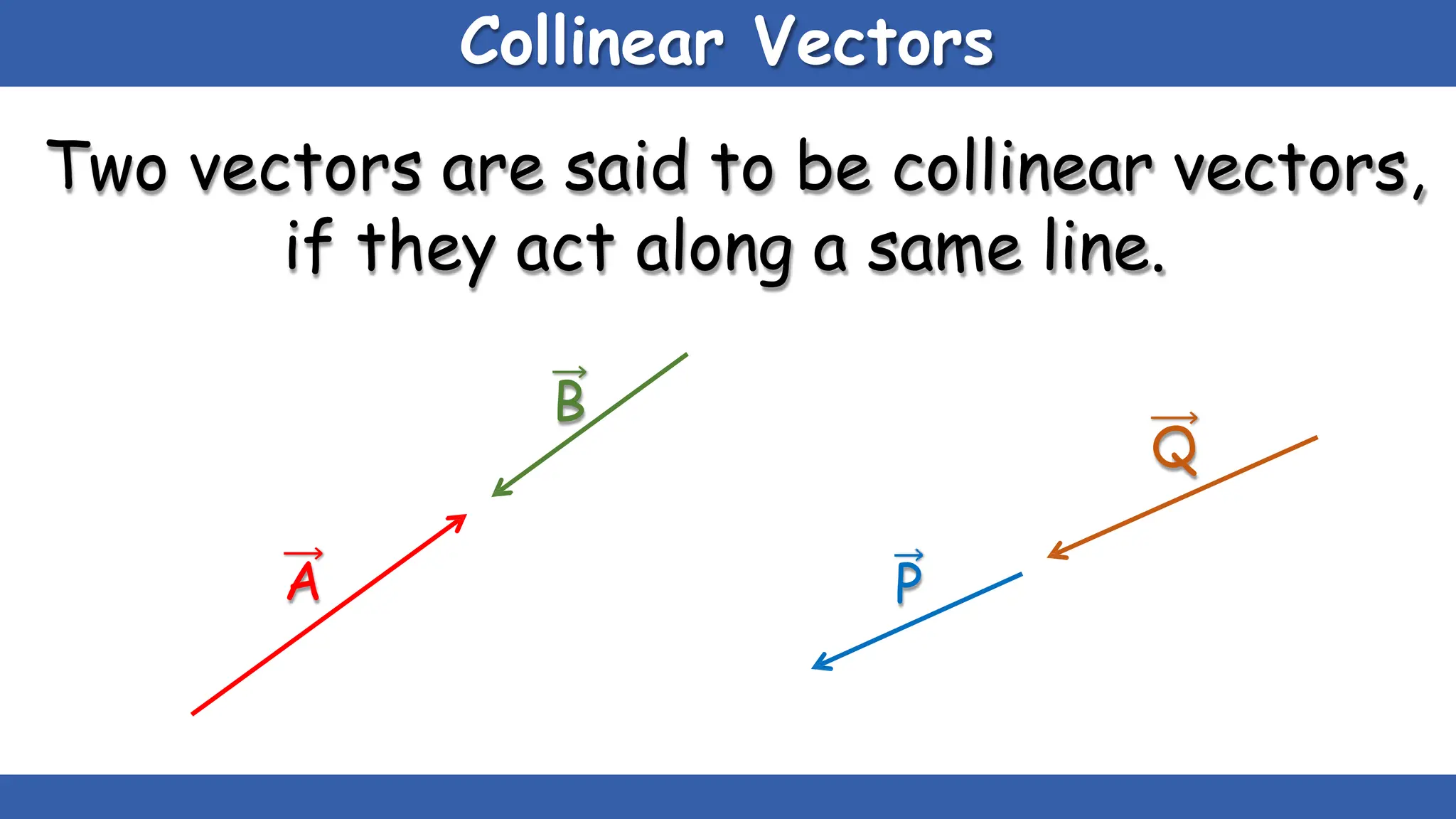
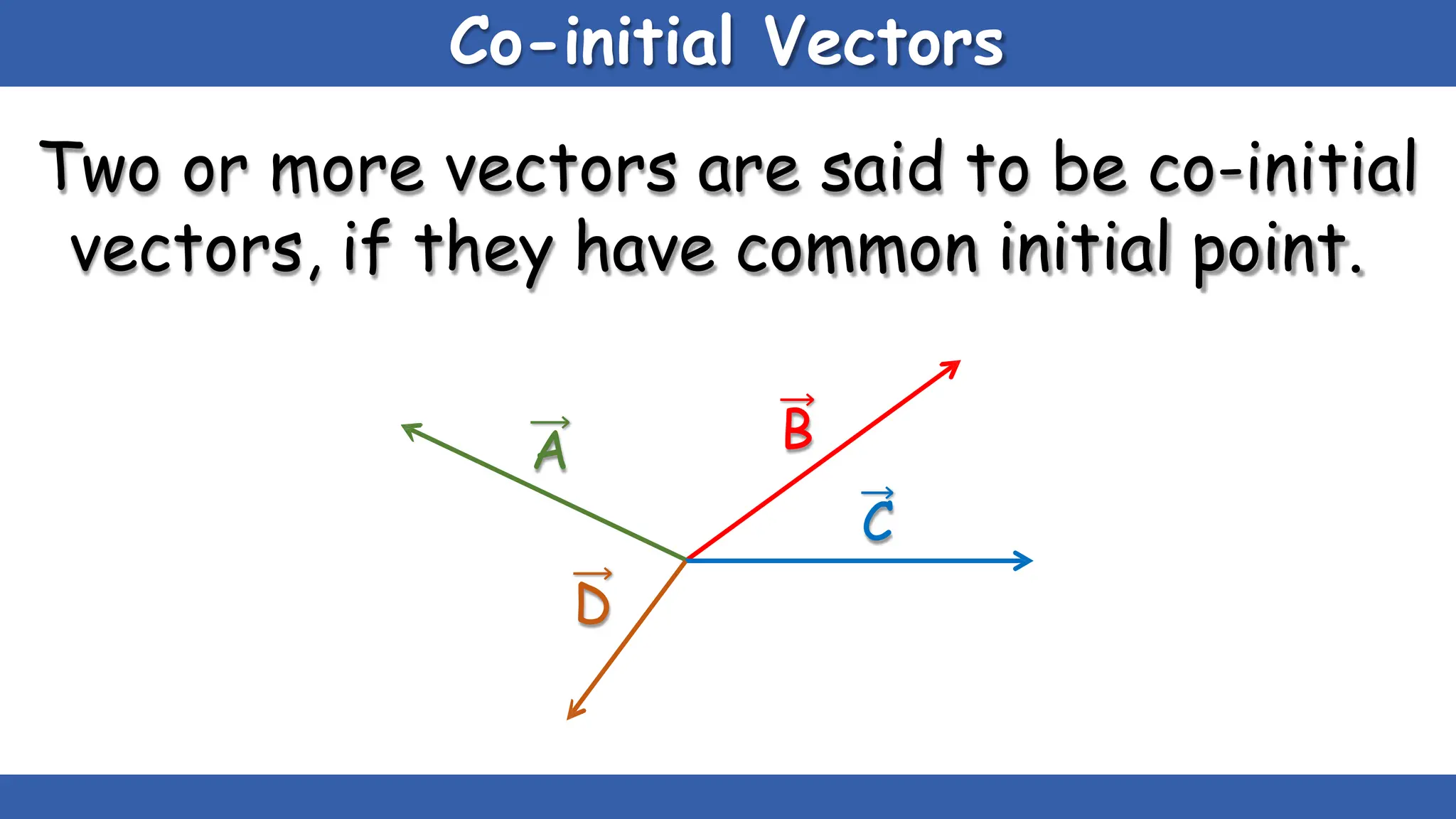
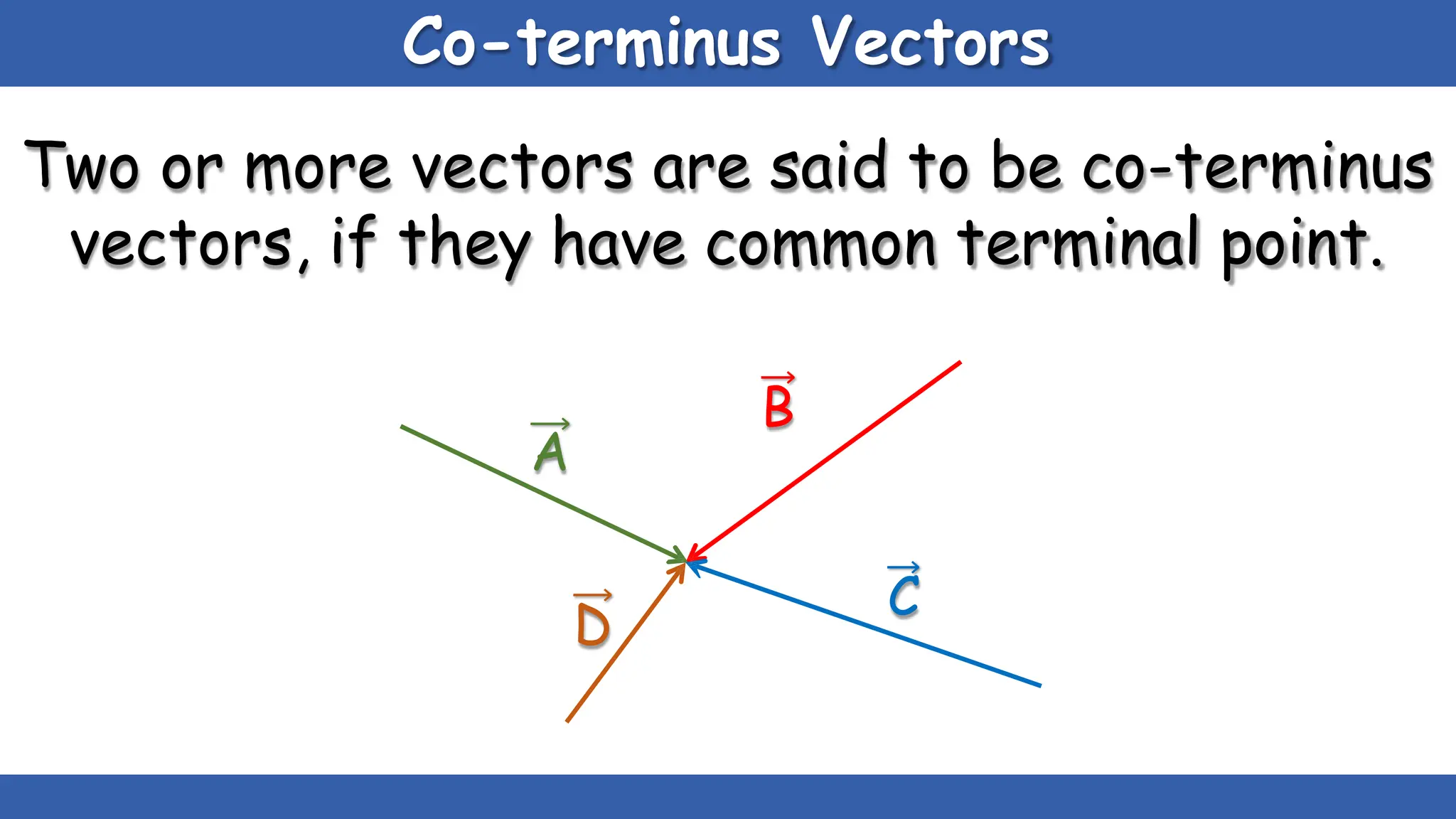
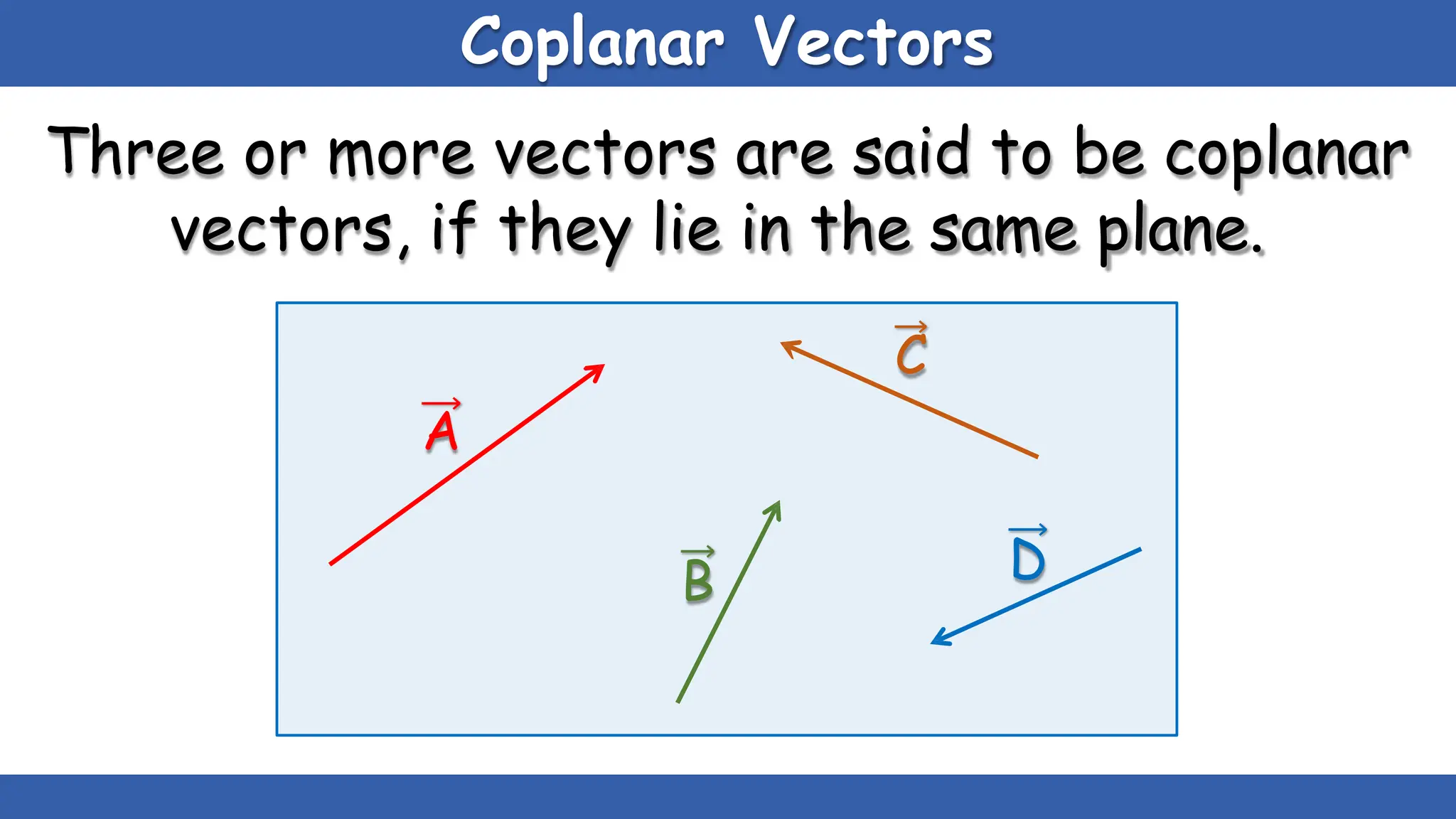
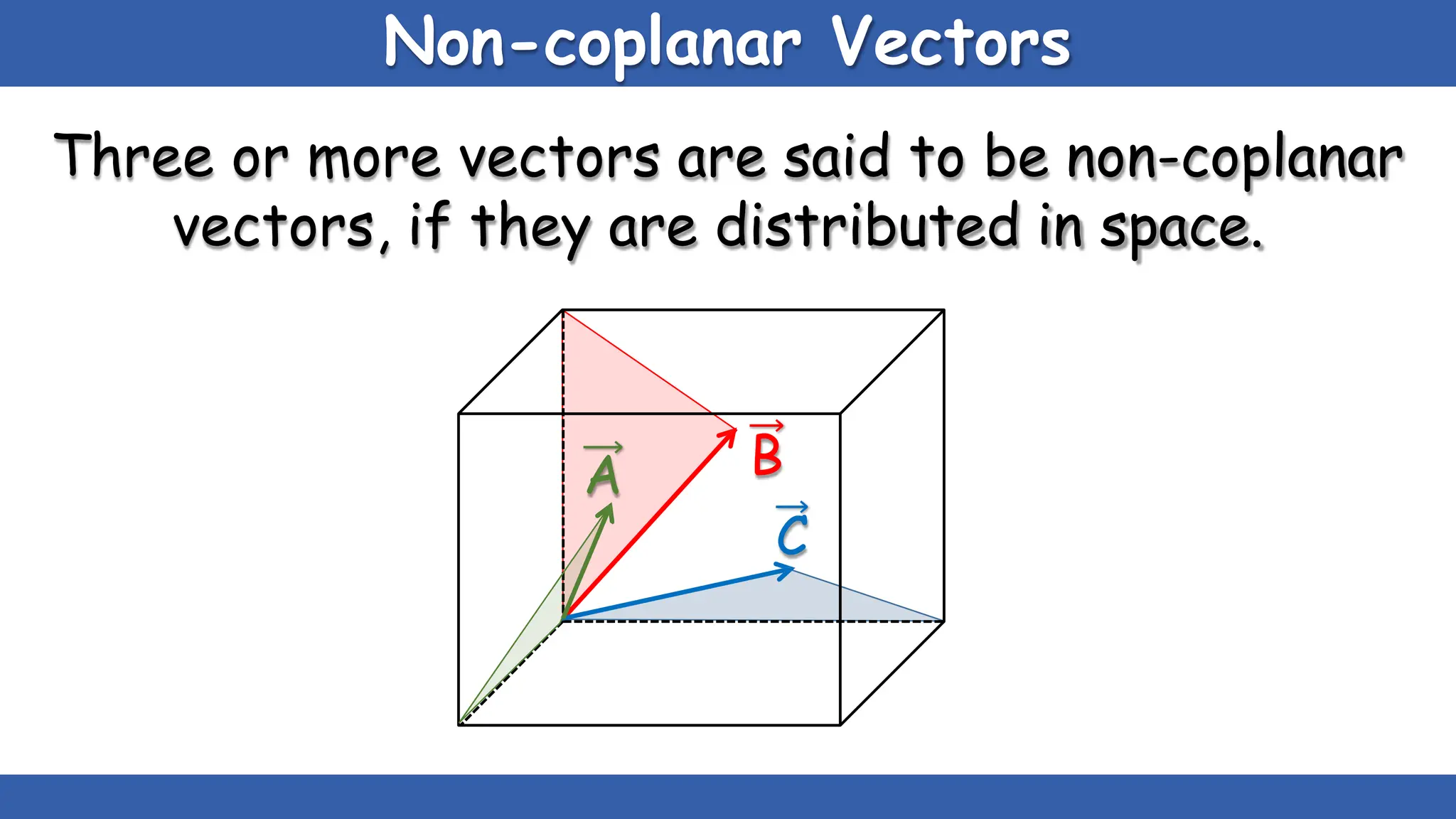
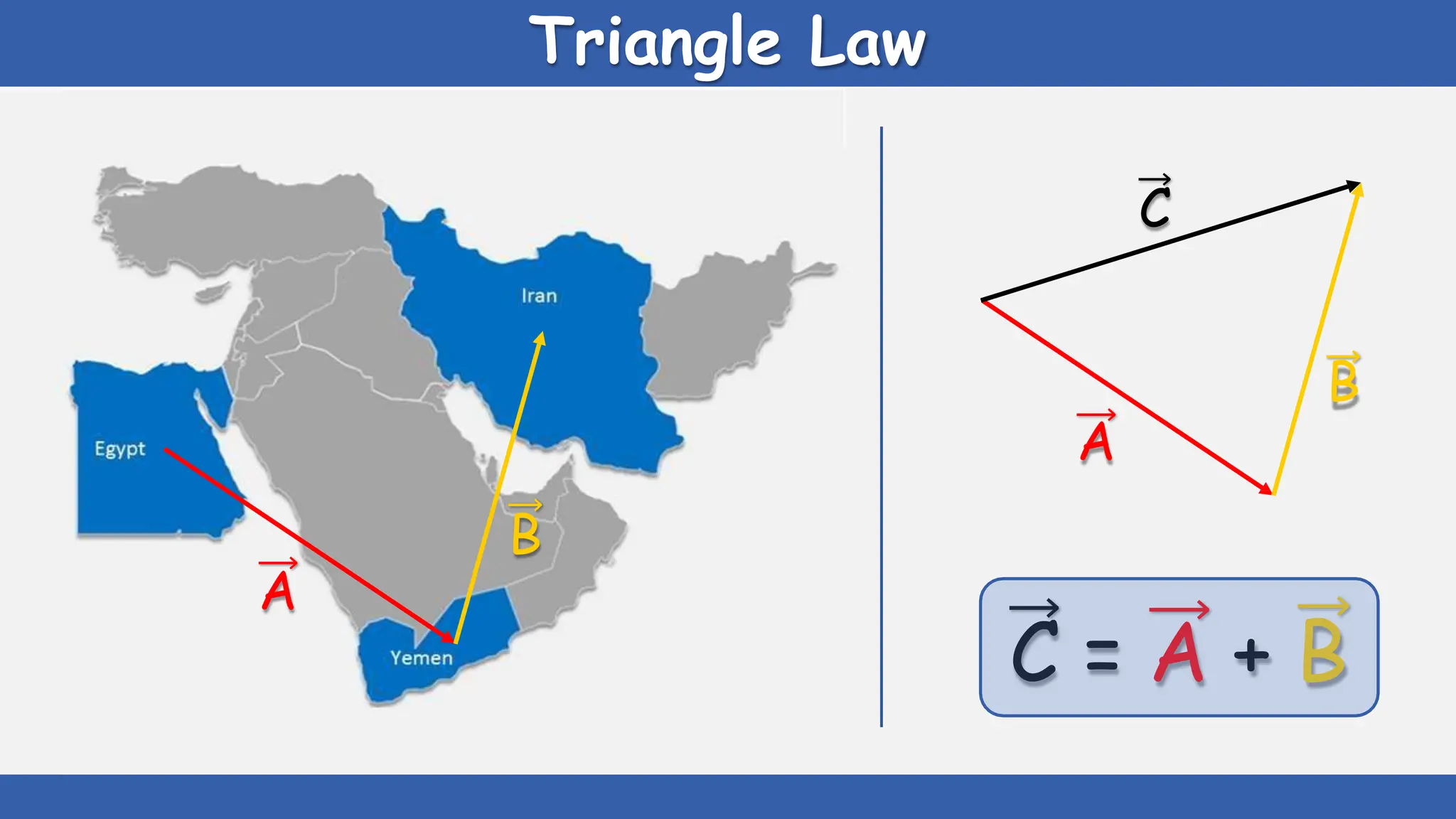
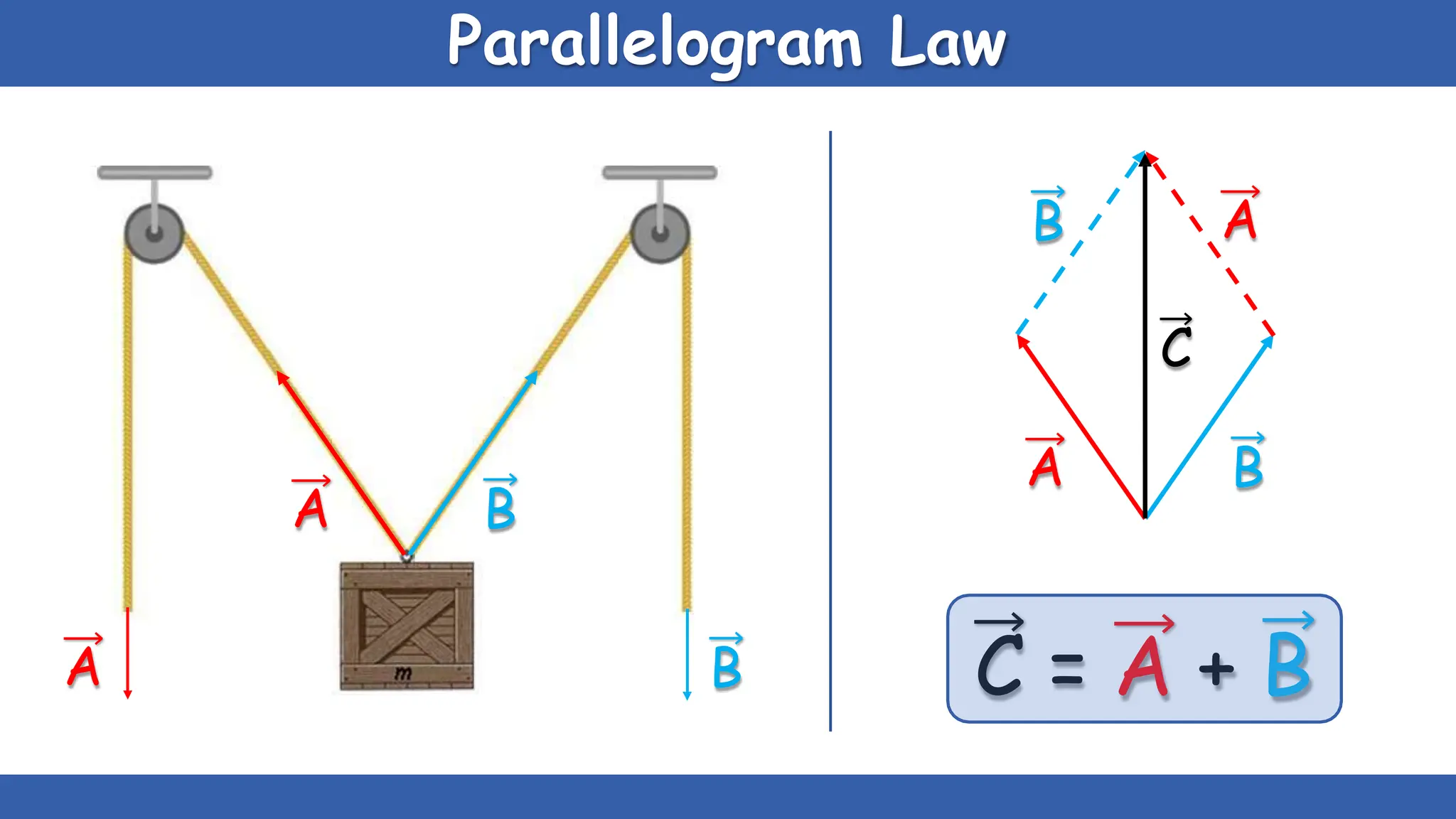
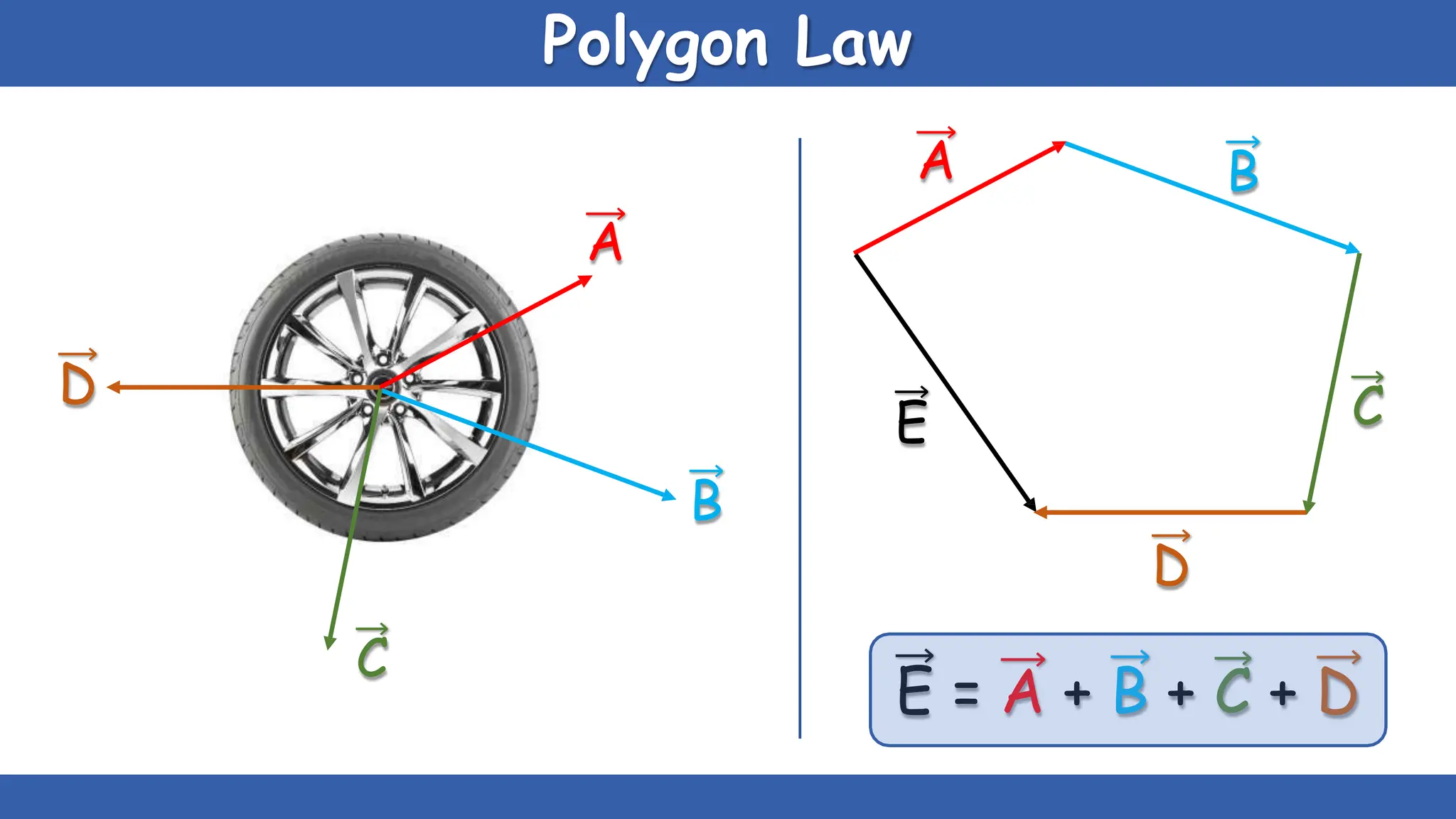
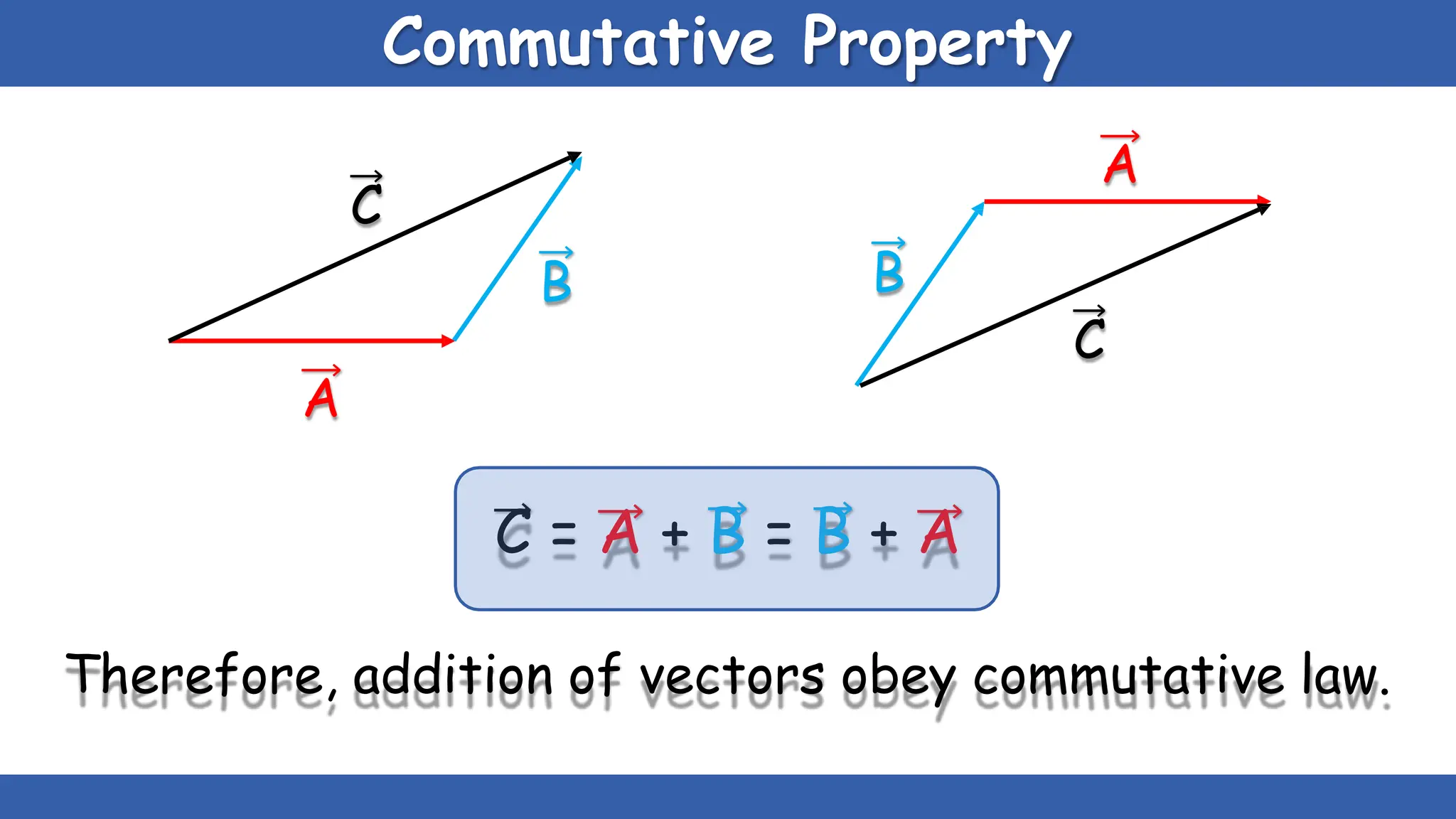
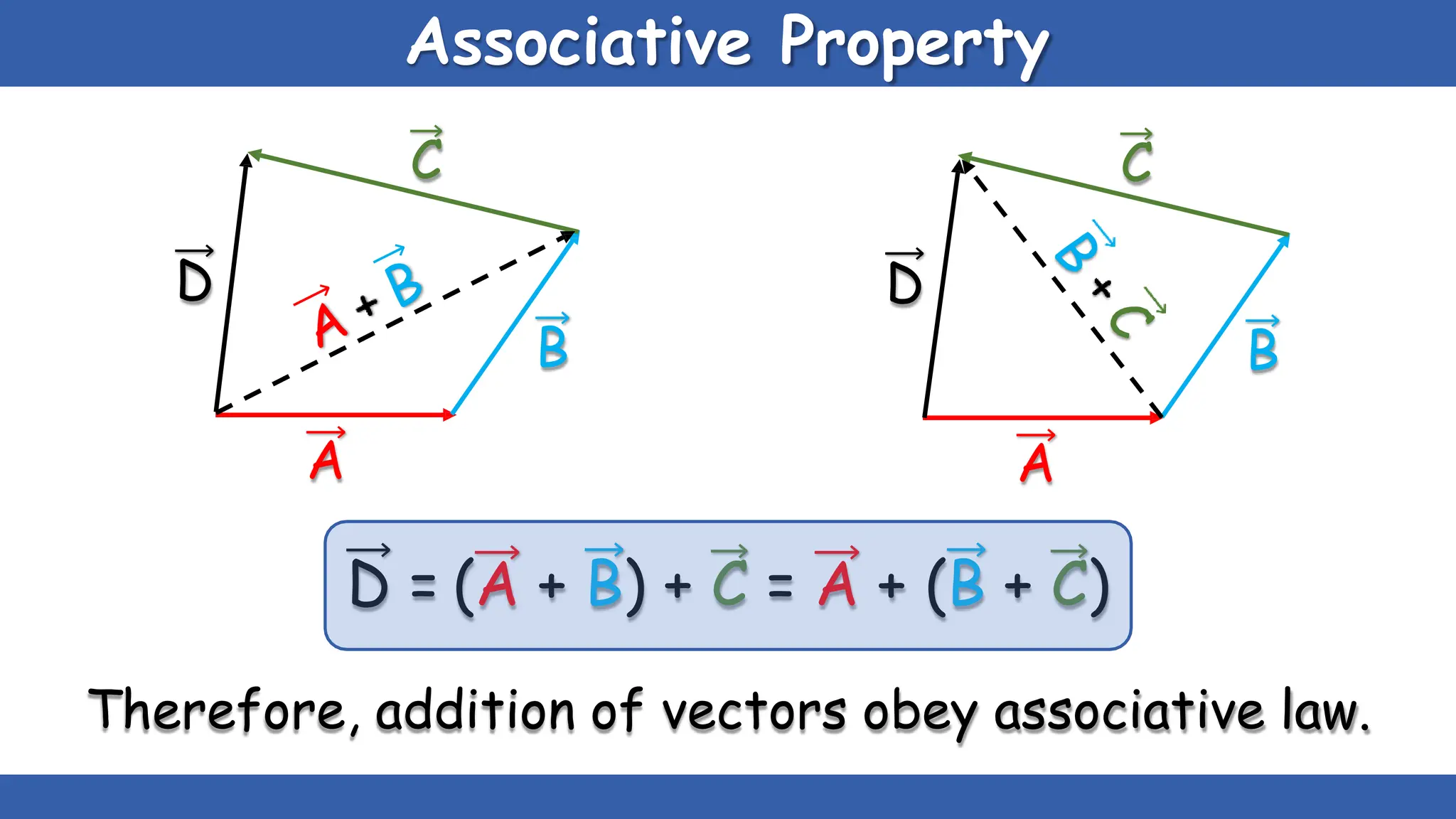
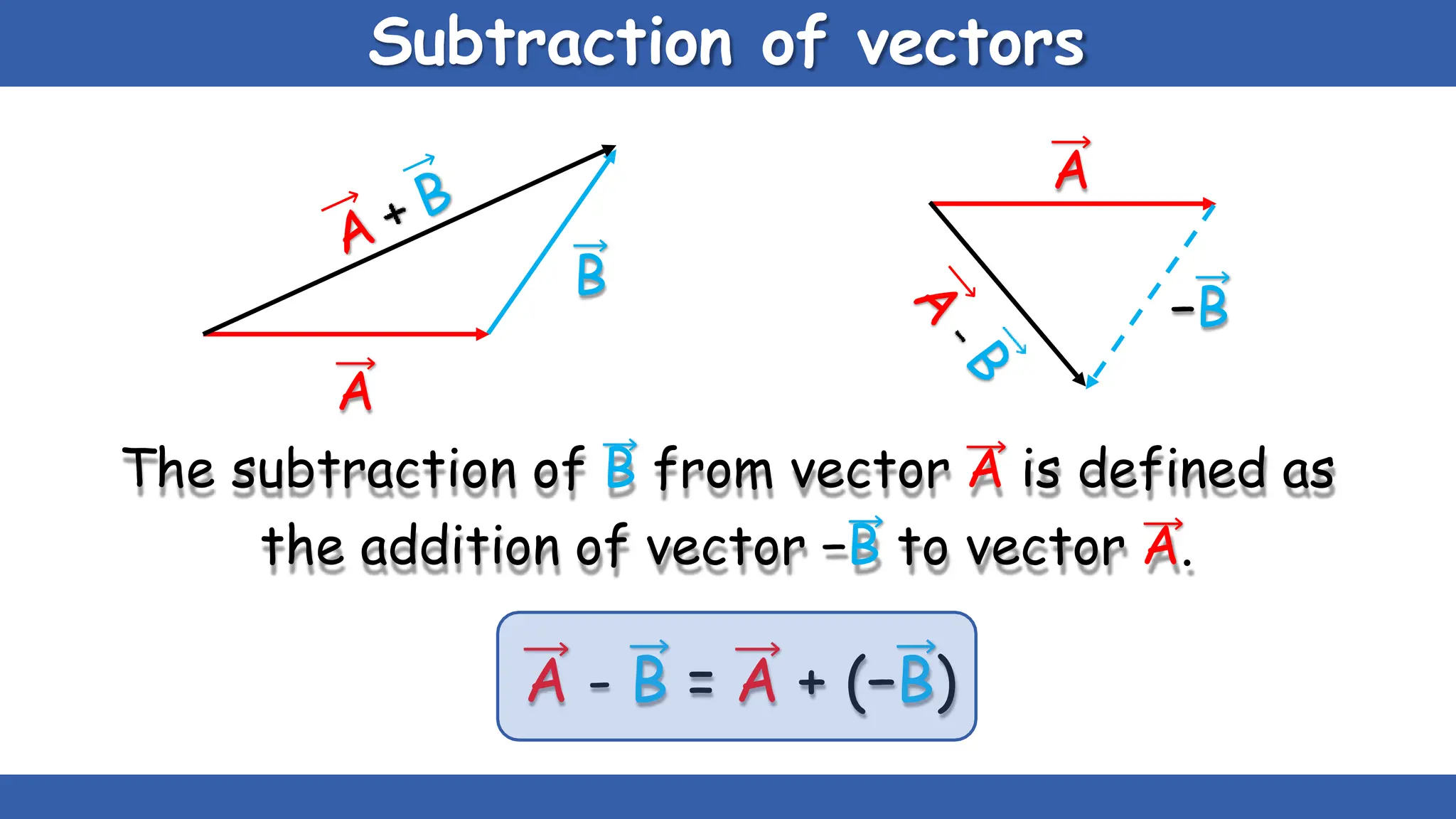
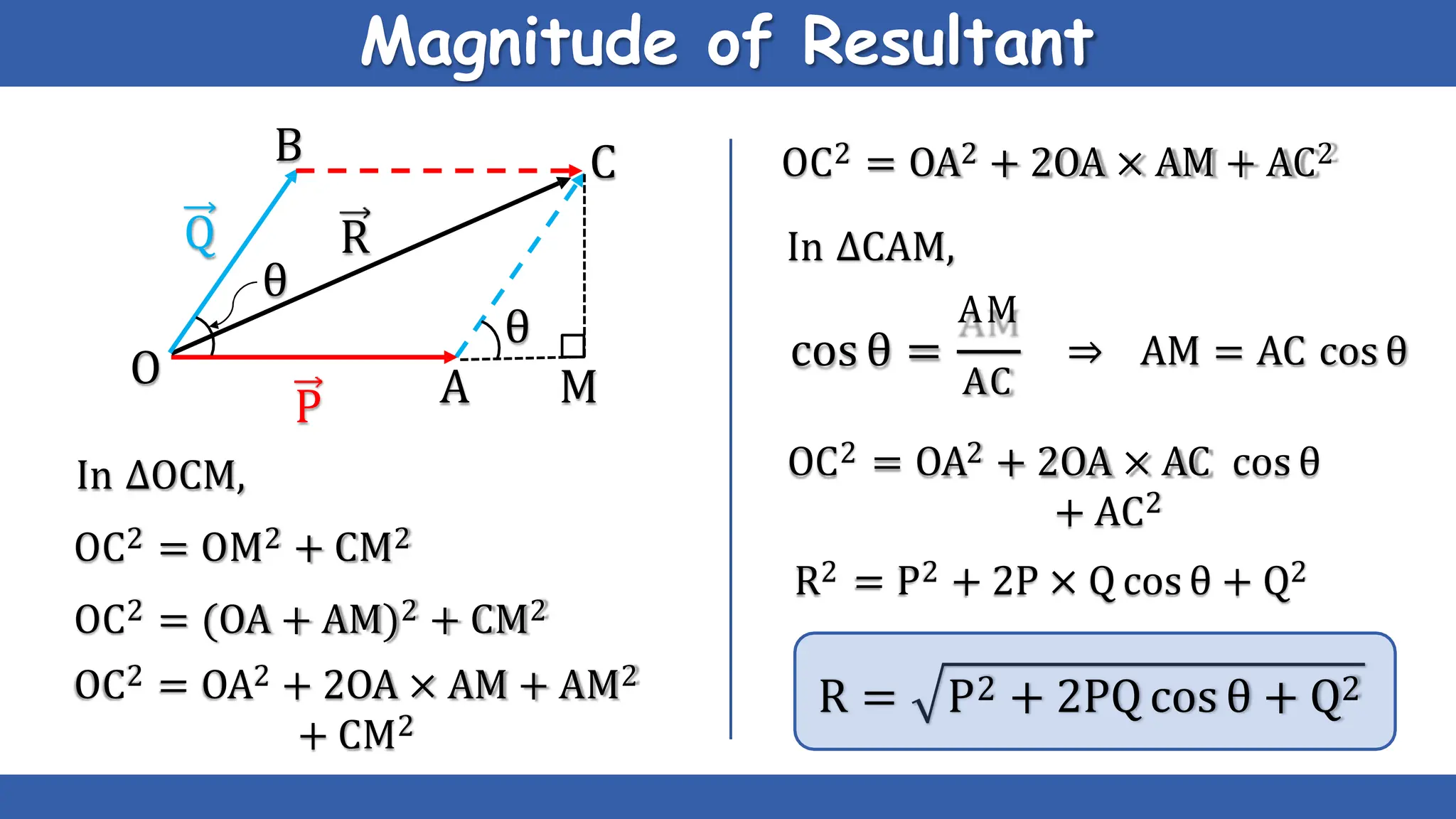
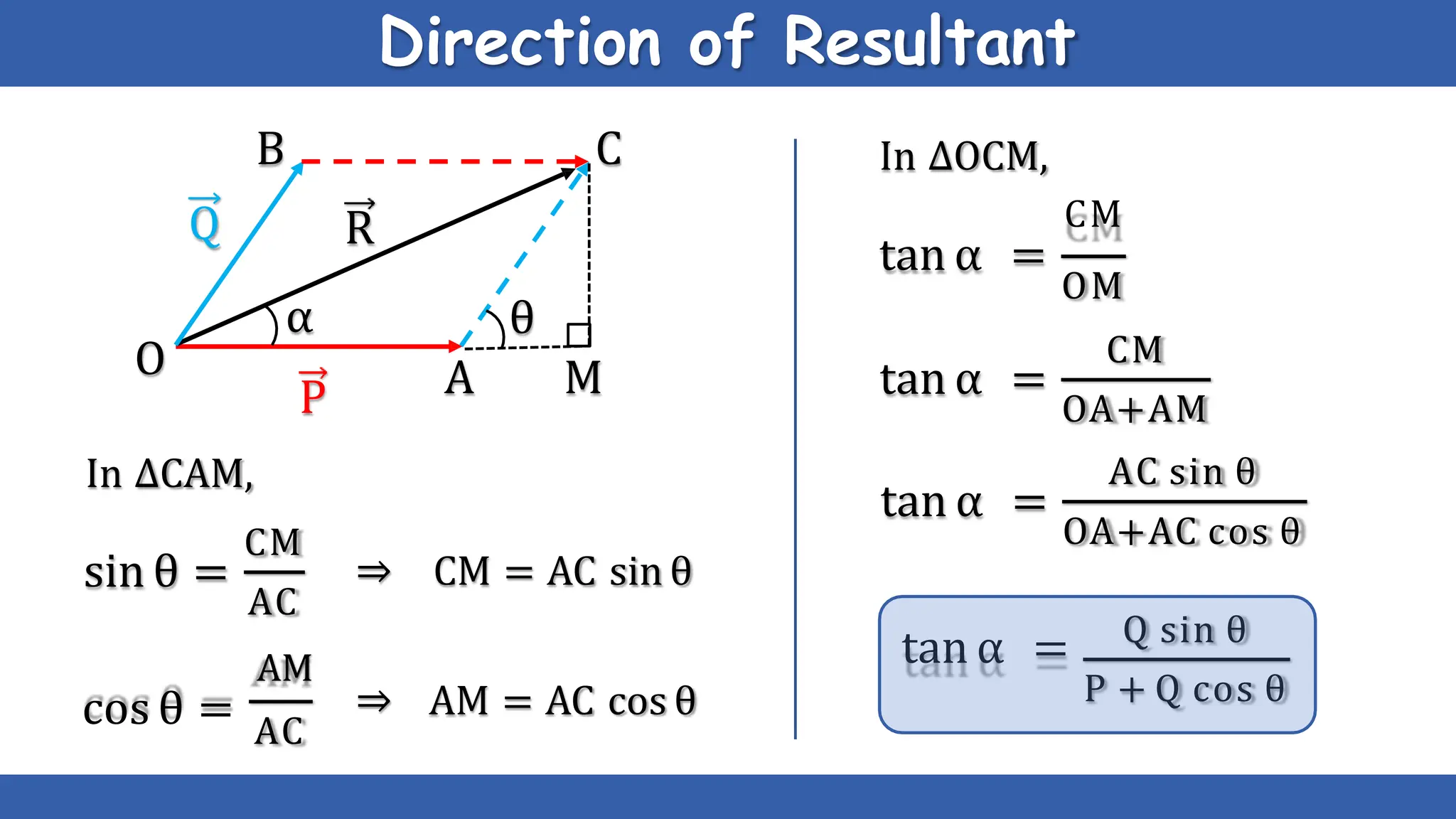
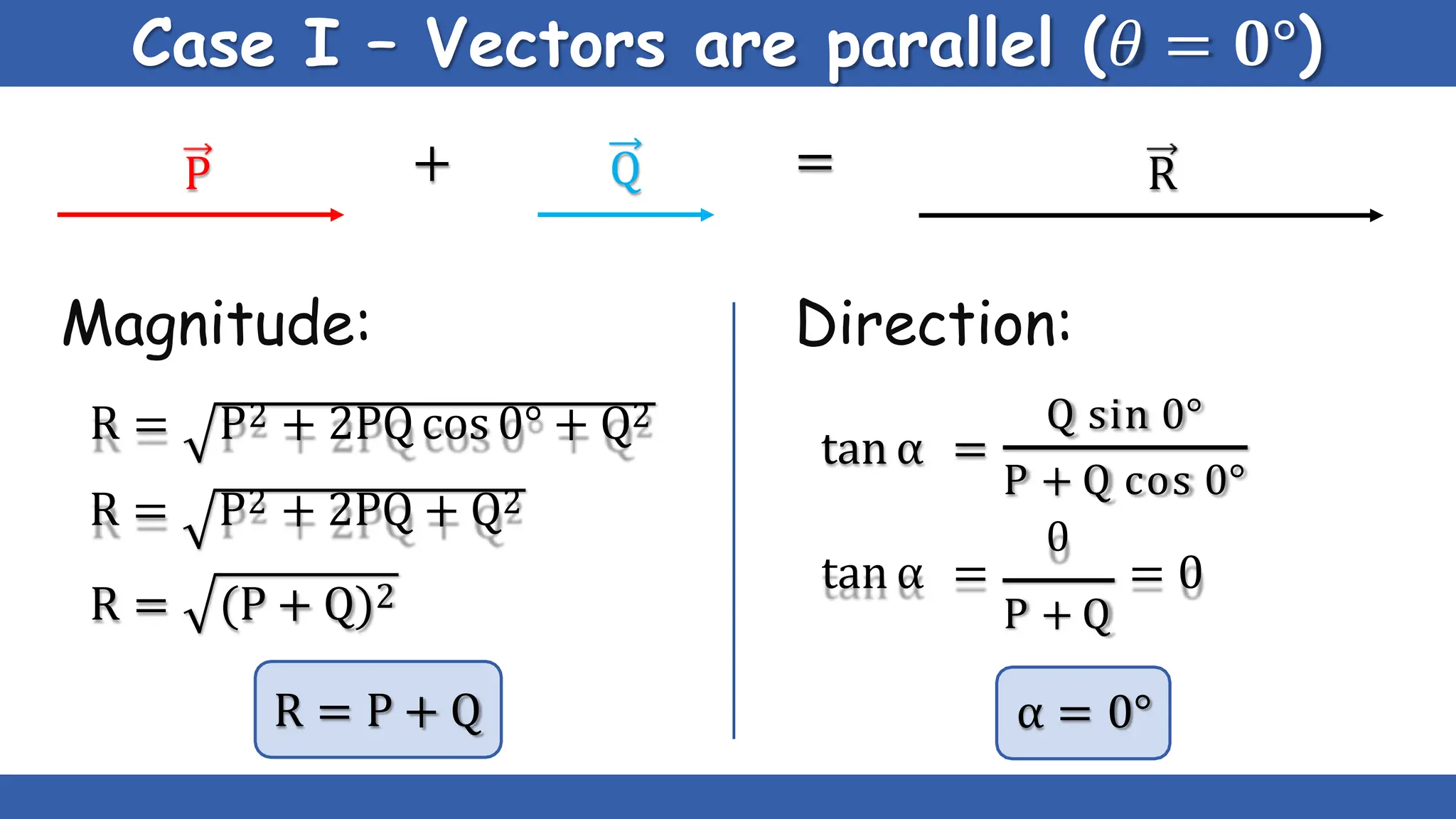
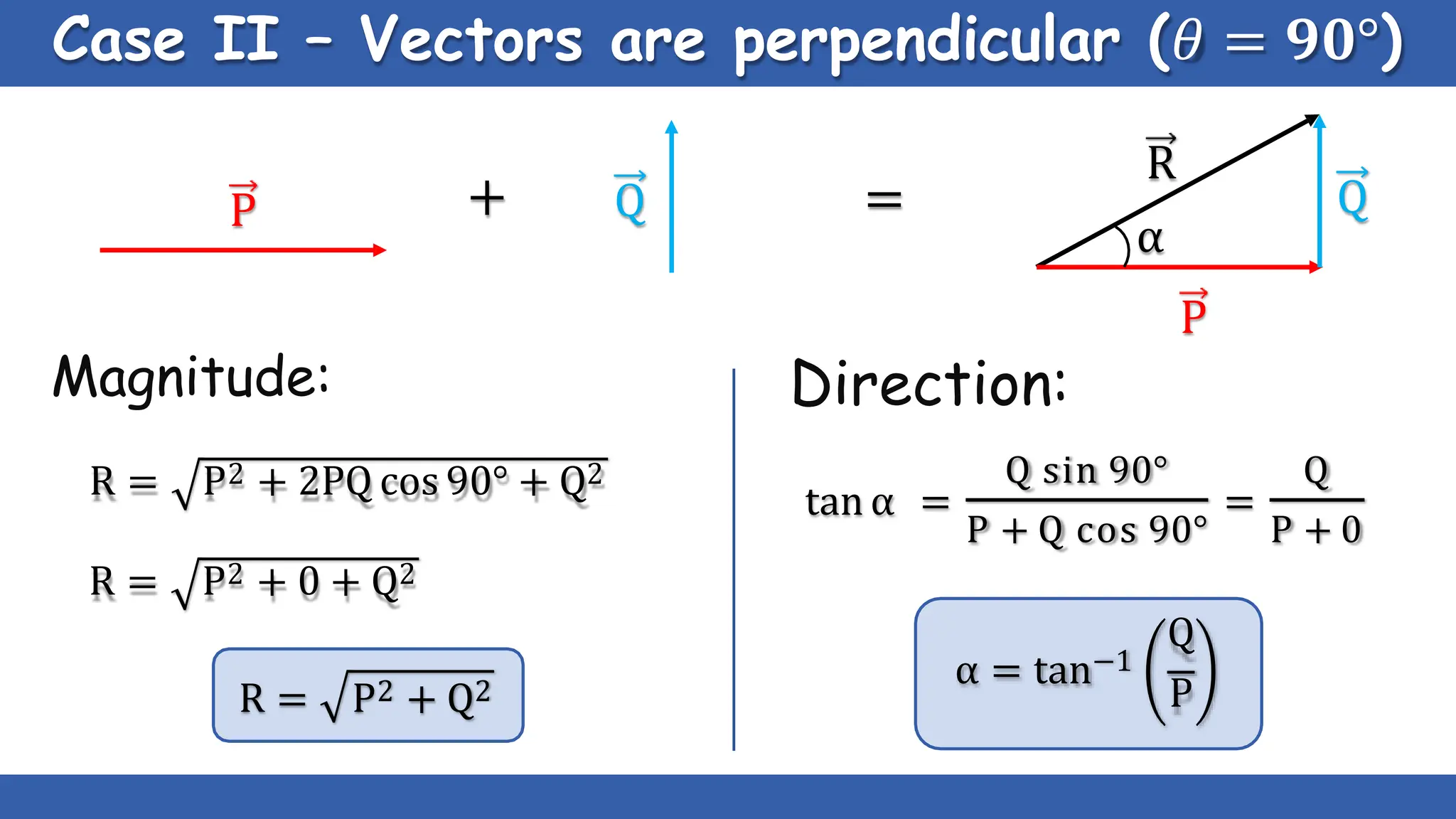
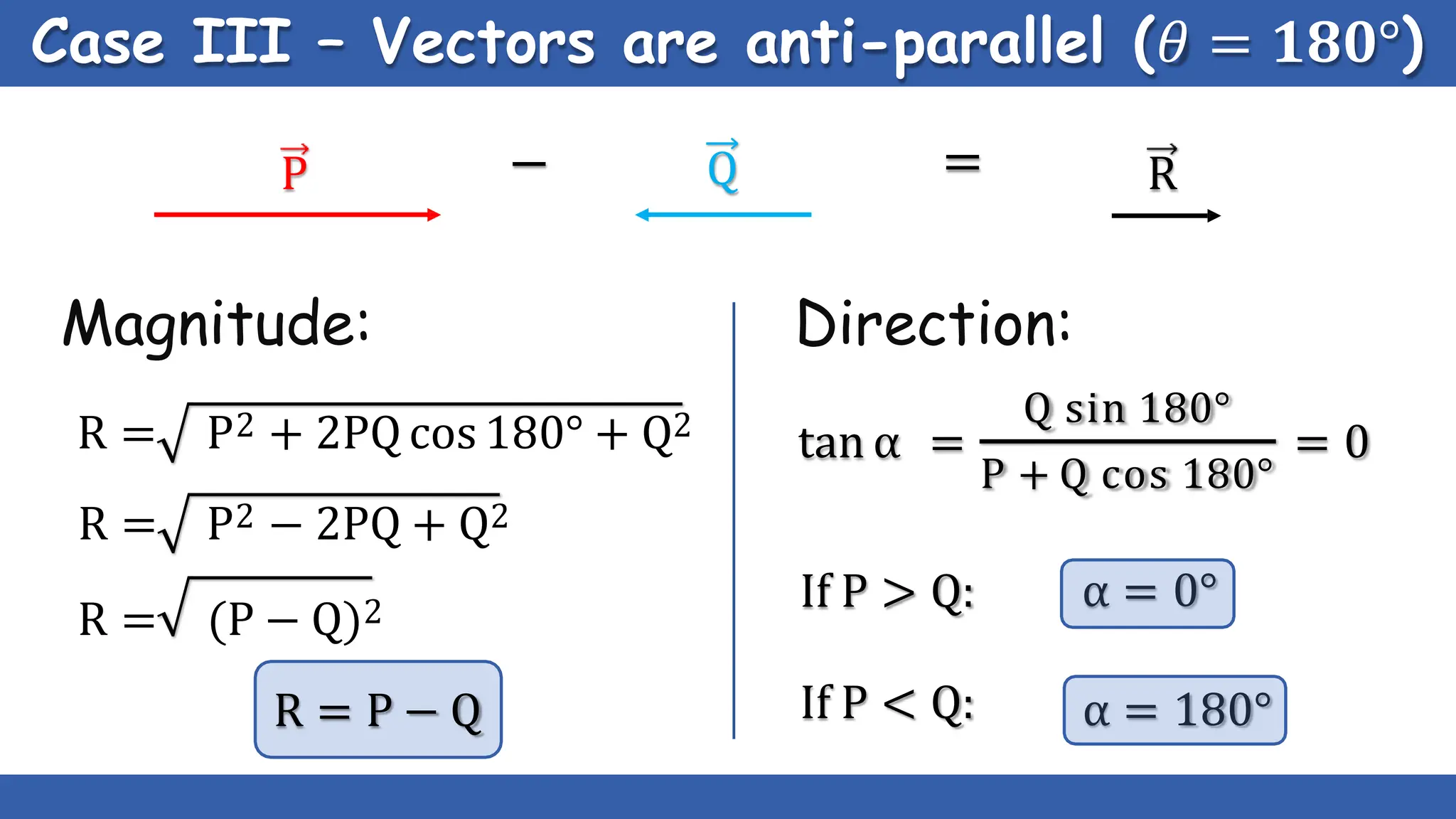
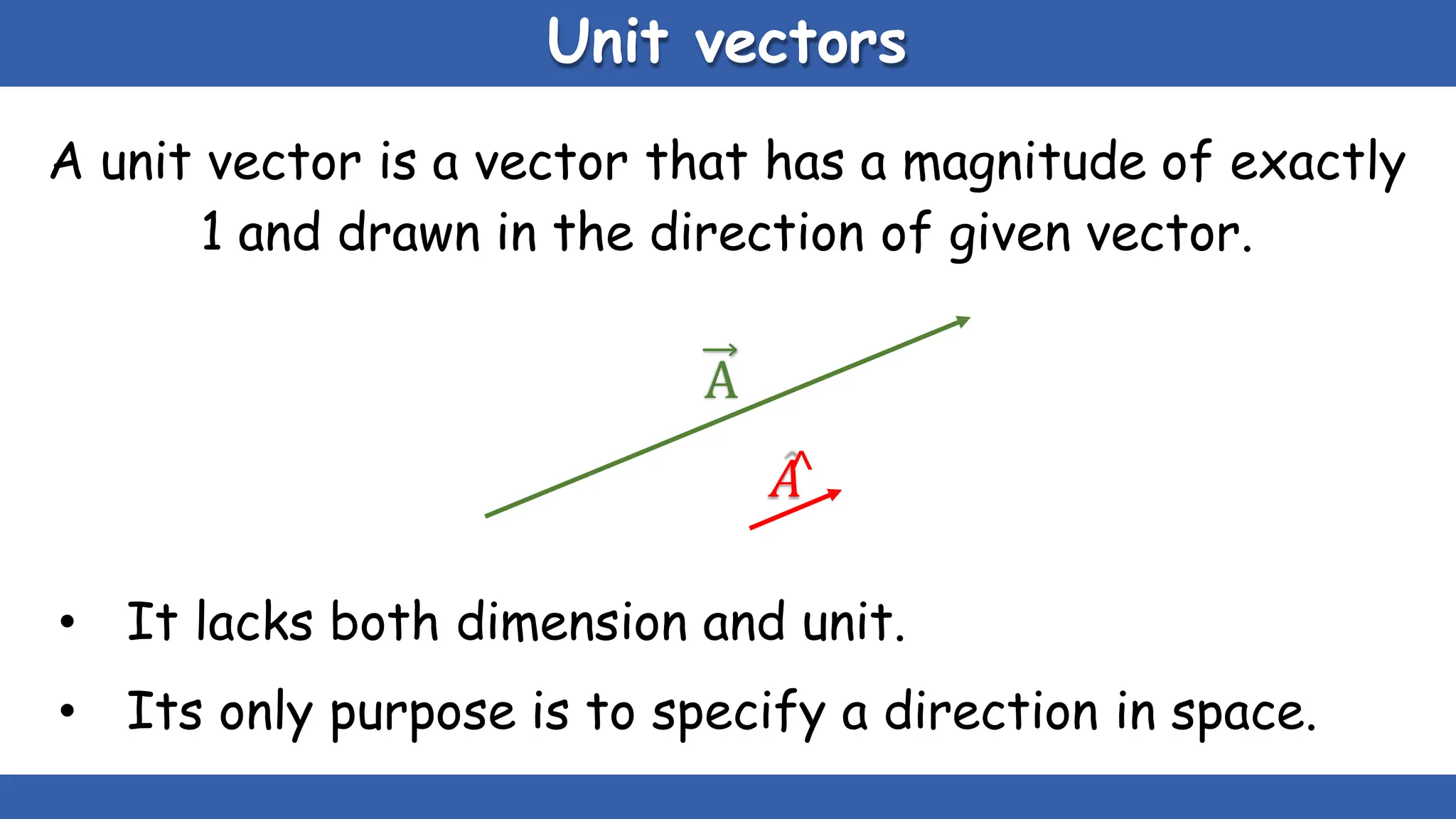
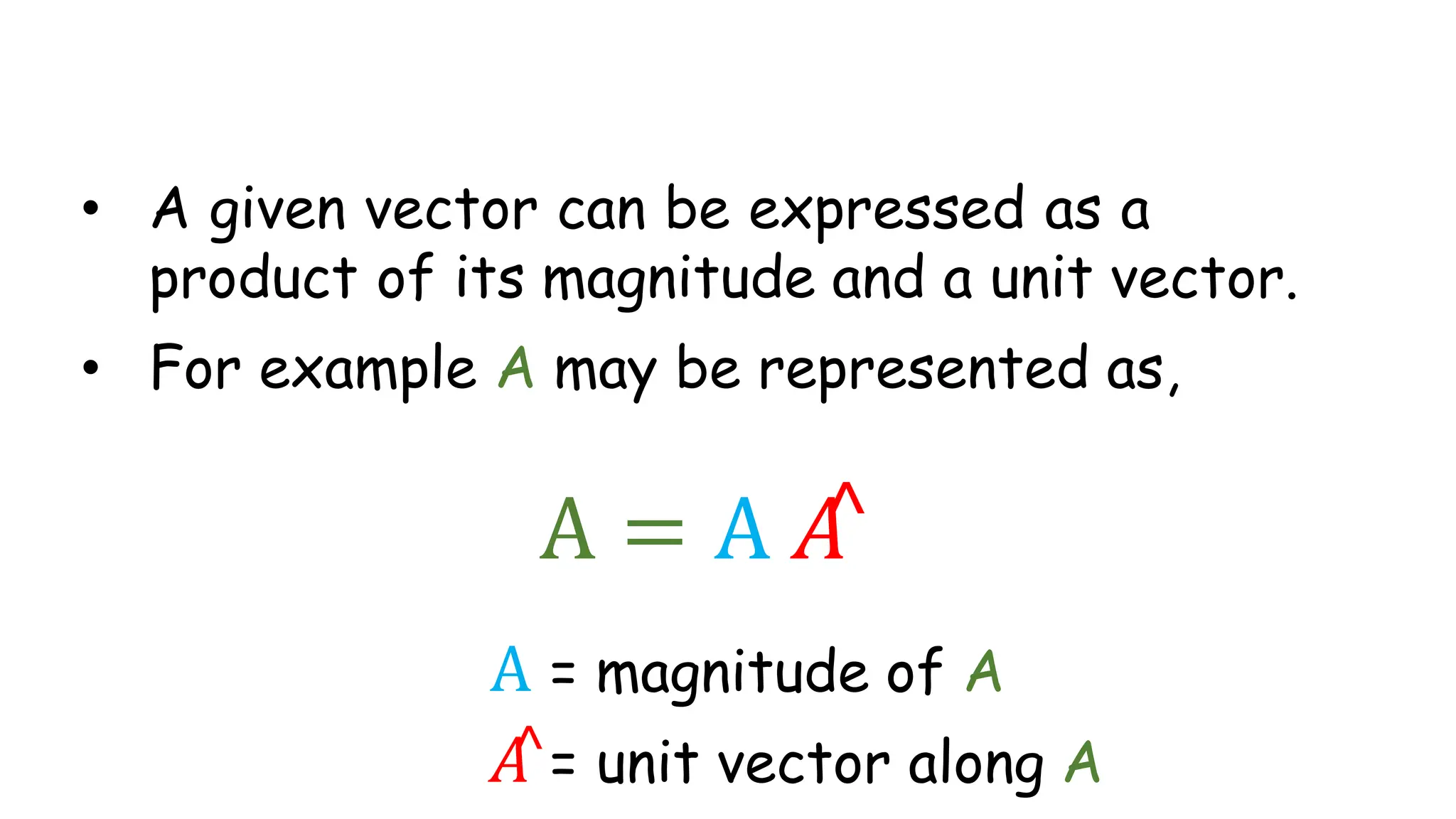
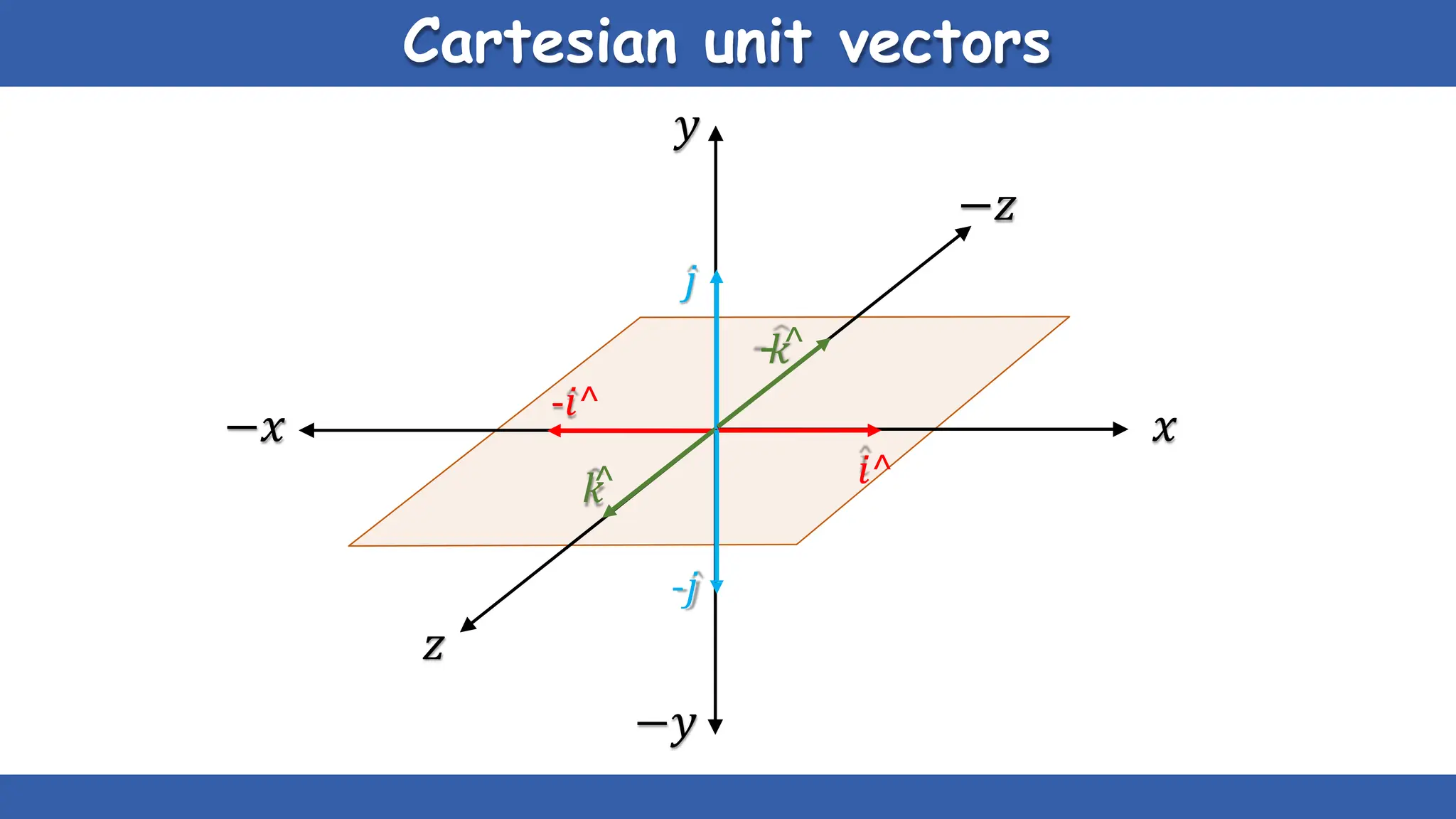
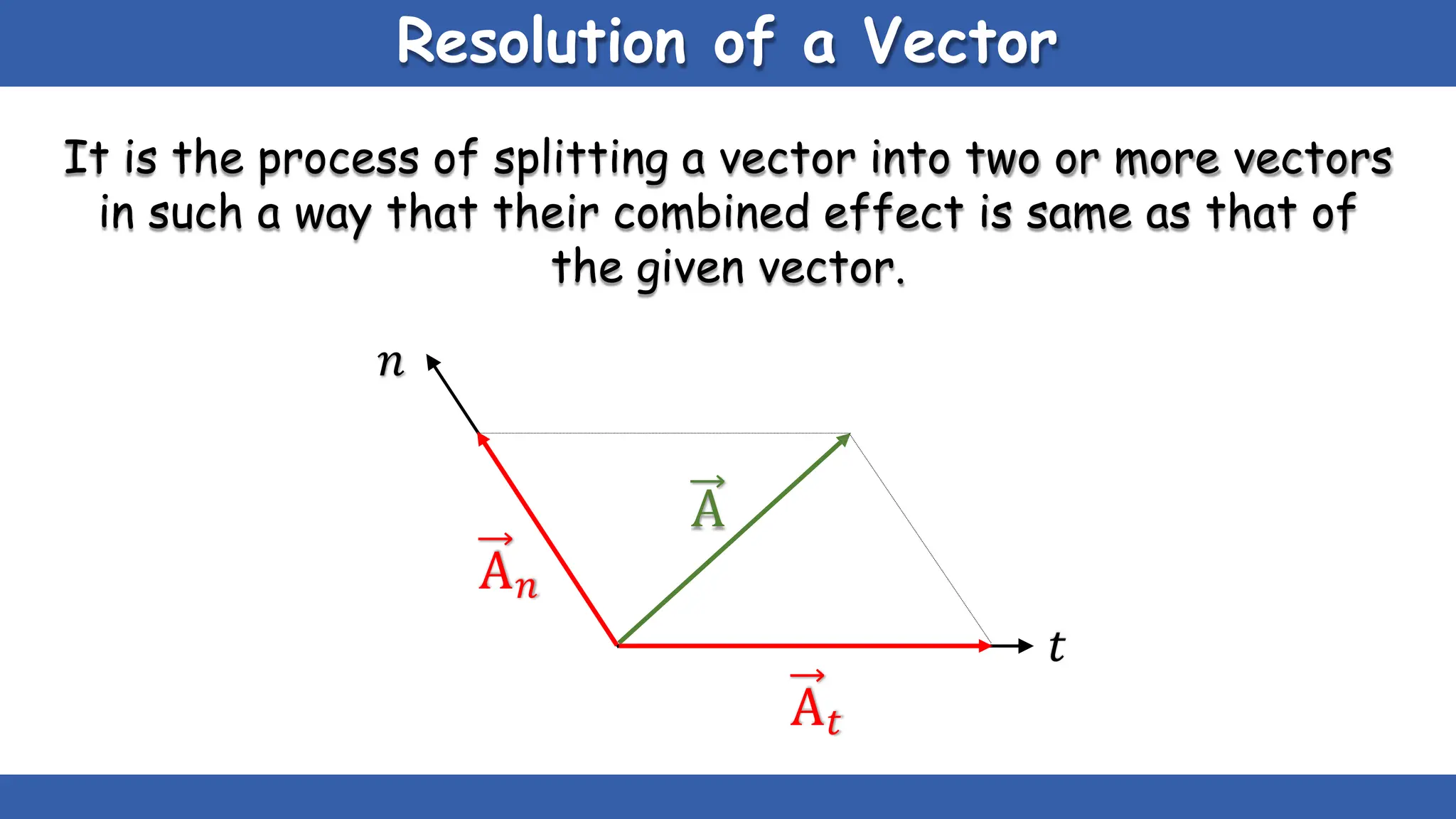
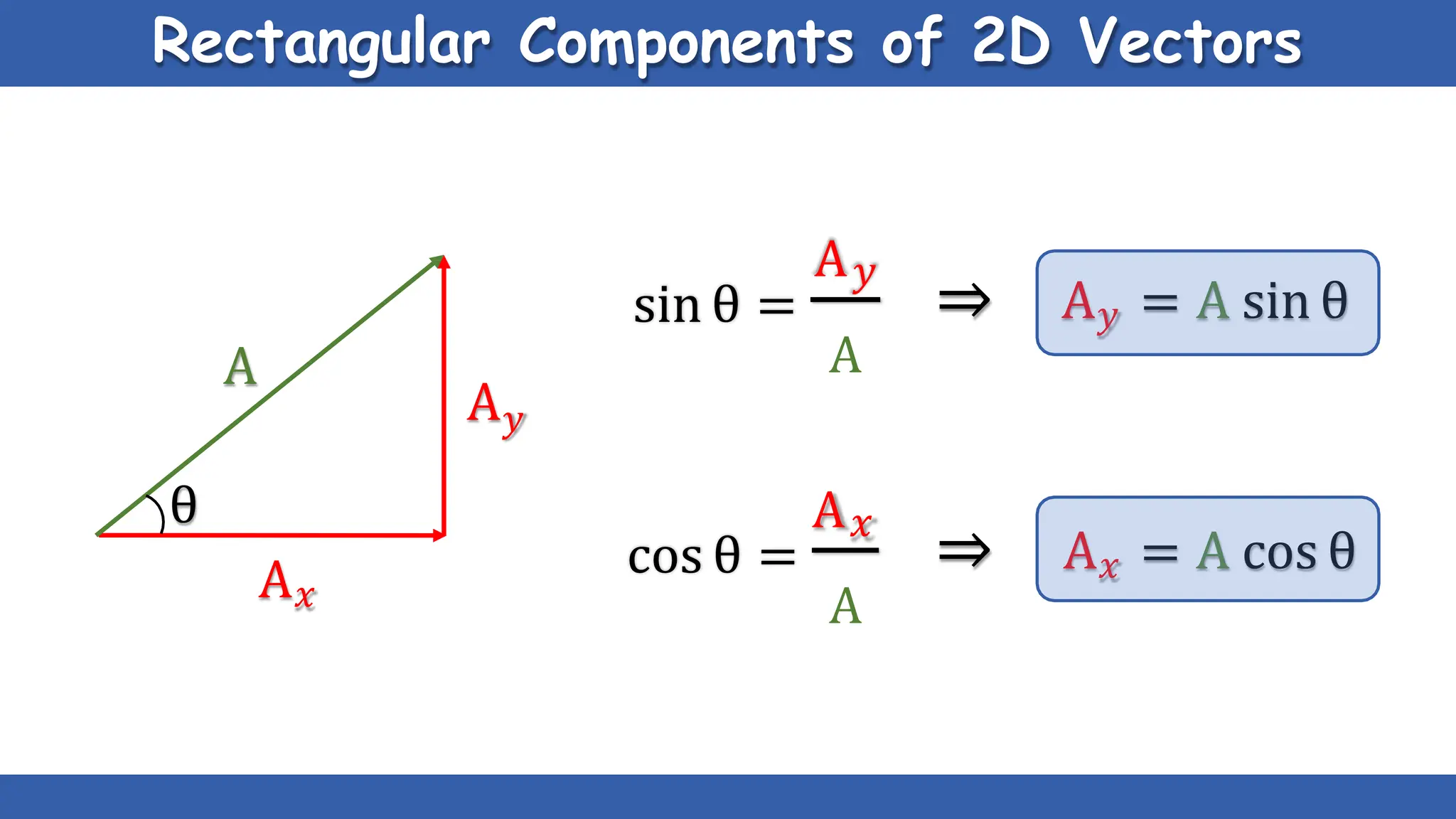
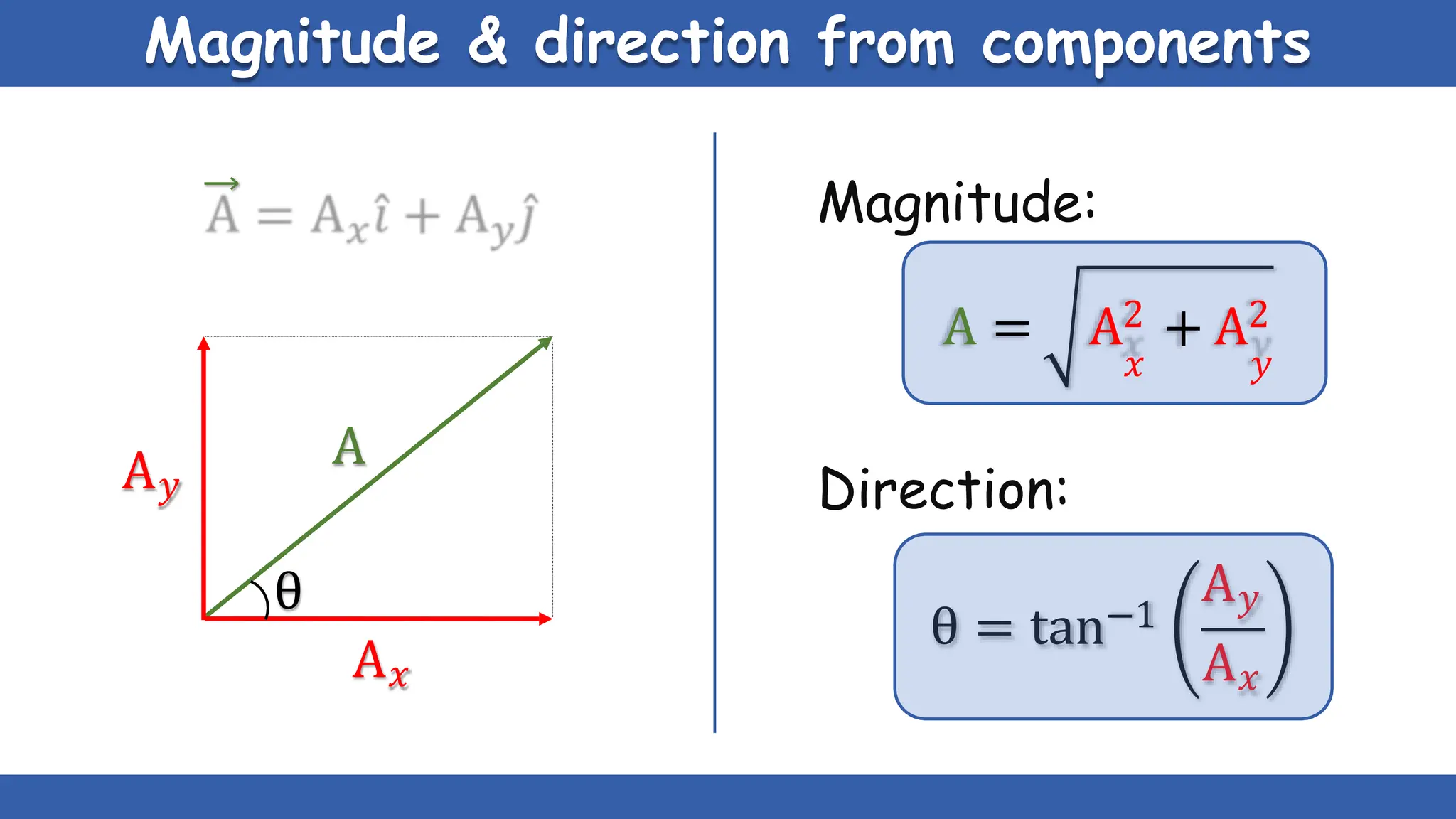
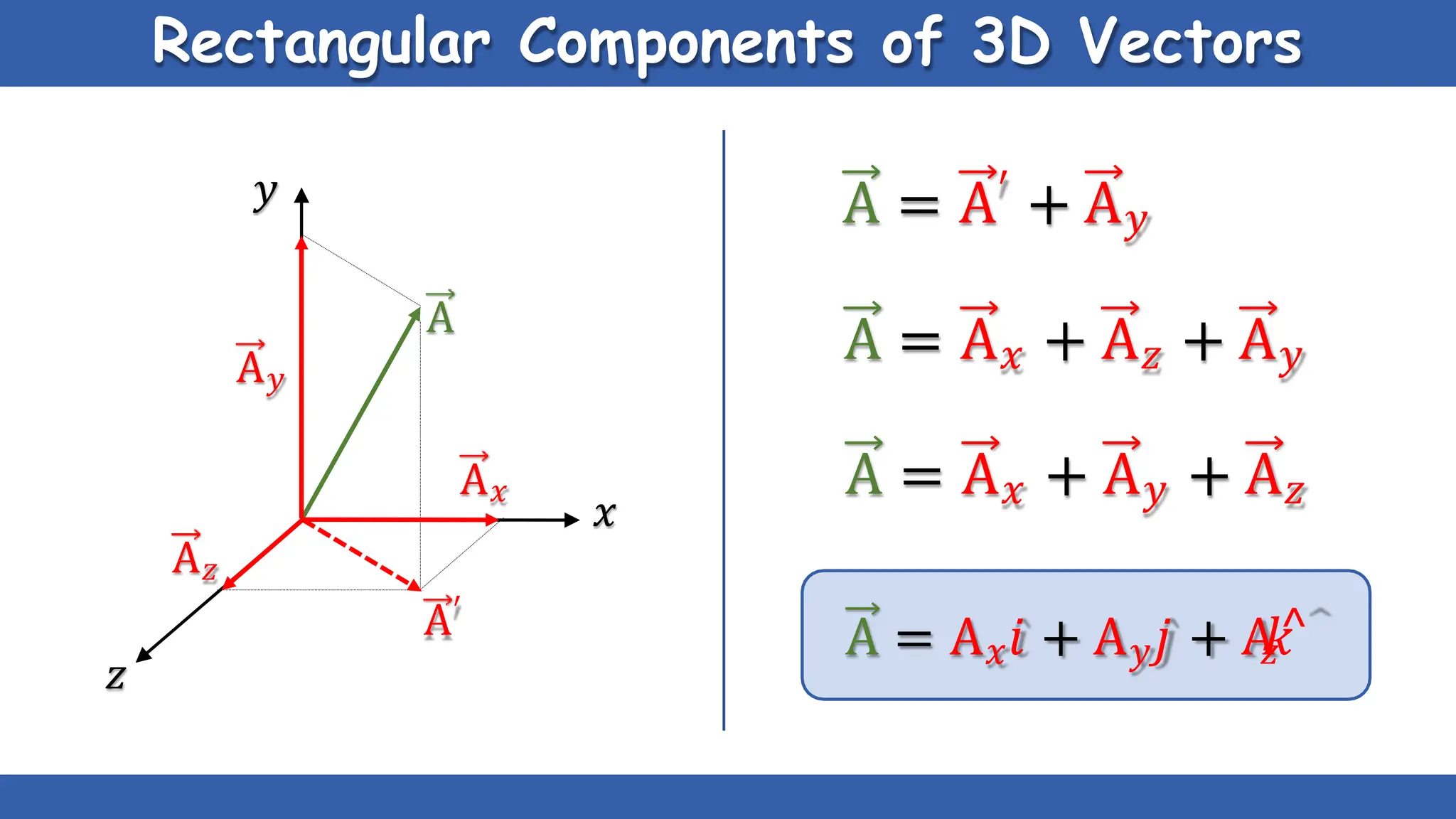
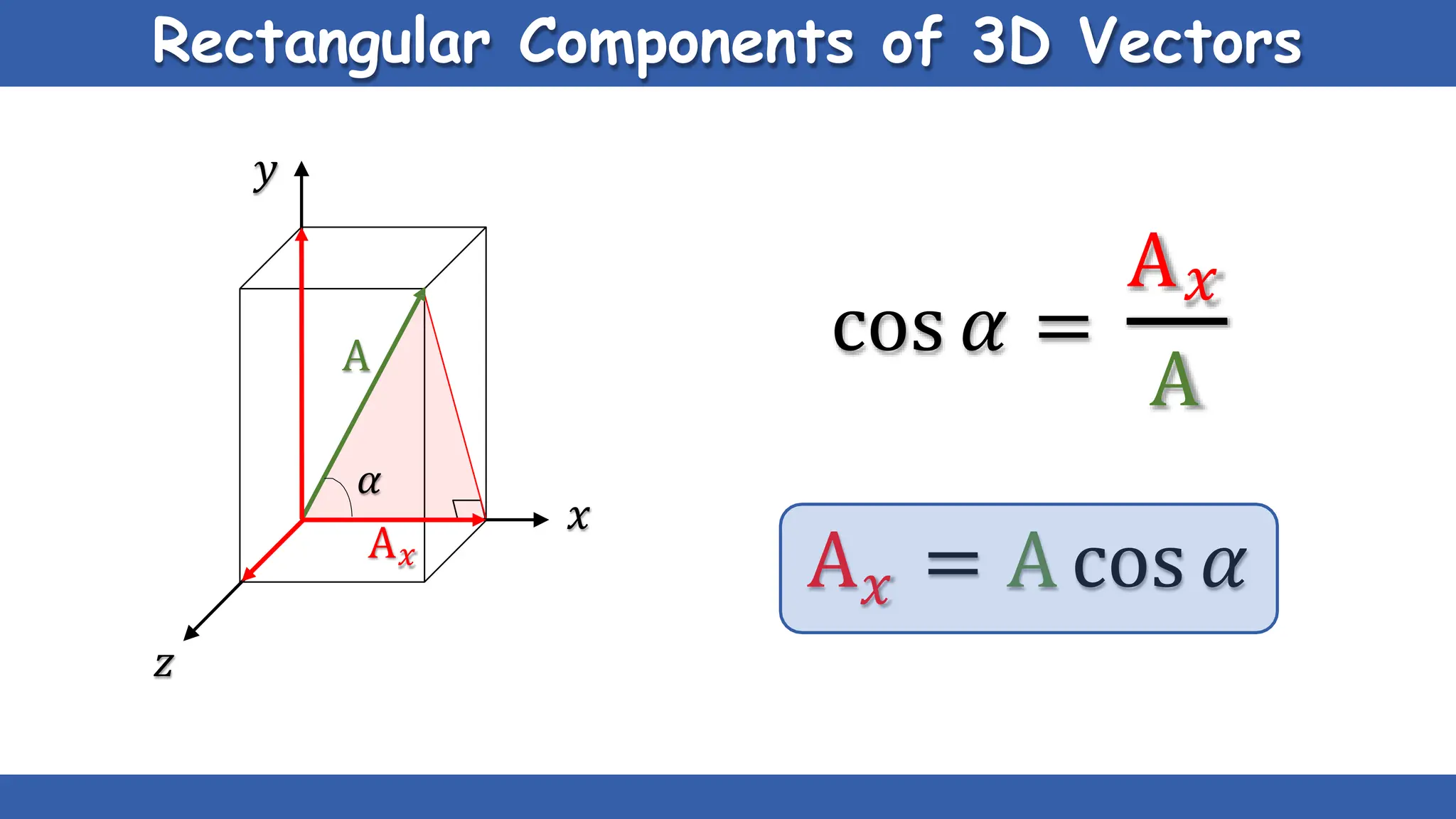
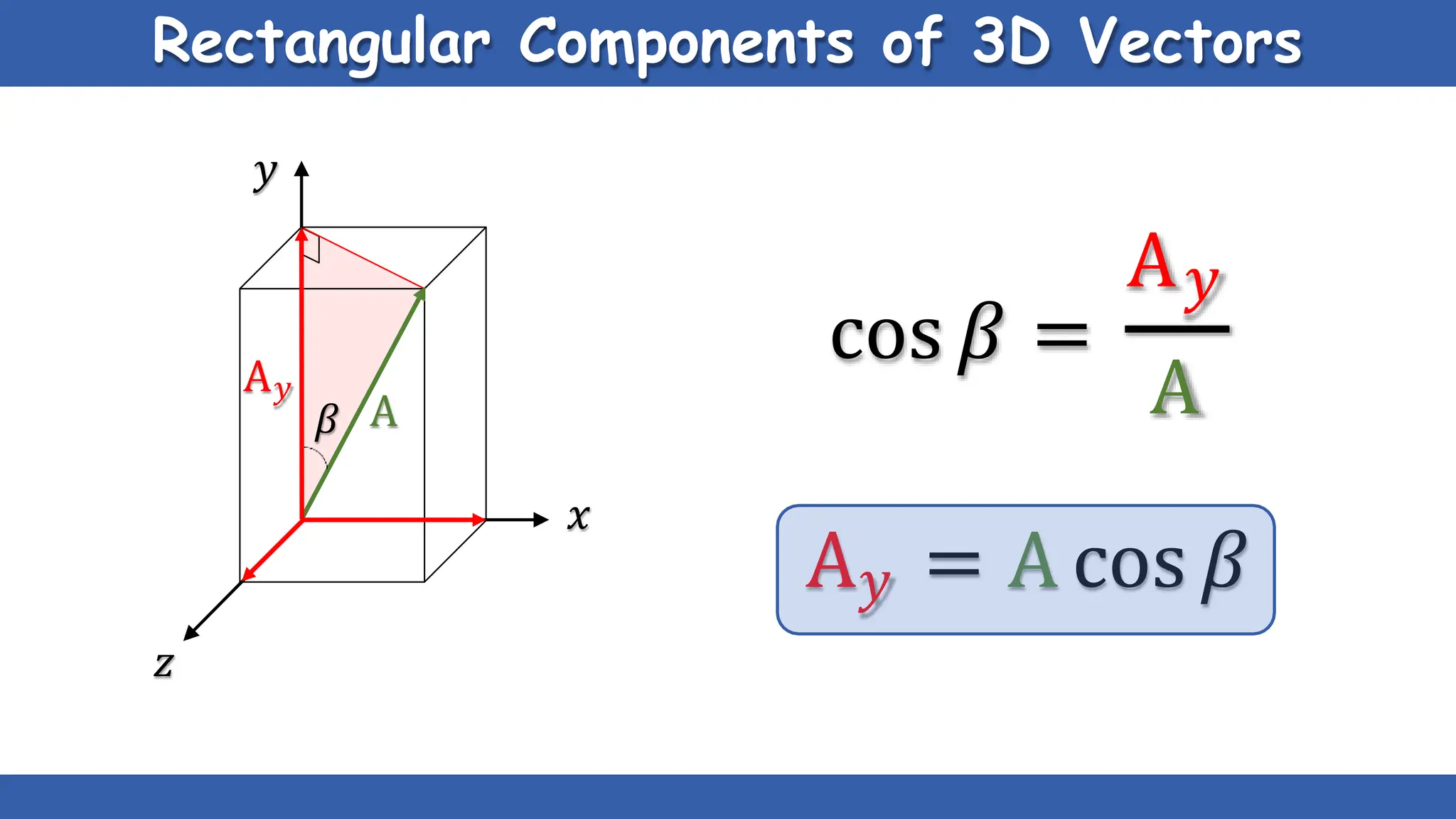
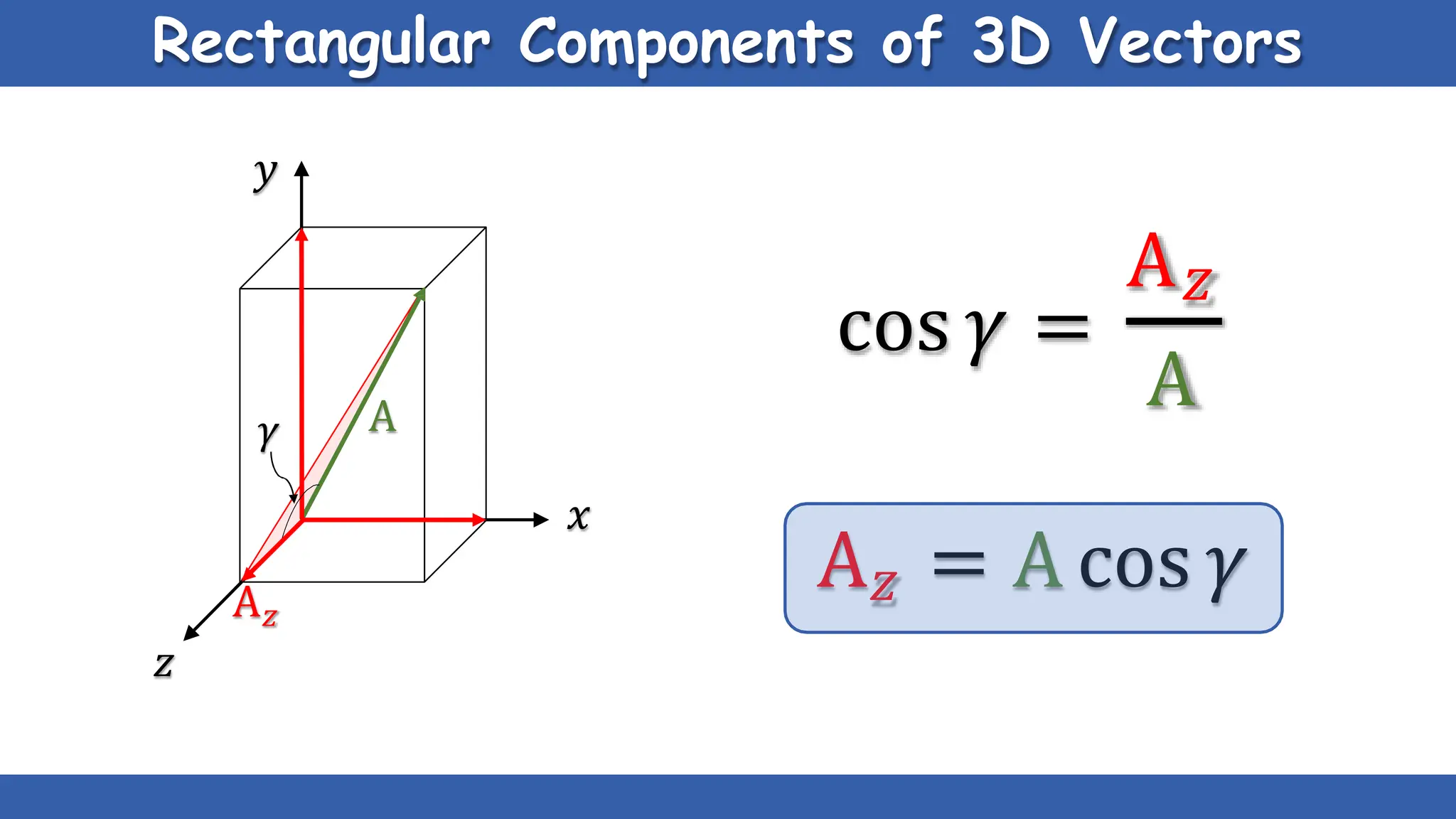
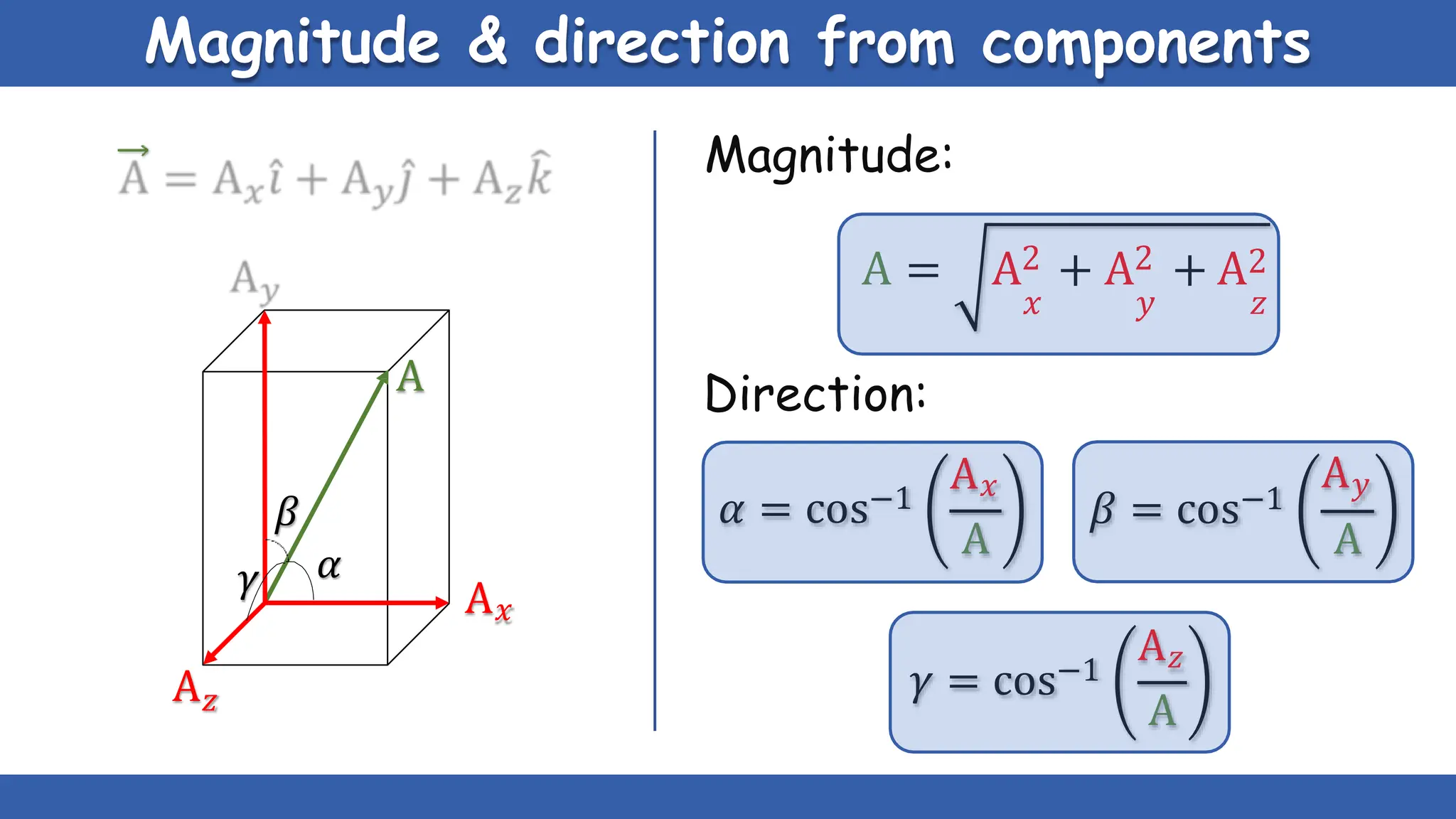
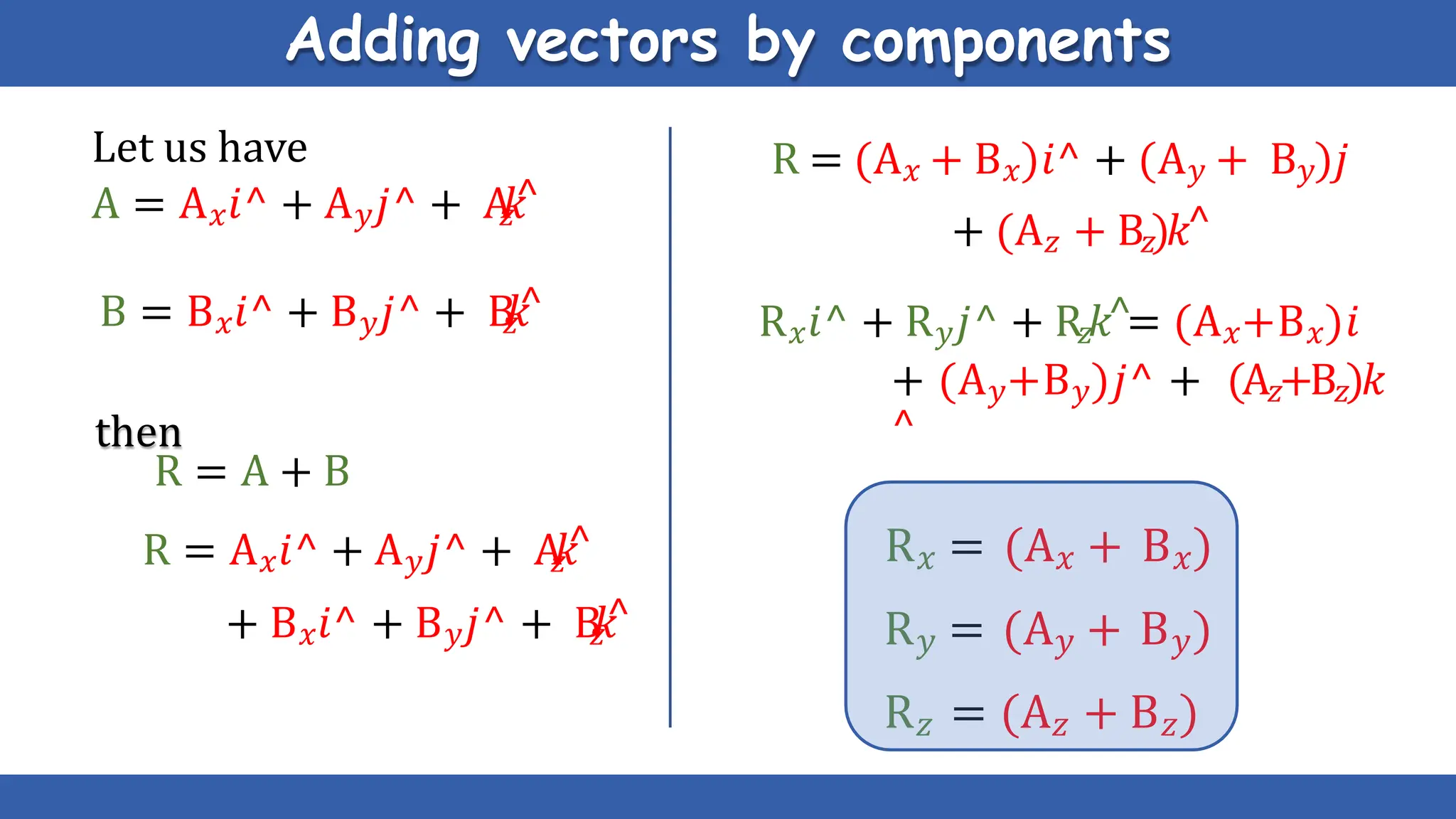
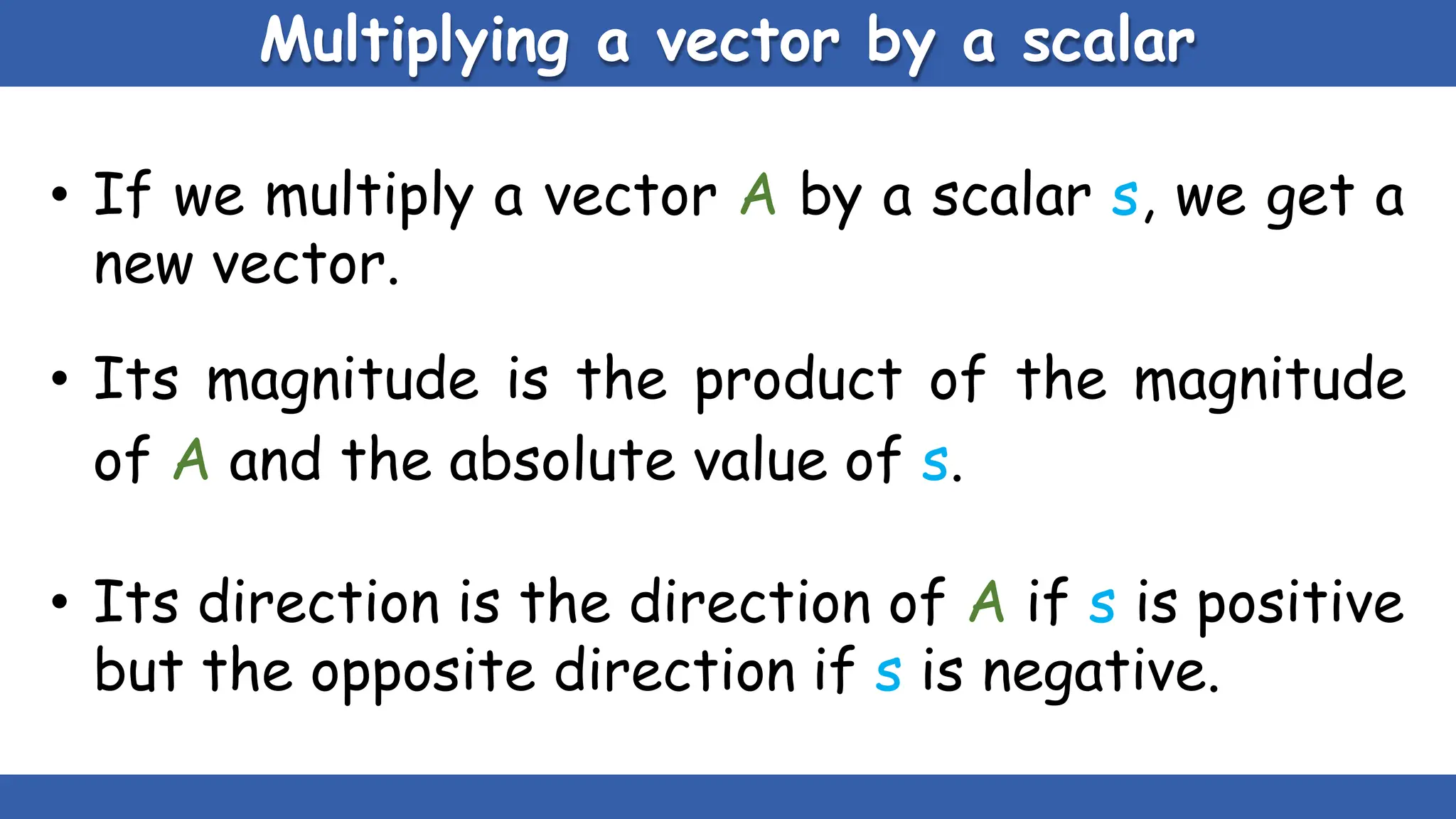
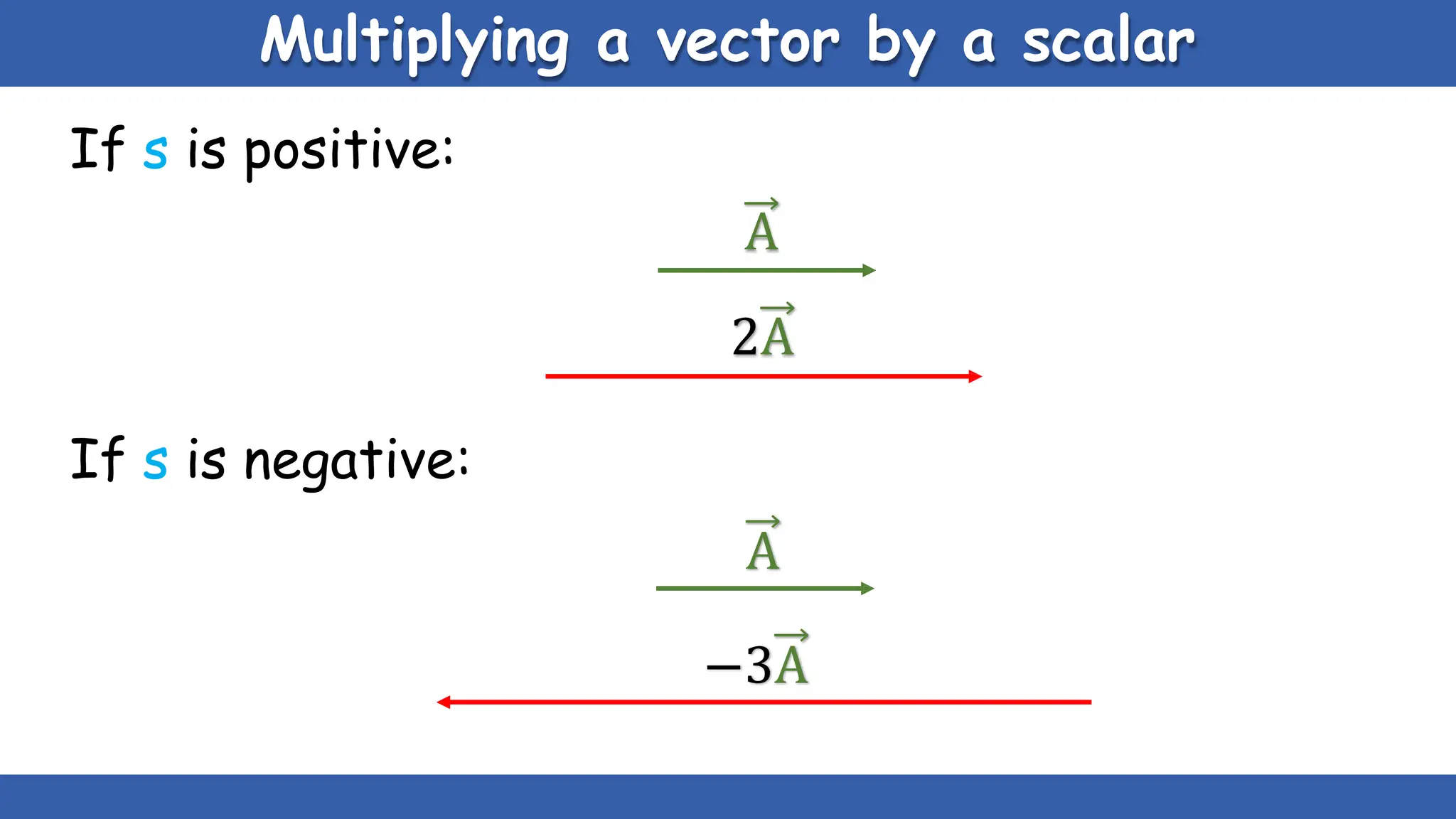
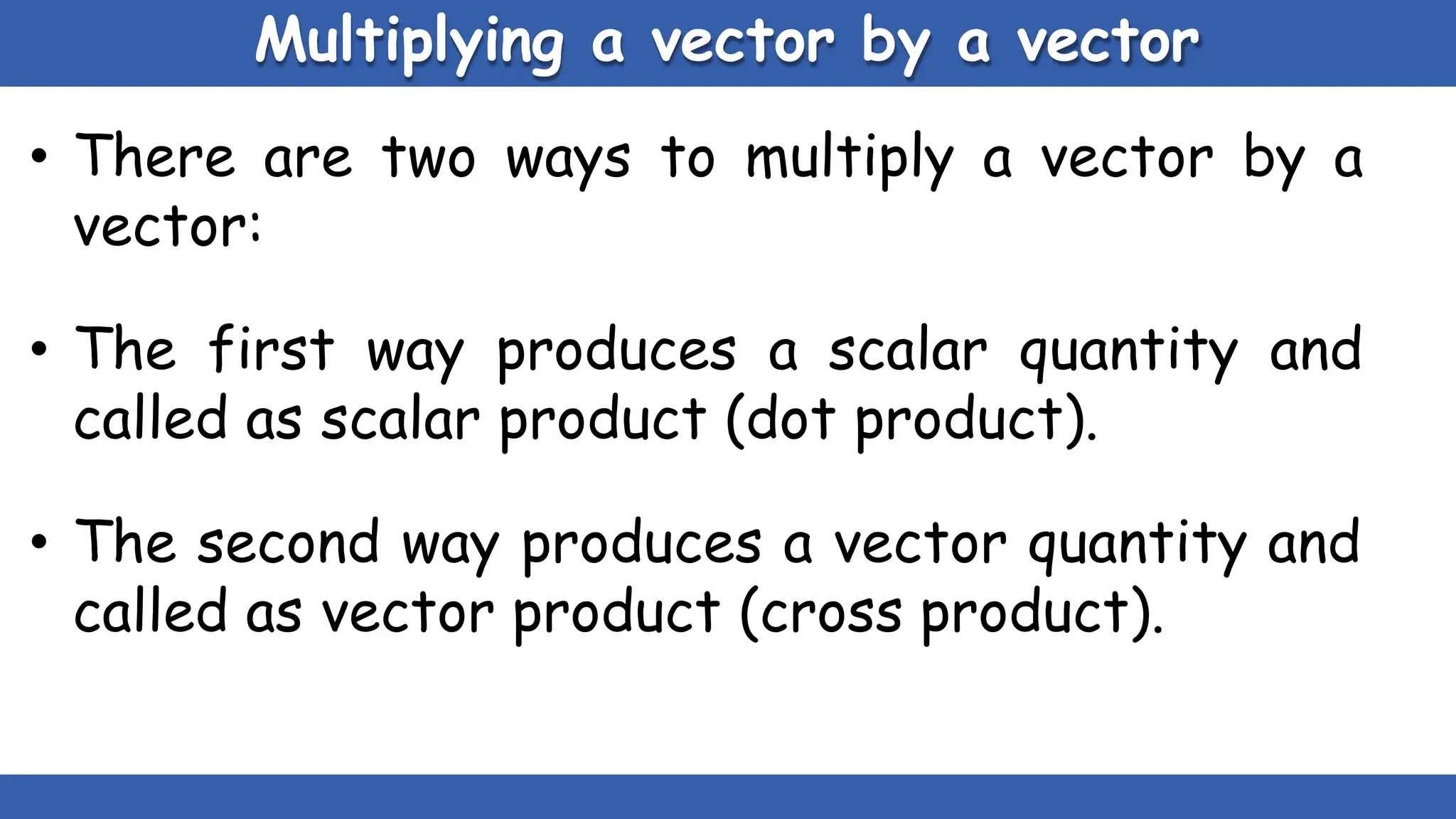
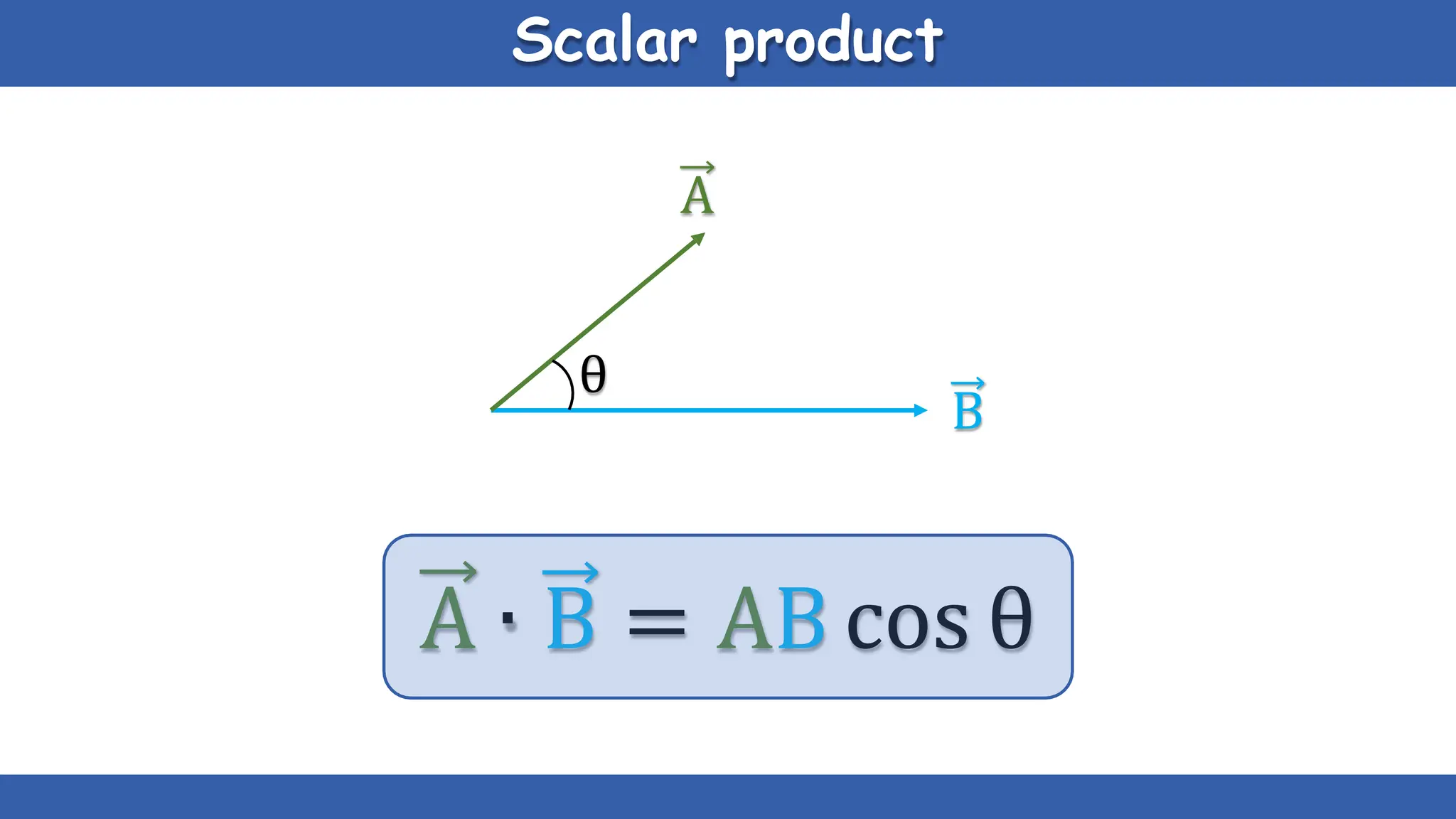
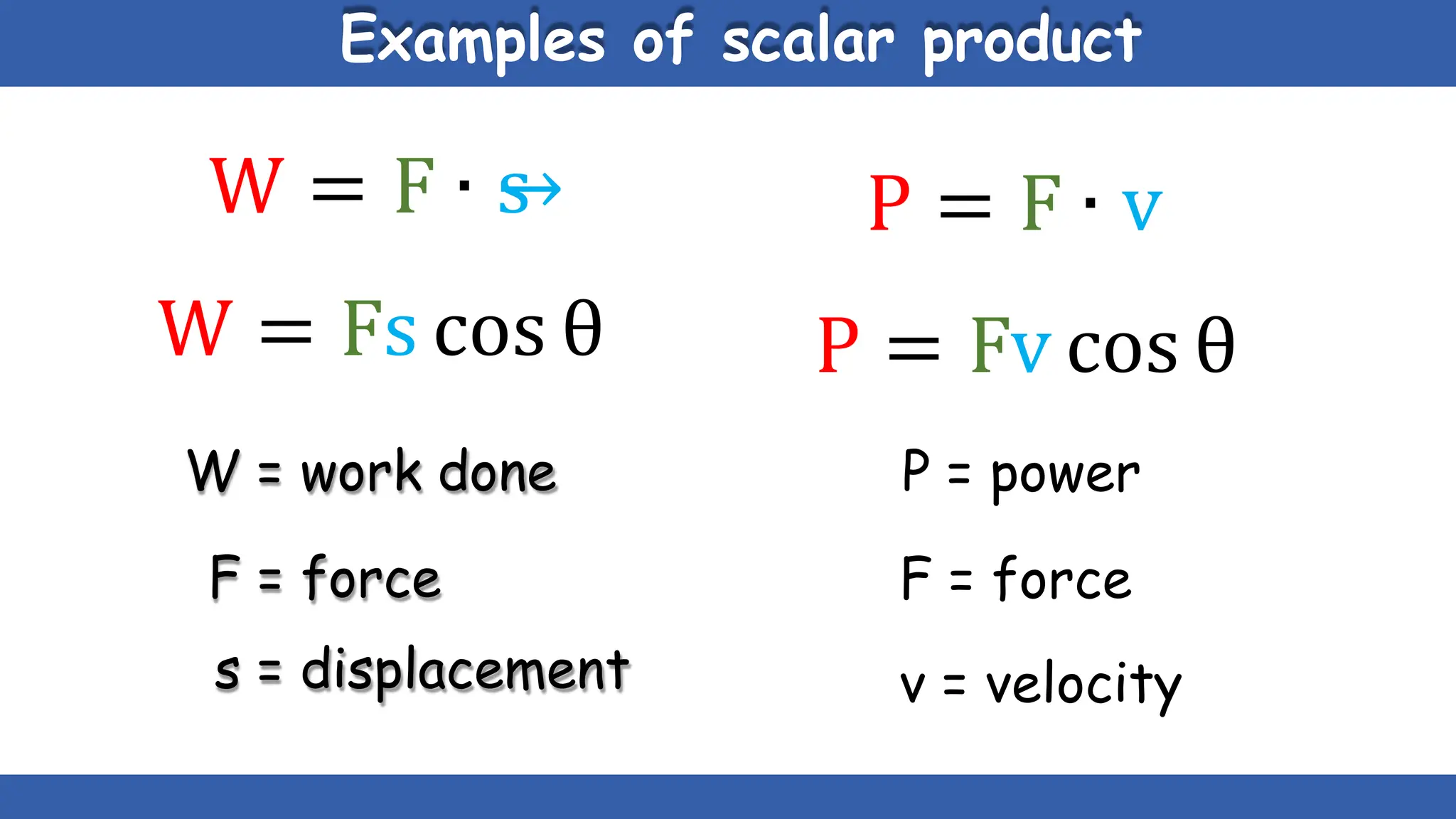
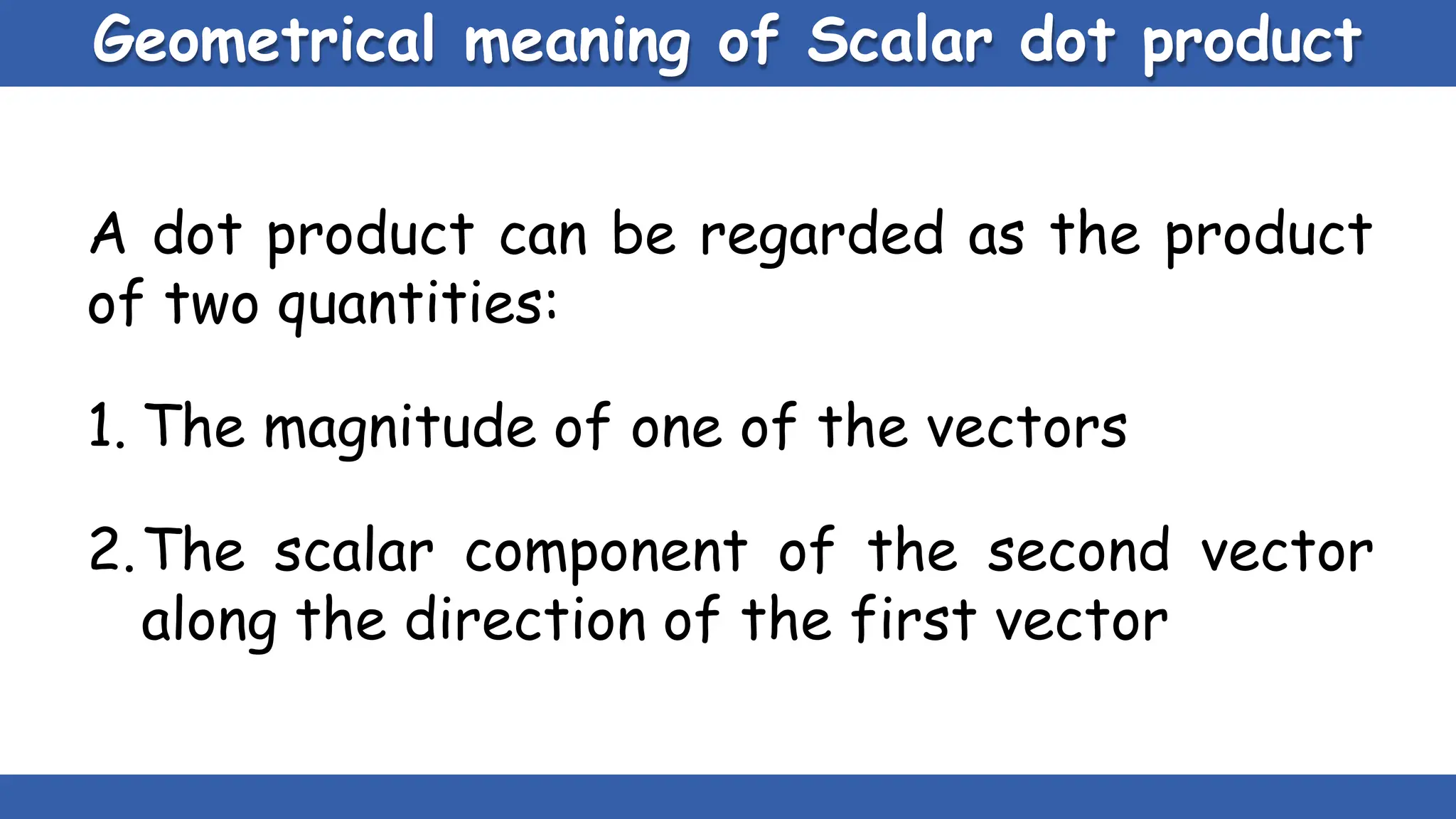
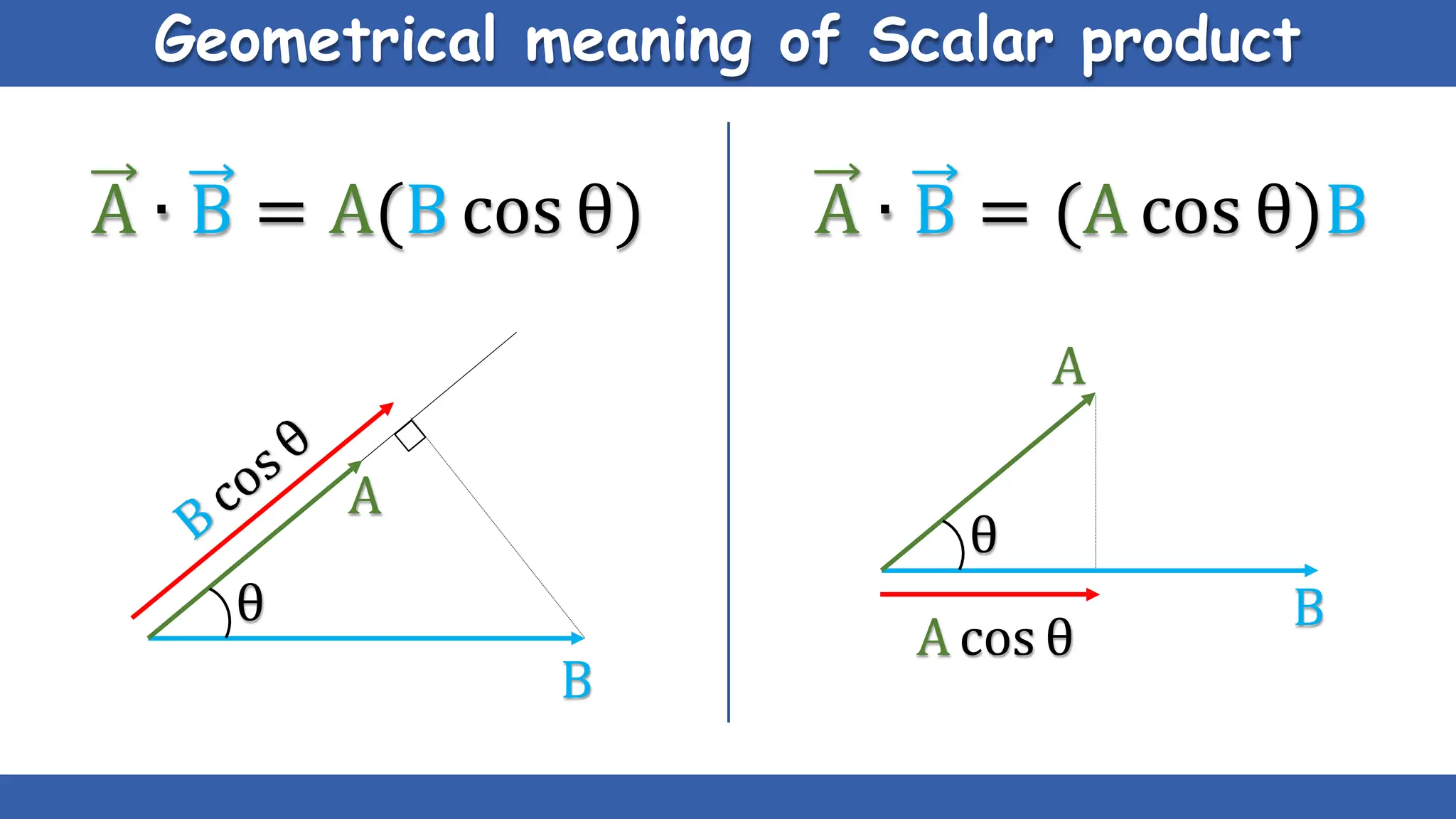
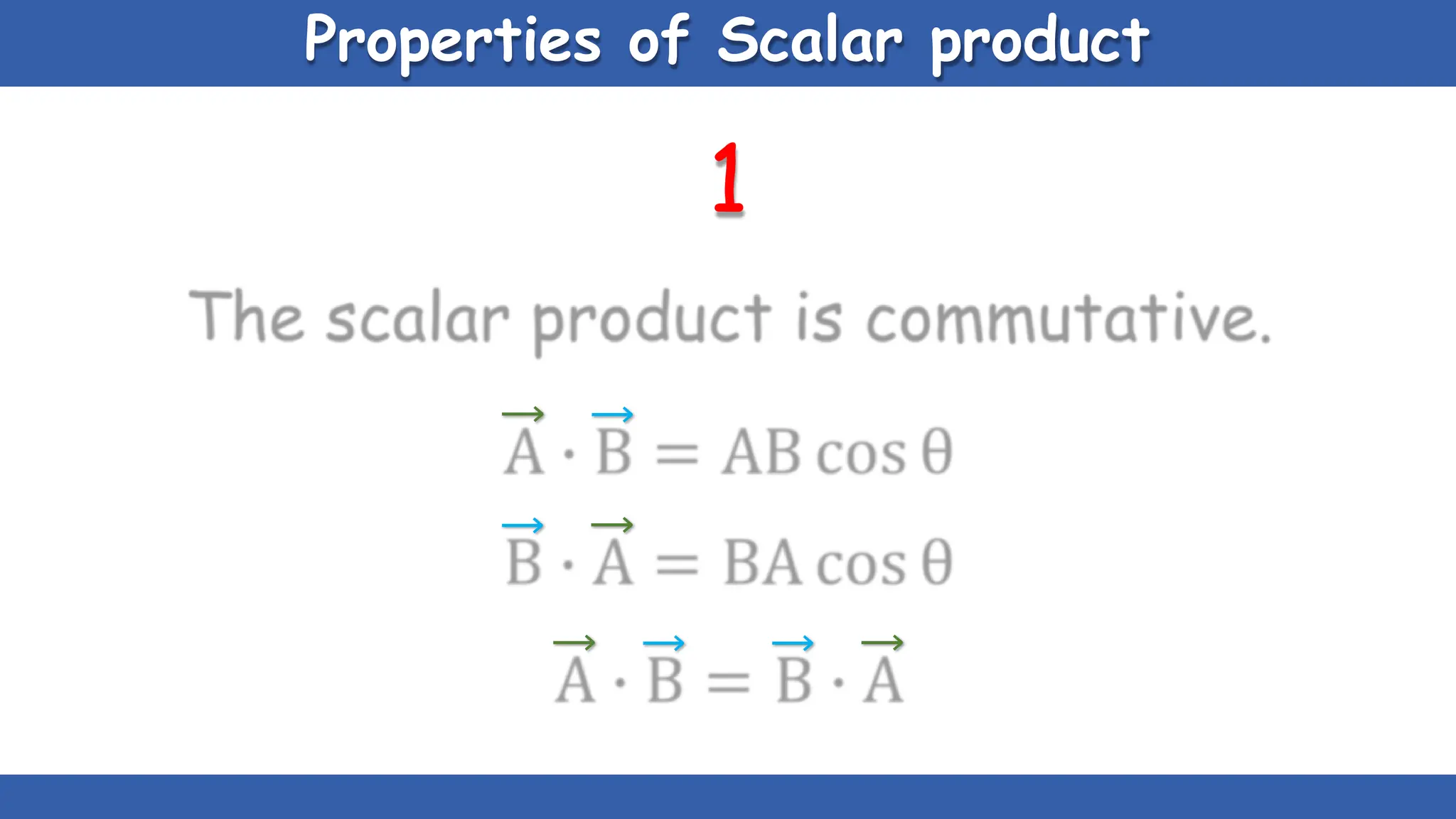
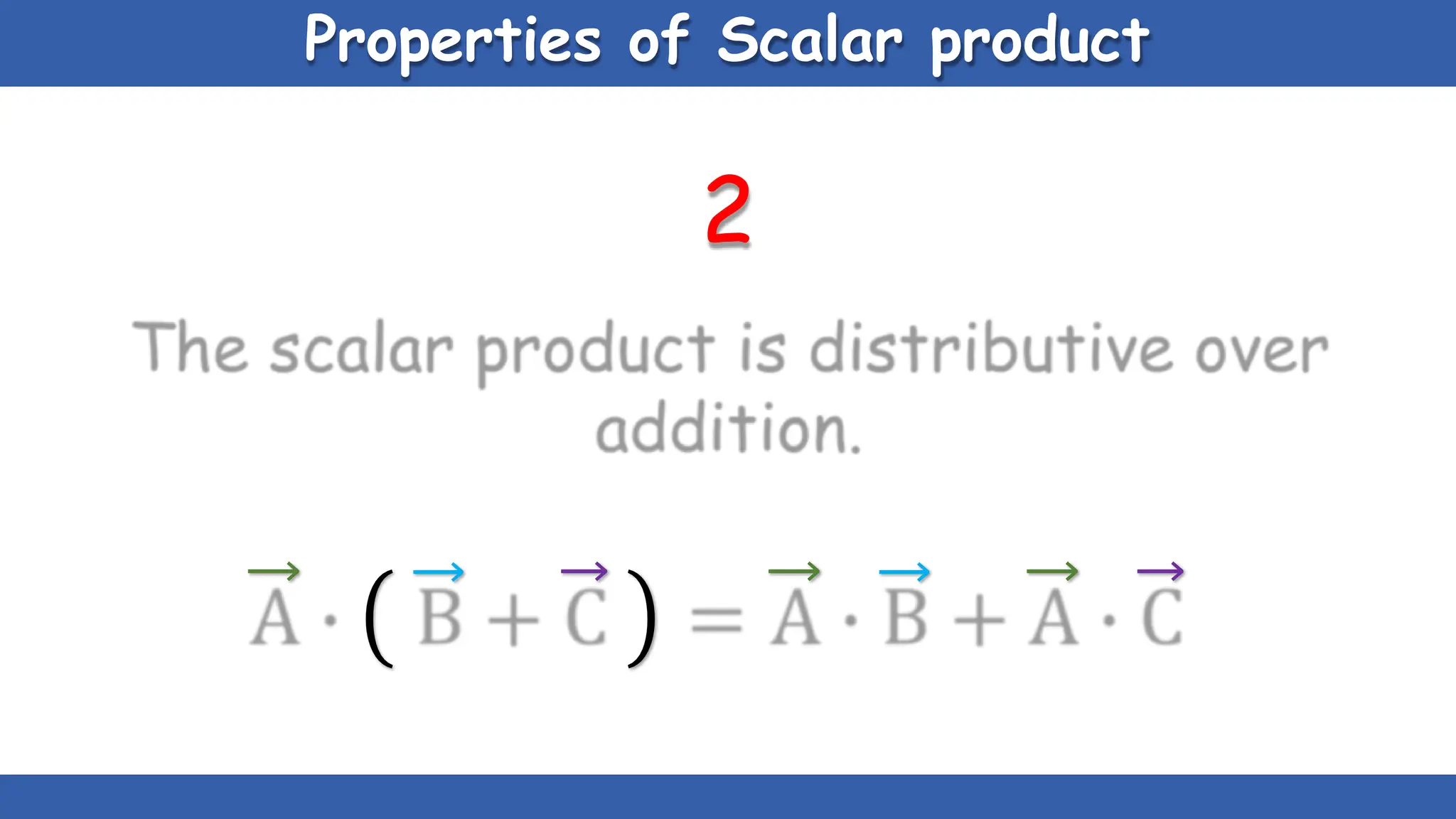
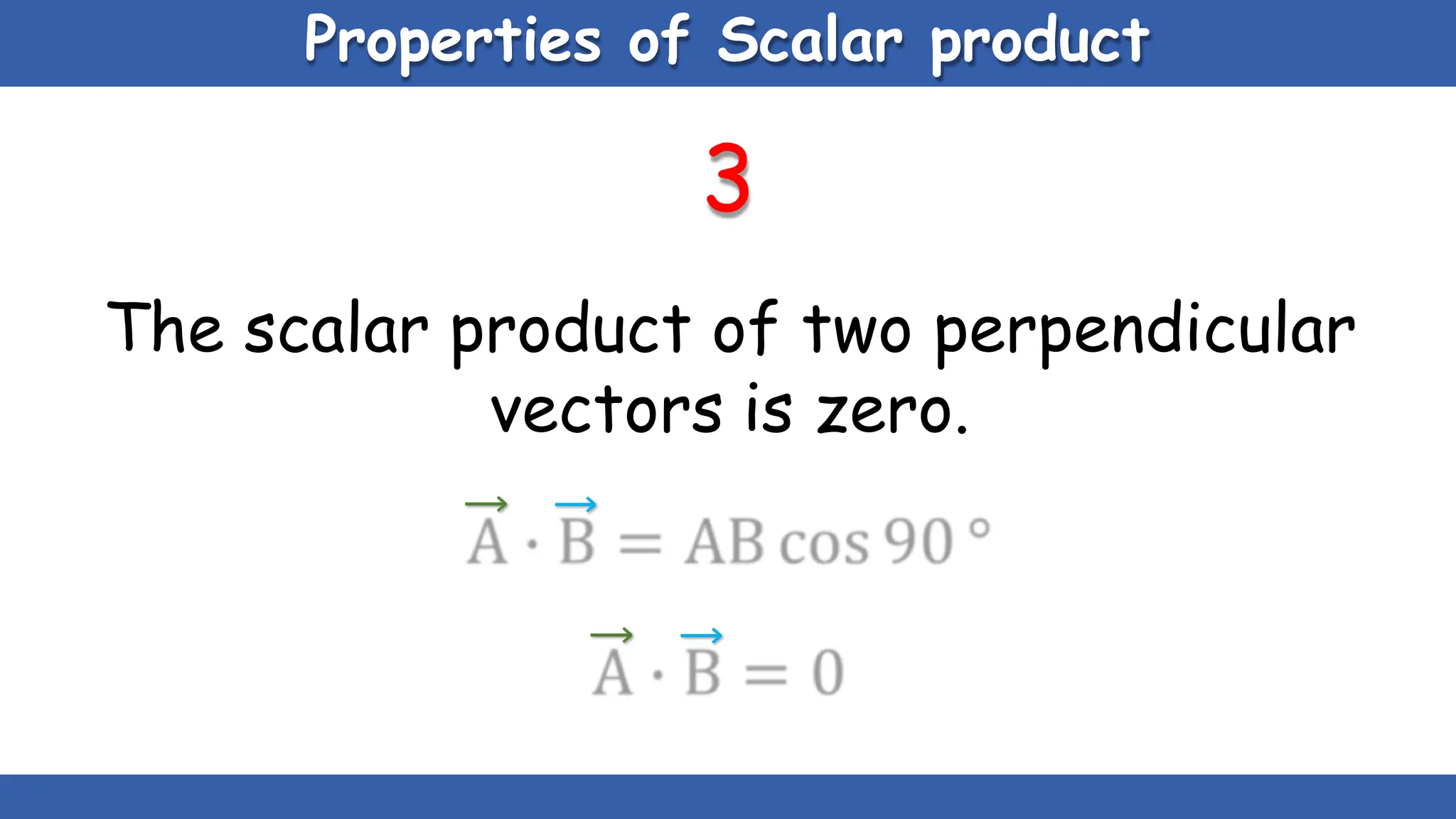
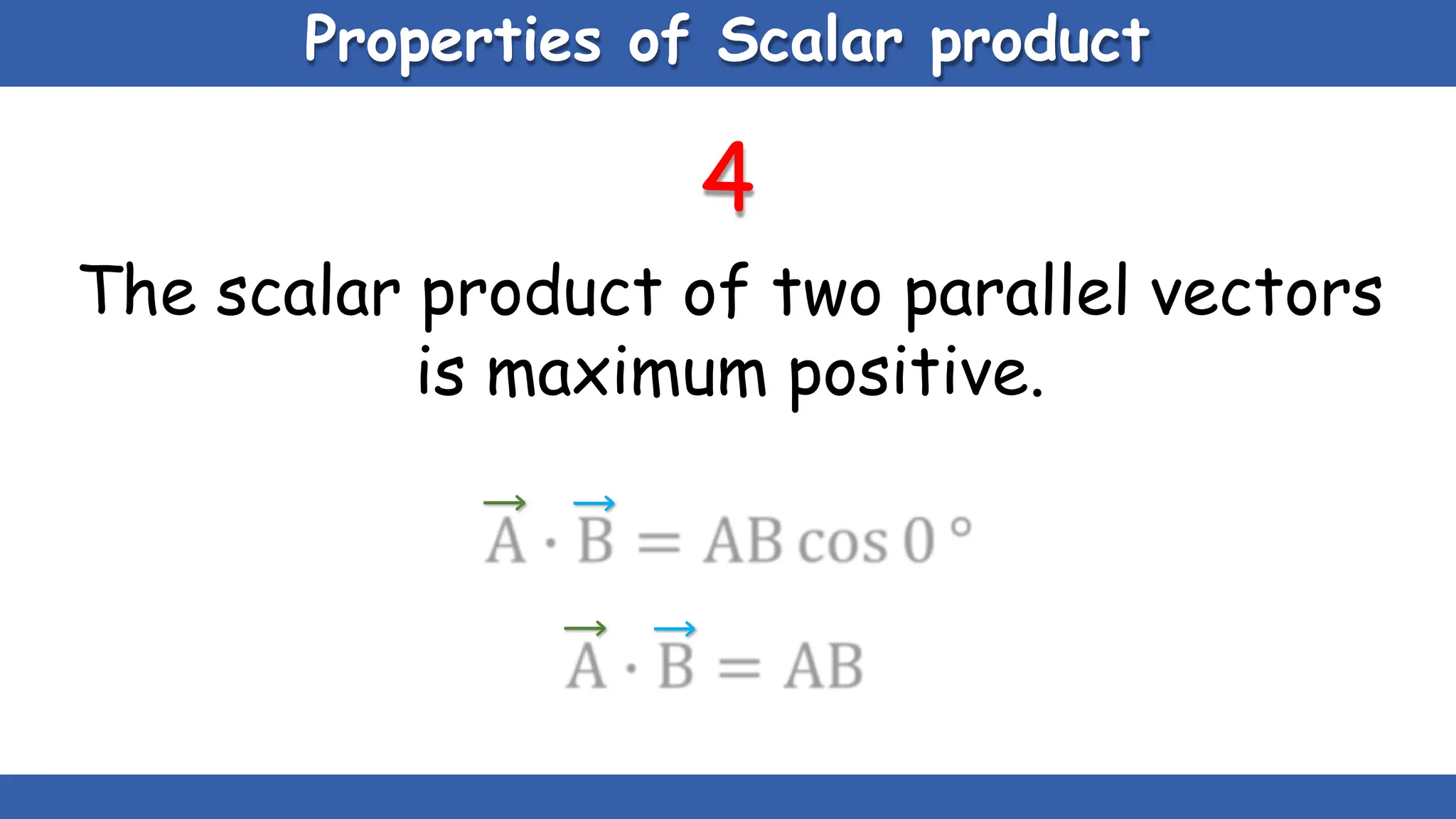
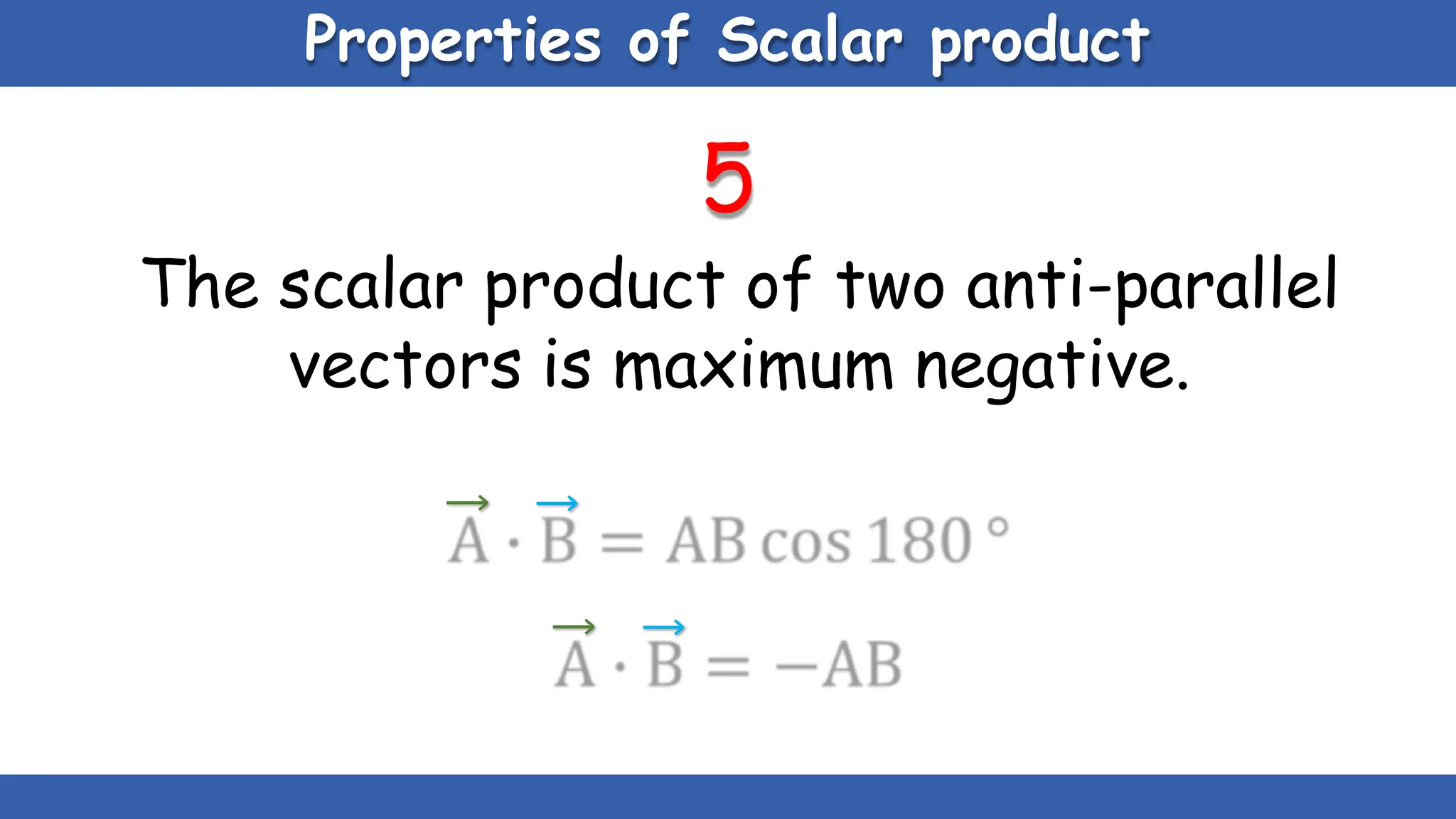
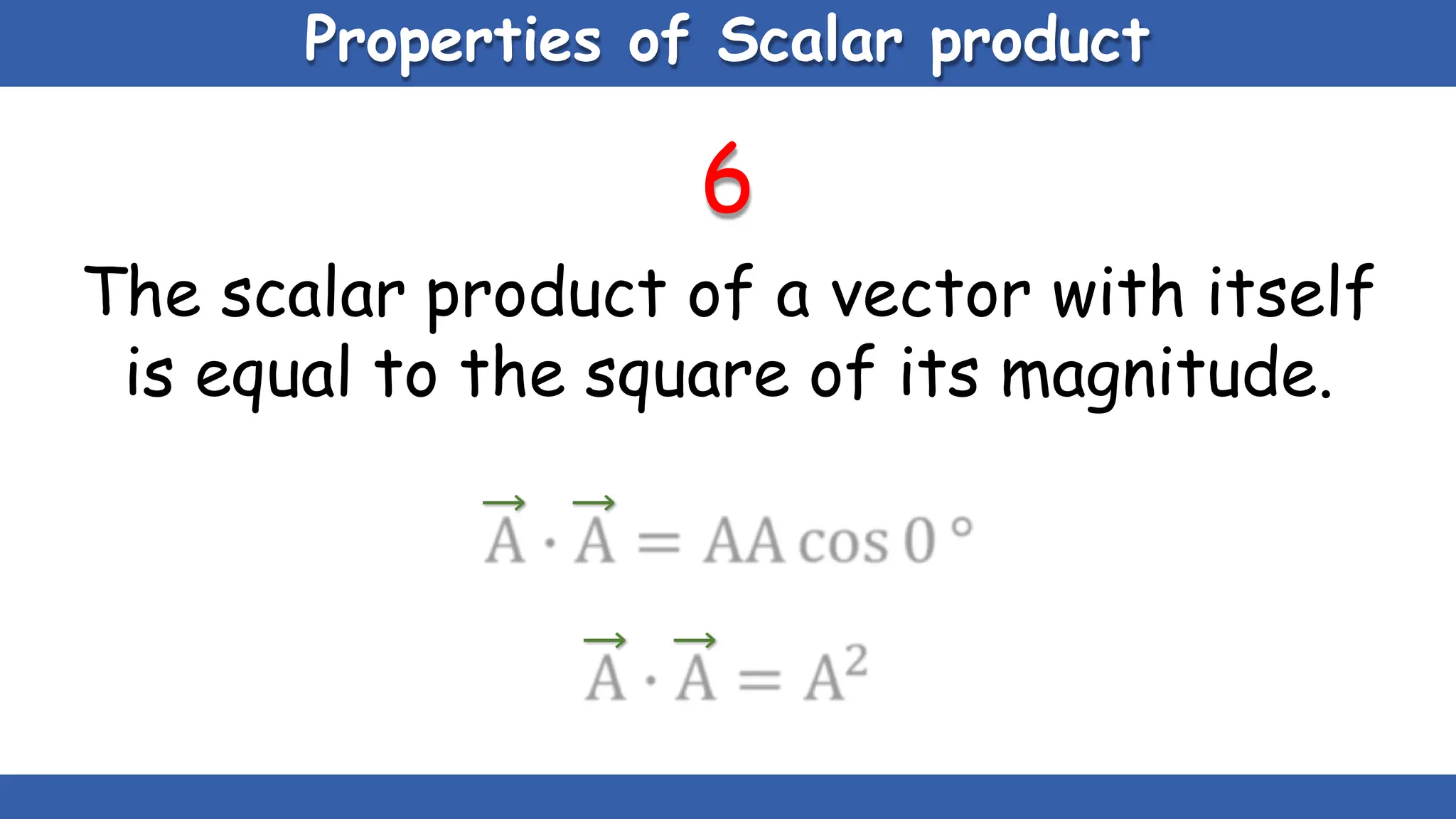
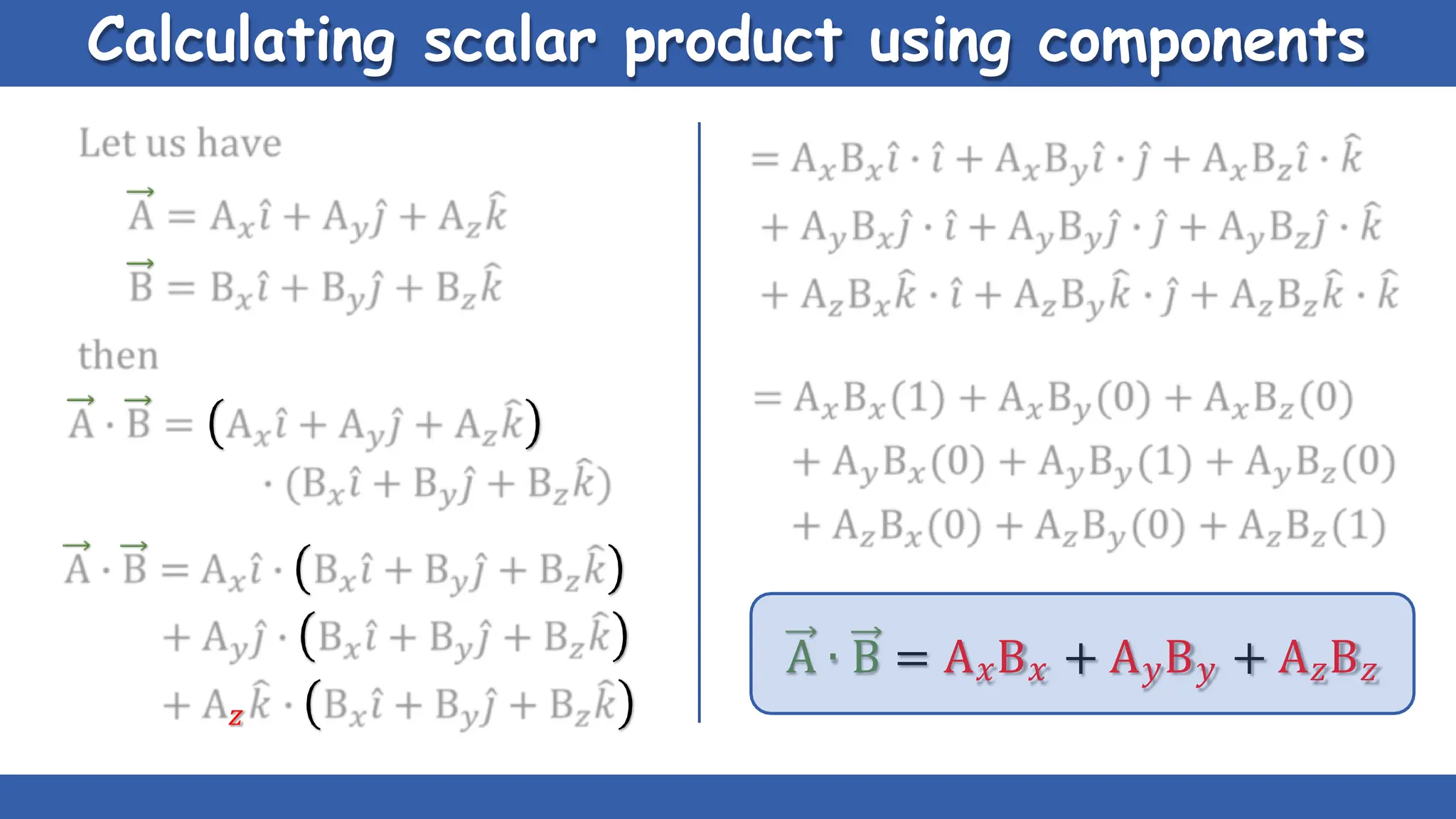
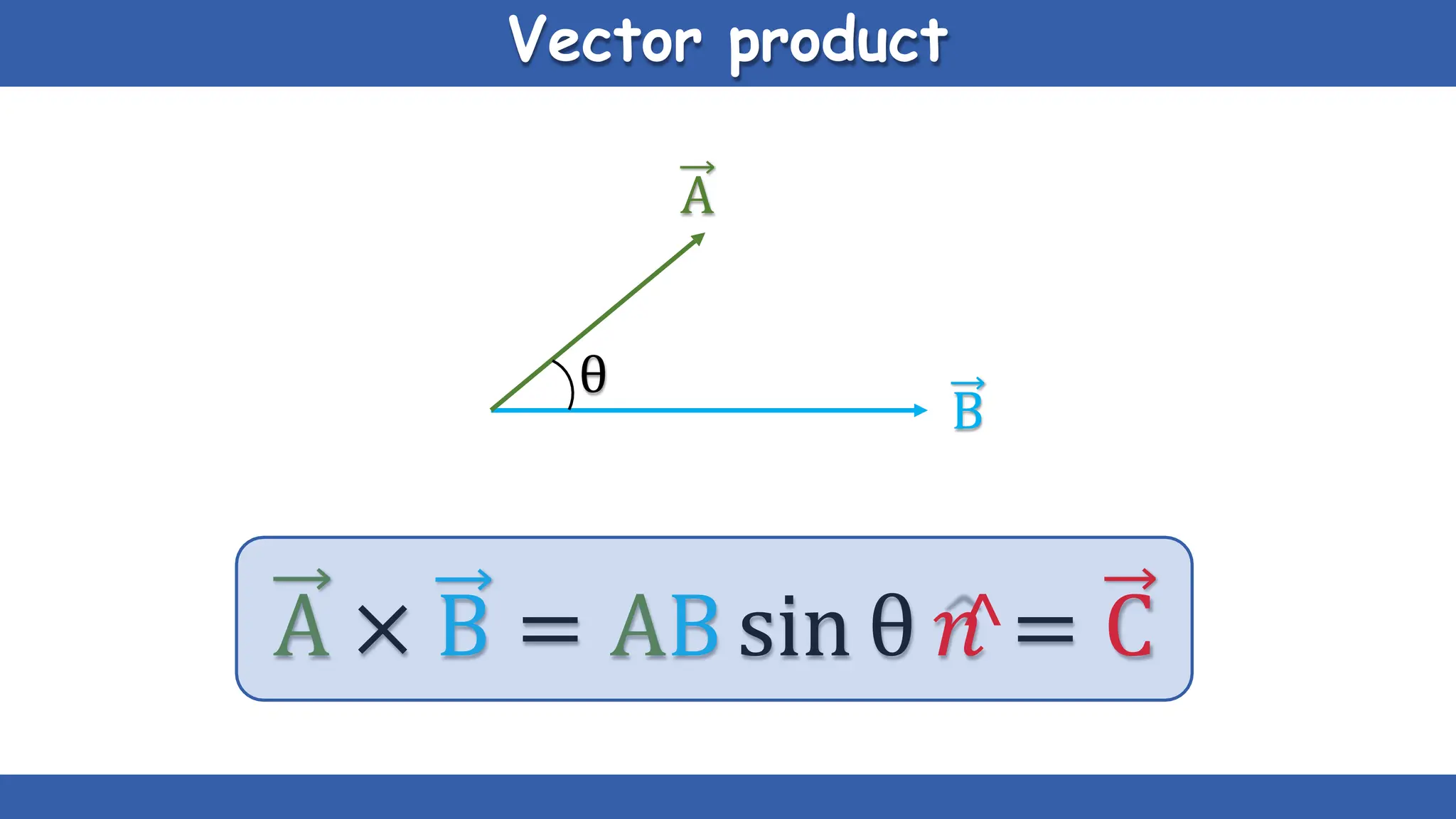
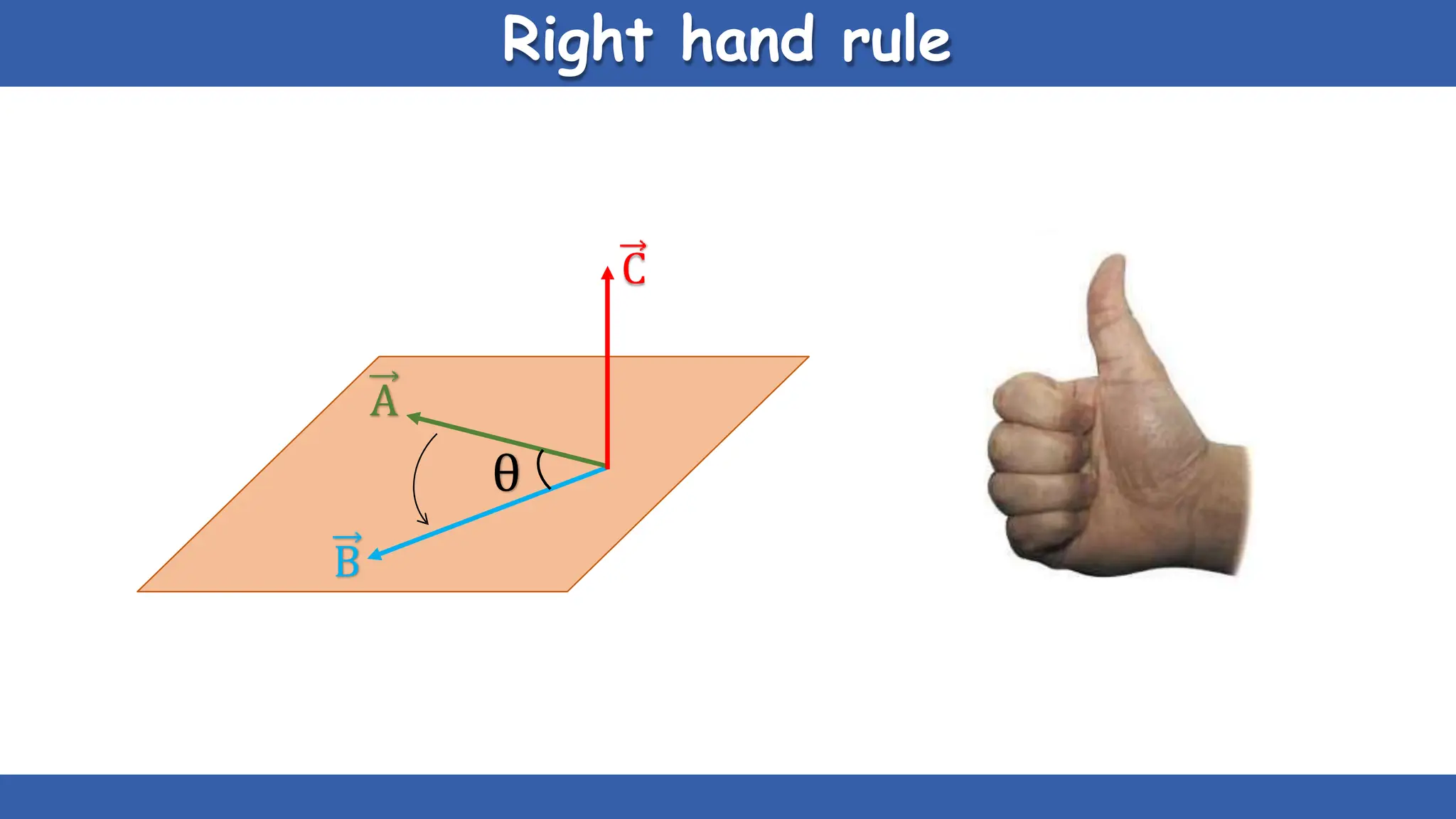
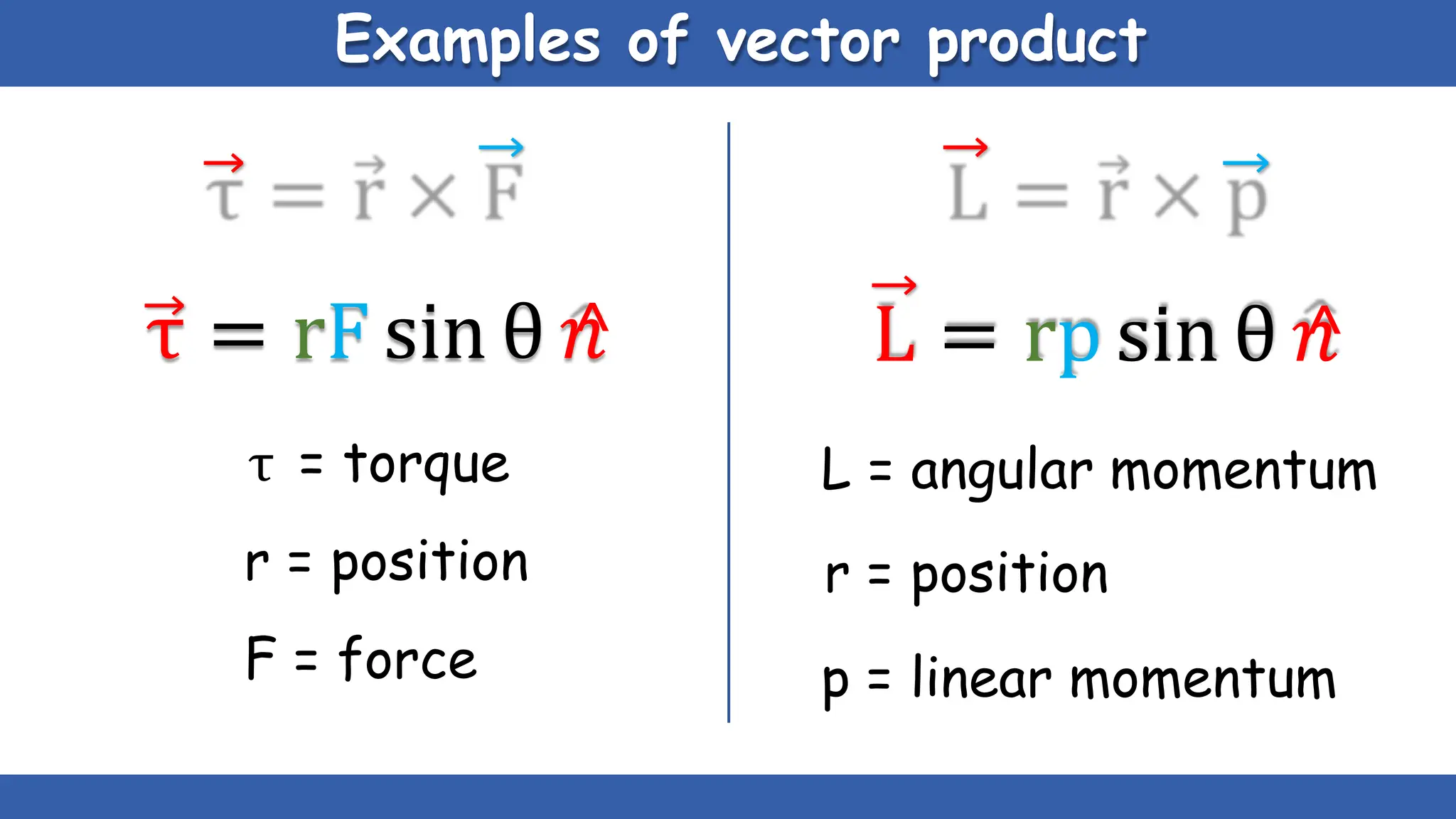
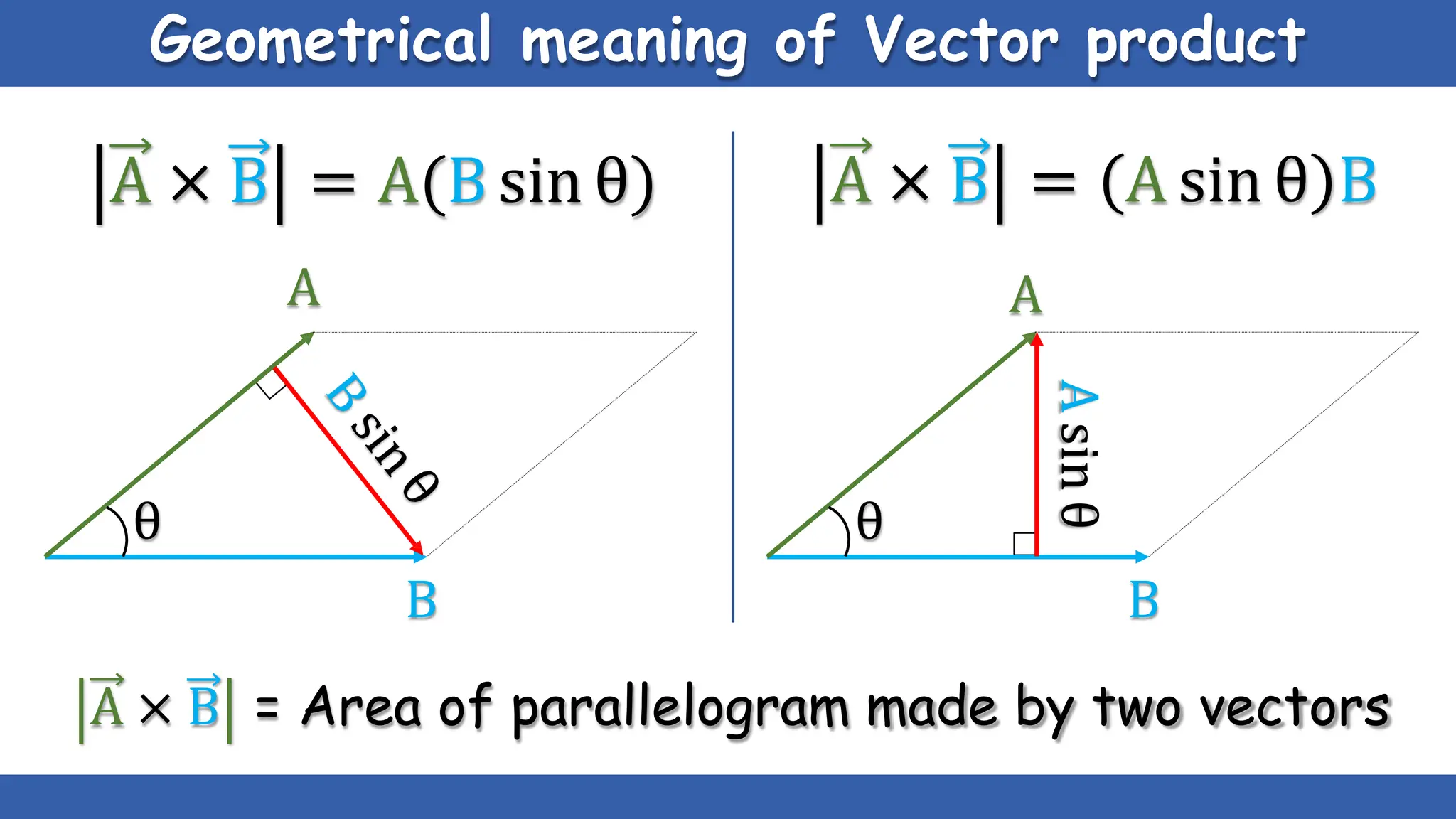
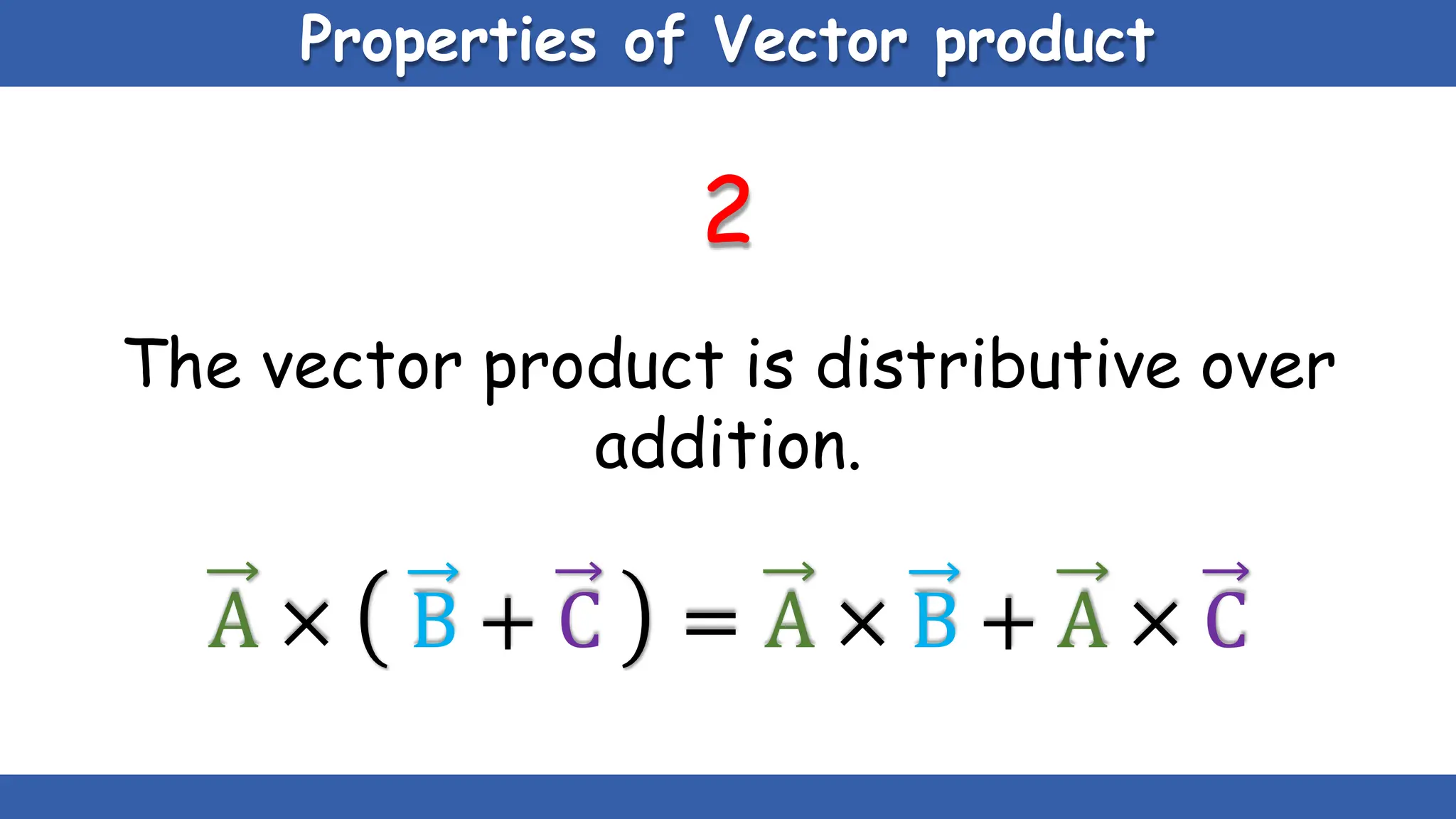
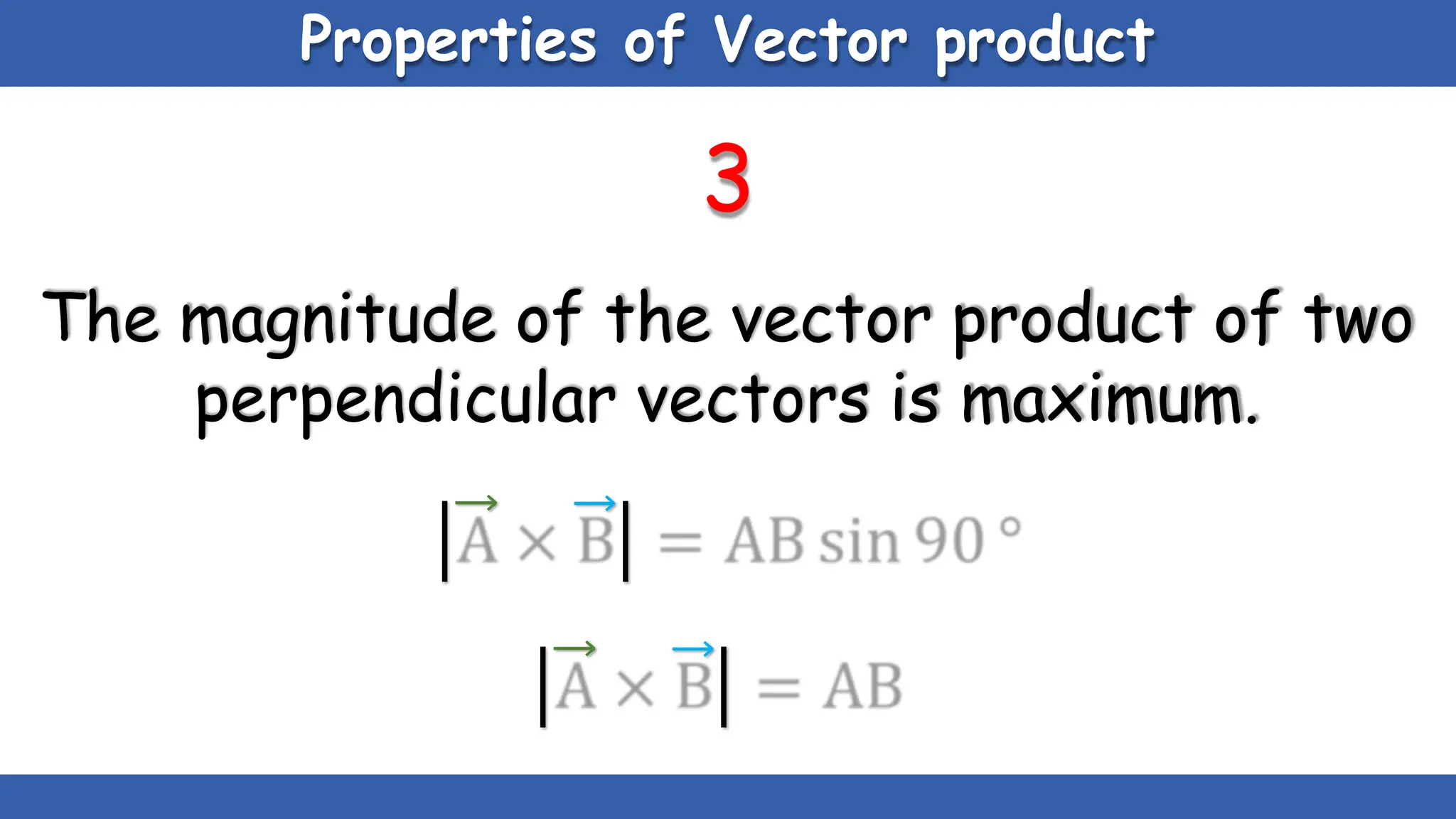
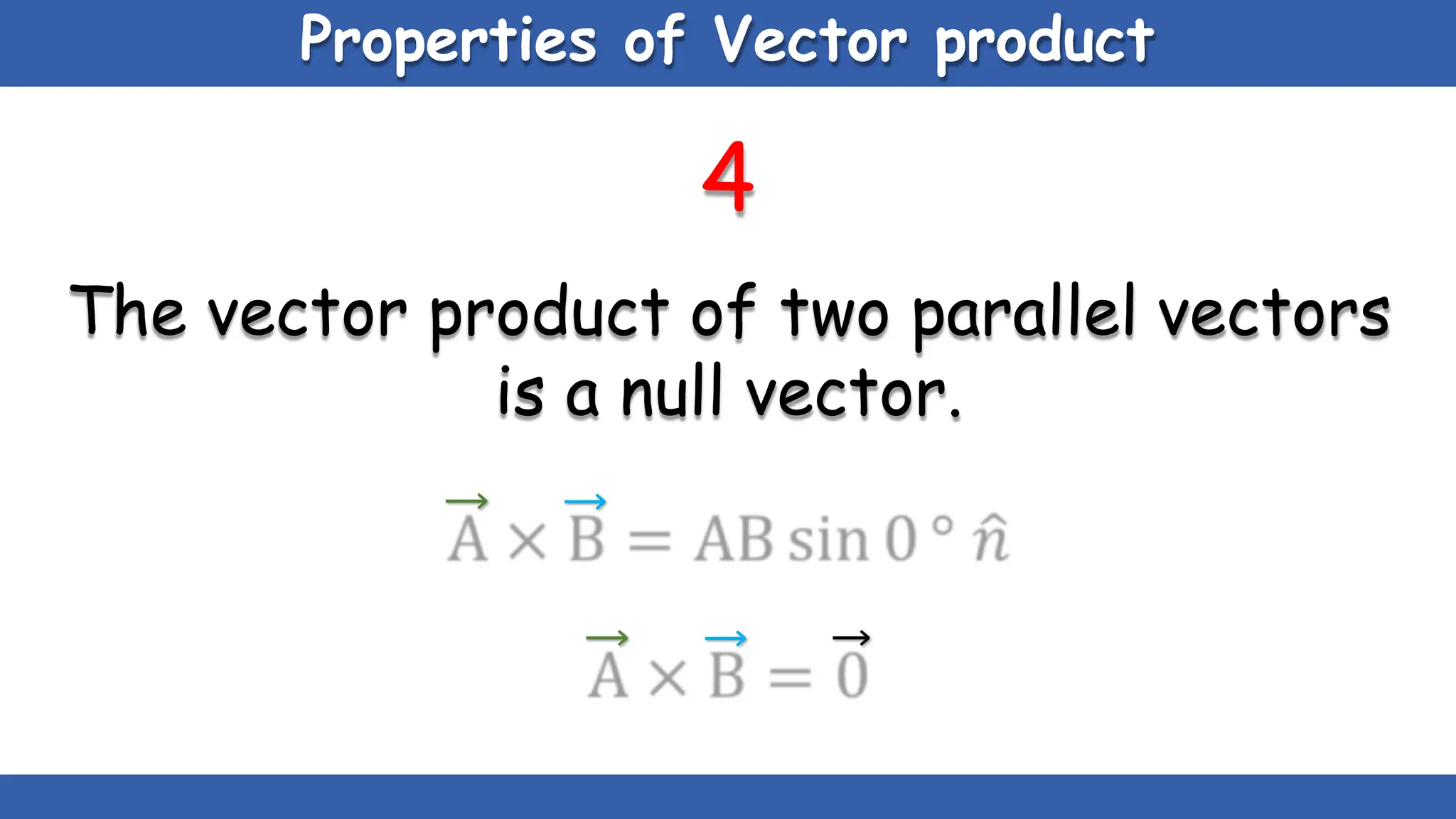
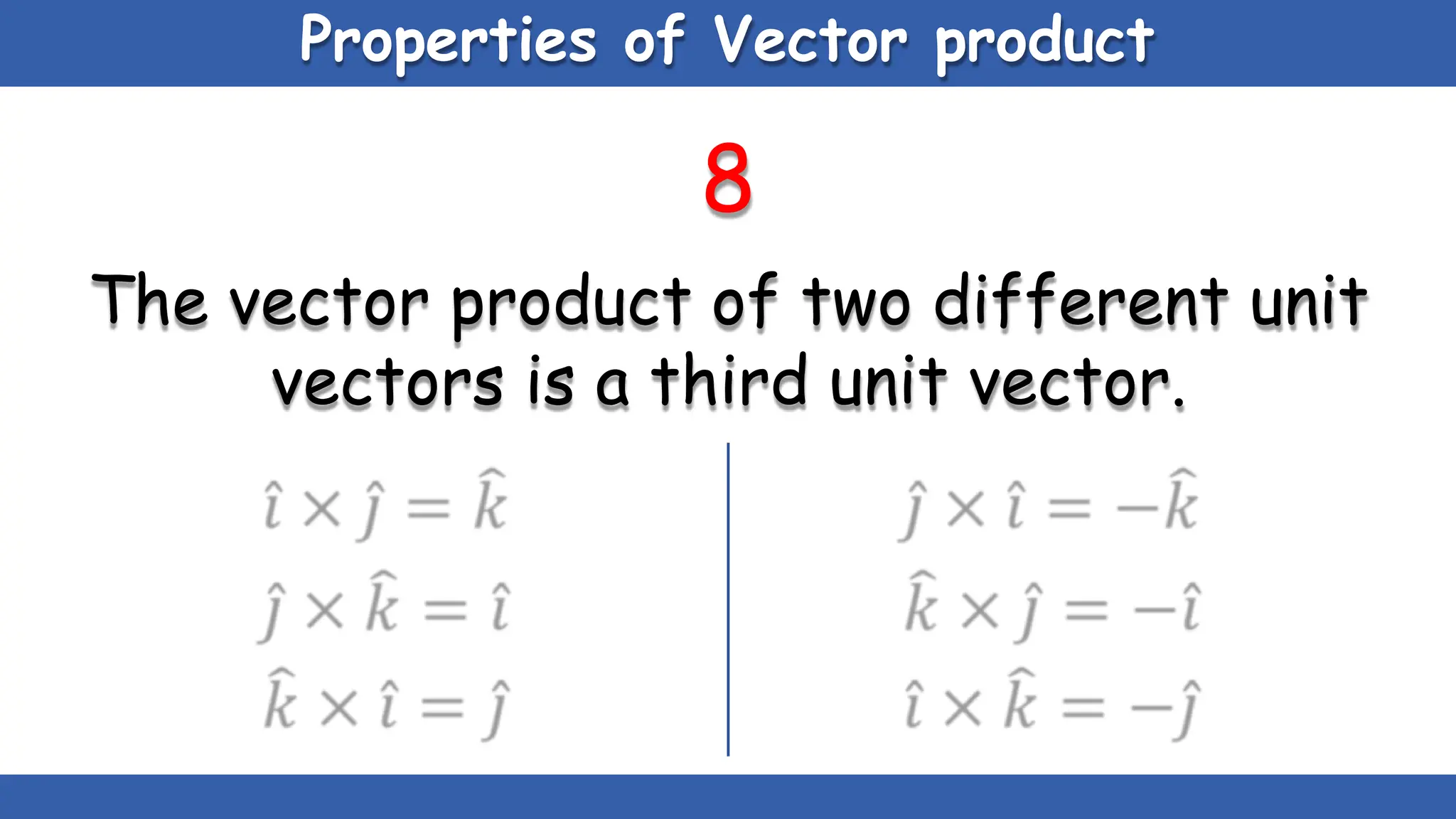
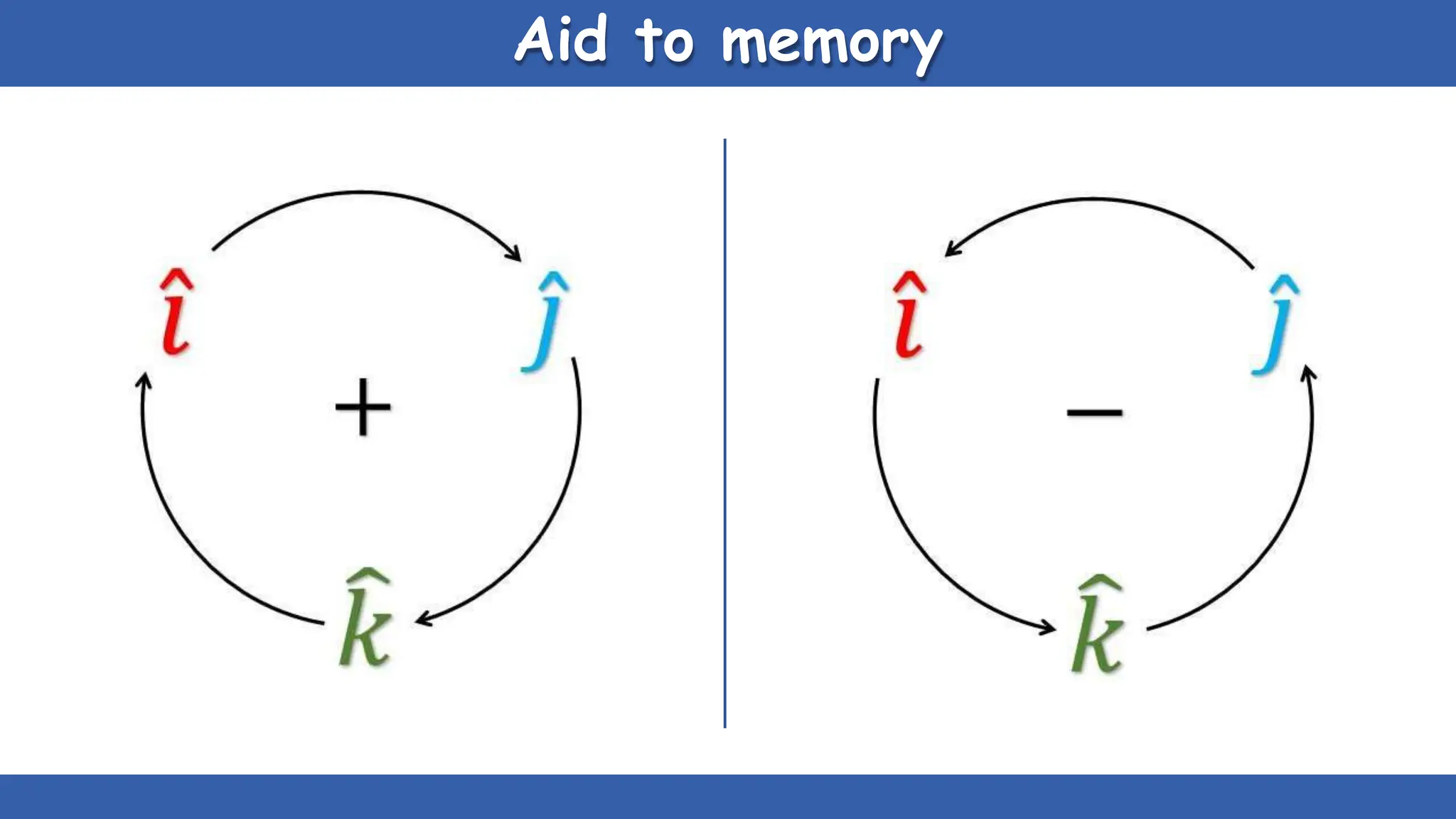
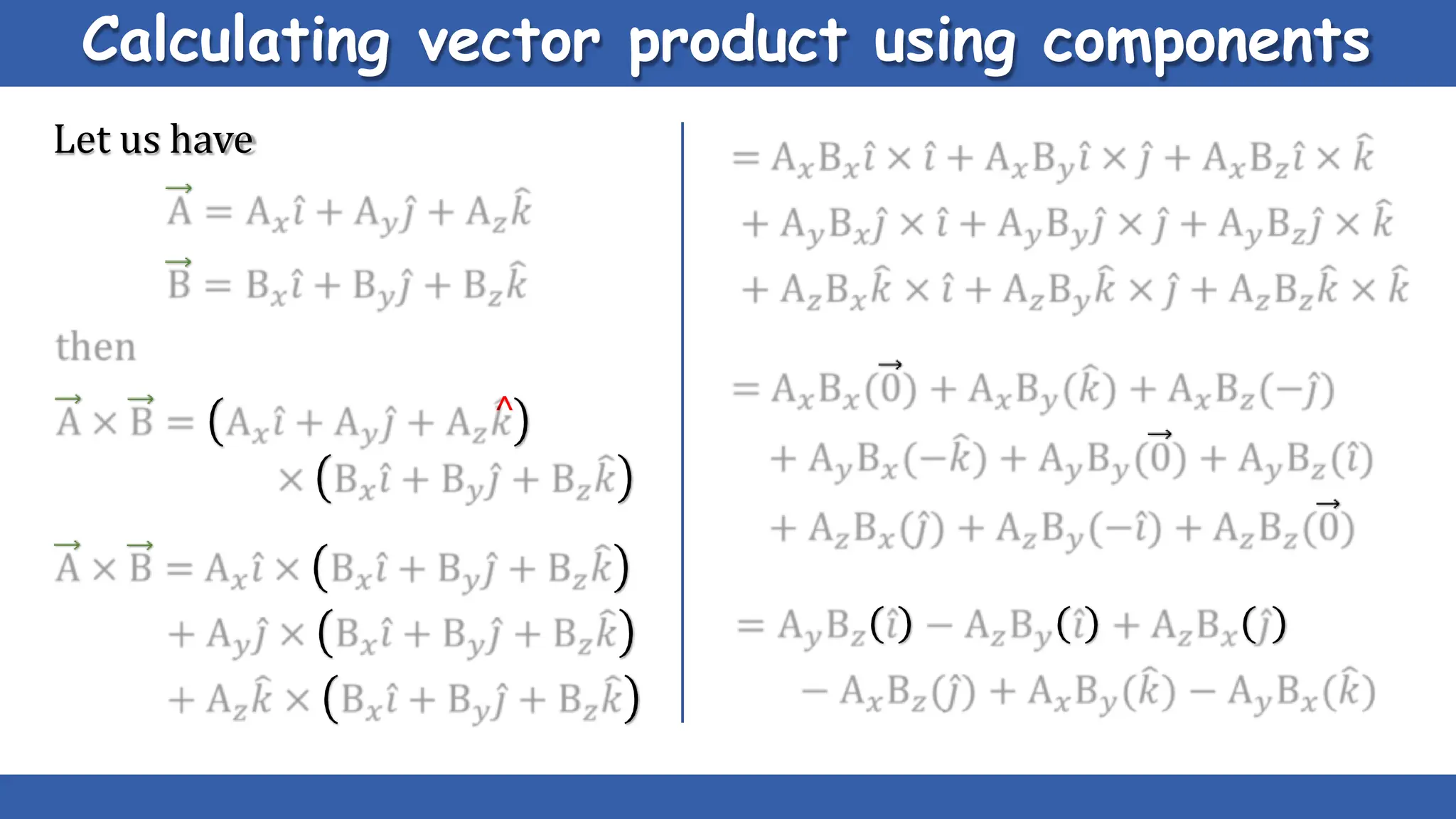
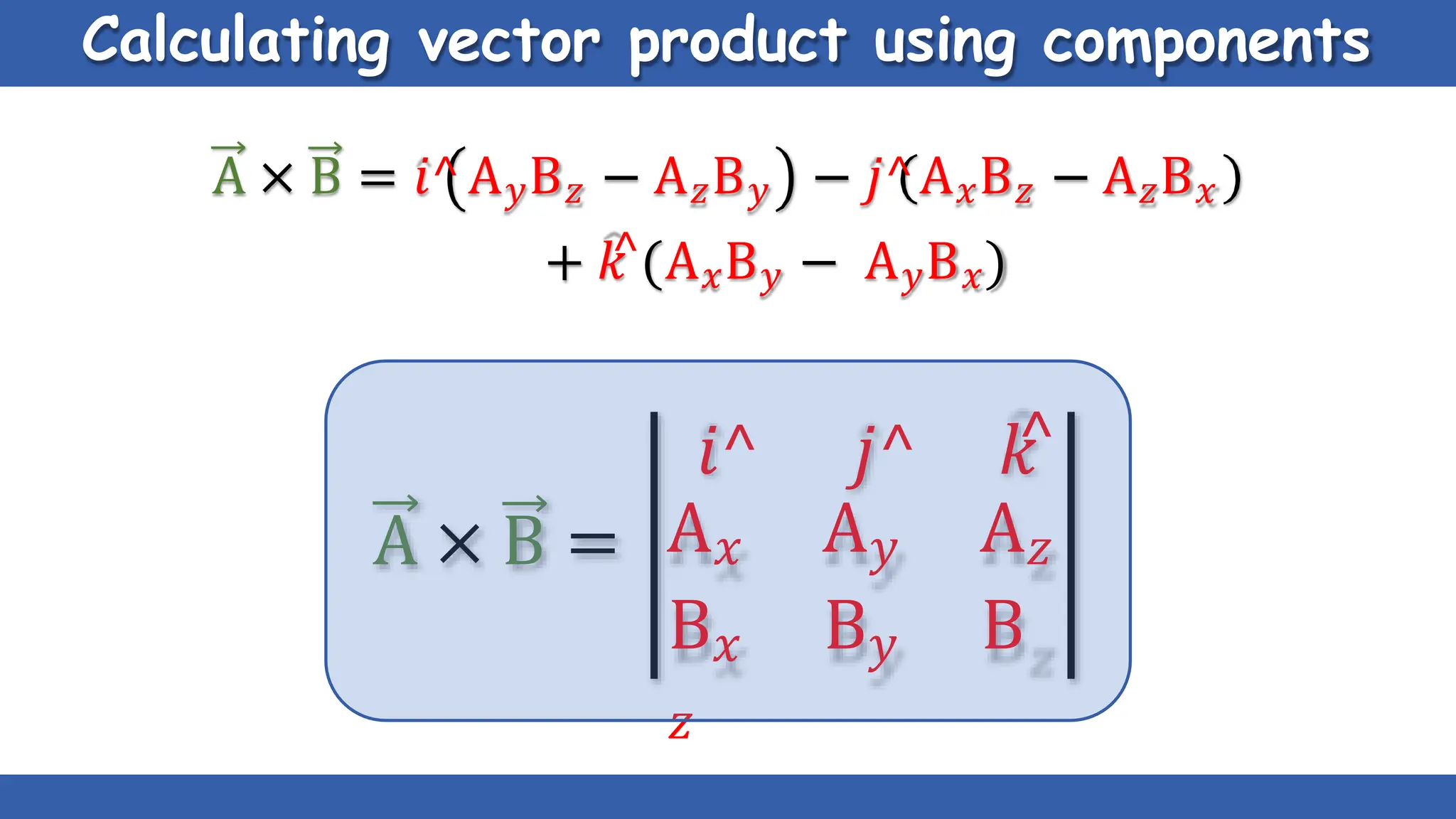
Vectors have both magnitude and direction, while scalars only have magnitude. There are two main types of vector operations: scalar (dot) product and vector (cross) product. The scalar product produces a scalar quantity and results in the magnitudes of the vectors multiplied together. The vector product produces another vector that is perpendicular to the plane of the two original vectors. Vector addition and subtraction can be done geometrically using parallelogram law or analytically by adding/subtracting the corresponding components. Multiplying a vector by a scalar scales its magnitude proportionally while preserving its direction.