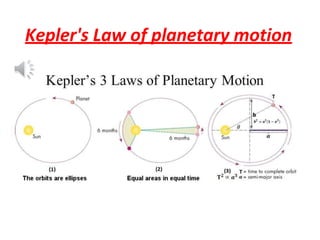
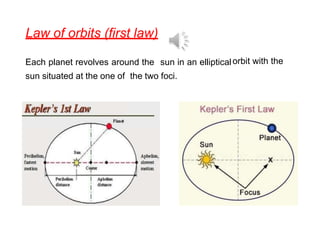
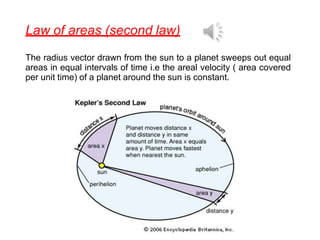
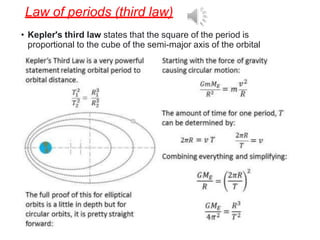
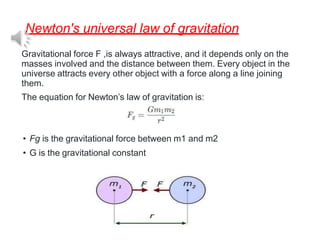
1. The document discusses gravitation and the laws governing it, including Kepler's laws of planetary motion and Newton's universal law of gravitation.
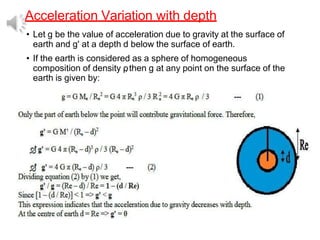
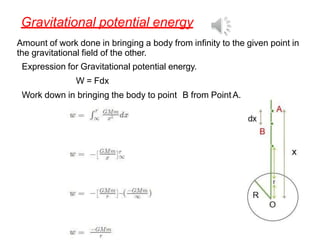
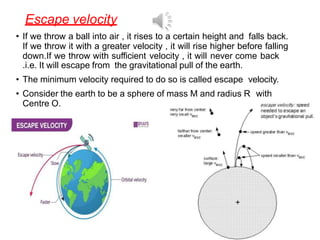
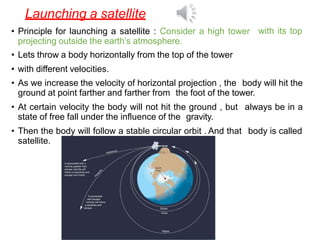
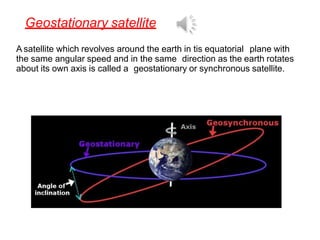
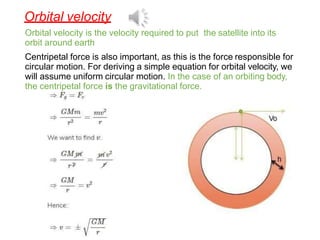
2. It also covers topics like acceleration due to gravity, gravitational potential energy, escape velocity, satellites (both natural and artificial), and different types of satellites like geostationary and polar satellites.
3. The document concludes by explaining weightlessness experienced by astronauts in satellites due to everything being in a state of free fall under the satellite's acceleration due to gravity.