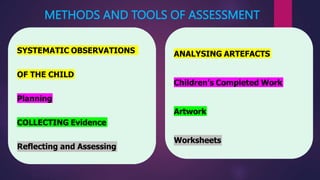
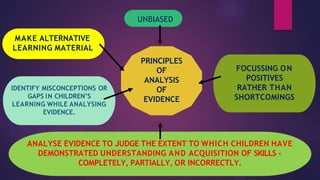
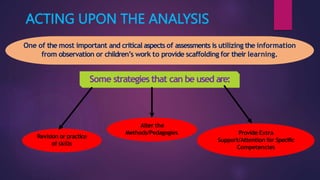
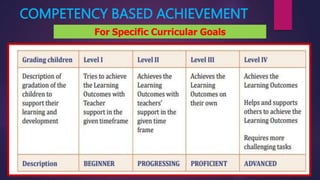
The document outlines the importance and purpose of assessments in the foundational stage of education, emphasizing how they guide teachers in understanding children's learning achievements and designing appropriate interventions. It highlights the necessity for assessment methods that alleviate stress on young learners, such as systematic observations and anecdotal records, while avoiding traditional tests. Additionally, it discusses the creation of a holistic progress card to encompass various aspects of a child's development and inform teaching strategies.