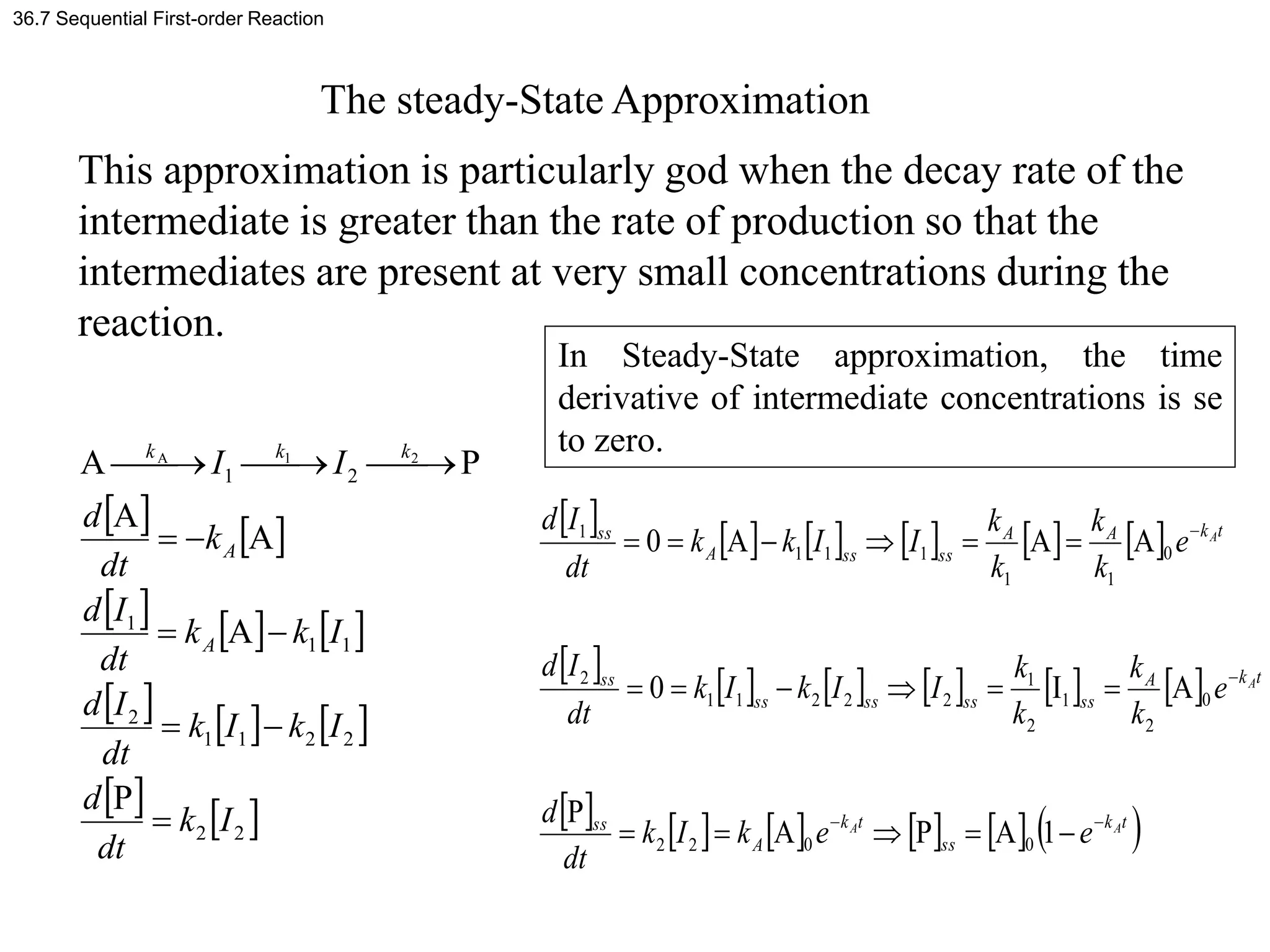
This document discusses elementary chemical kinetics and reaction rates. It defines reaction rate and rate laws. Reaction rate is the change in concentration of a reactant or product over time. The rate of a reaction is often proportional to the concentrations of reactants raised to a power defined by the reaction order. Reaction orders are determined experimentally and have no relation to stoichiometric coefficients. Integrated rate laws relate the concentrations of reactants and products over time for reactions of different orders (zero, first, second). Examples are provided to demonstrate determining reaction order from rate data and calculating time for specific conversions using integrated rate laws.

![Figure 36.1
Figure 36.1 Concentration as a function of time for the conversion of
reactant A into product B. The concentration of A at time 0 is [A]0, and
the concentration of B is zero. As the reaction proceeds, the loss of A
results in the production of B.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-2-2048.jpg)
![36.2 reaction rate
0
A B C+ D
The number of moles os a species during any point of the reaction
:advancement of the reaction
1
Reaction rate
Reaction rate in intensive expression R=
i i i
i
i
i
i
a b c d
n n v
dn d
v
dt dt
dn
d
Rate
dt v dt
rate 1 1 1 [ ]
V
i
i i
dn d i
V v dt v dt
2 5
2 2
2 (g) 2 (g) 2 5 (g)
N O
NO O
4NO O 2N O
1 1
4 2
dn
dn dn
Rate
dt dt dt
Example](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-3-2048.jpg)
![36.3 rate laws
Rate law : R = k [A]a
[B]b
...
Rate Constant
Reaction
order
• The rate of reaction is often found to be proportional to the molar
concentrations of the reactants raised to a simple power.
• It cannot be overemphasized that reaction orders have no relation
to stoichiometric coefficients, and they are determined by
experiment.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-4-2048.jpg)

![36.3.2 Determining Reaction Orders
A + B C
[ ] [ ]
k
R k A B
a b
Strategy 1. Isolation method
The reaction is performed with all species but one in excess.
Under these conditions, only the concentration of one species will
vary to a significant extent during the reaction.
R = k’[B]b](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-7-2048.jpg)
![36.3.2 Determining Reaction Orders
Strategy 2. Method of initial rates
The concentration of a single reactant is changed while
holding all other concentrations constant, and the initial
rate of the reaction is determined.
A + B C
[ ] [ ]
k
R k A B
a b
1 0
1 1
2 2 0 2
1 1
2 2
A
[A] [B]
[A] [B] [A]
A
ln ln
[A]
k
R
R k
R
R
a
a b
a b
a
](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-8-2048.jpg)
![Example Problem 36.2
Using the following data for the reaction illustrated in equation
36.13. Determine the order of the reaction with respect to A and
B, and the rate constant for the reaction
[A] (M) [B] (M) Initial Rate (Ms-1)
2.3010-4 3.1010-5 5.2510-4
4.6010-4 6.2010-5 4.2010-3
9.2010-4 6.2010-5 1.7010-2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-9-2048.jpg)
![
3 4
2 4
2
1 1 1
2
2 2 2
2
4 4 5
3 4 5
2
2
4 -1 4
4.20 10 4.60 10
ln ln 2
1.70 10 9.20 10
[A] [B]
[A] [B]
5.25 10 2.30 10 3.10 10
1
4.20 10 4.60 10 6.20 10
[A] [B]
5.2 10 Ms 2.3 10 M 3.1
R k
R k
R k
k
b
b
b
a a
b
5
8 -2 1
8 -2 1 2
10 M
3.17 10 M
3.17 10 M [A] [B]
k s
R s
Solution
Example 36.2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-10-2048.jpg)


![36.5 Integrated Rate Law Expressions
kt
e
e
kt
kdt
d
k
dt
d
dt
d
R
k
R
P
kt
kt
t
k
0
0
0
0
0
0
A
A
A
ln
A
ln
1
]
A
[
A]
[
]
A
[
]
P
[
A
]
A
[
;
A
A
ln
A
]
A
[
];
A
[
]
A
[
]
A
[
];
A
[
A
reaction
Order
-
First
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-13-2048.jpg)
![36.5 Integrated Rate Law Expressions
kt
0
A
ln
]
A
ln[
kt
e
0
A
]
A
[](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-14-2048.jpg)




![36.5 Integrated Rate Law Expressions
t
k
dt
k
d
k
dt
d
dt
d
R
k
R
P
eff
t
eff
k
0
0
A
A
2
2
2
A
1
A
1
A
]
A
[
;
]
A
[
2
]
A
[
]
A
[
2
1
;
]
A
[
A
2
I)
(Type
reaction
Order
-
Second
0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-19-2048.jpg)

![36.5 Integrated Rate Law Expressions
A
B
A
B
let
;
A
A
B
B
B
B
A
A
]
B
[
]
A
[
;
B
]
A
[
B
A
II)
(Type
reaction
Order
-
Second
0
0
0
0
0
0
dt
d
dt
d
R
k
R
P
k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-22-2048.jpg)
![
kt
kt
kt
kt
kdt
d
k
k
dt
d
t
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
A
A
0
A
A
]
A
/[
]
A
[
]
B
/[
]
B
[
ln
A
B
1
]
B
[
]
B
[
ln
]
A
[
]
B
[
ln
1
]
A
[
]
A
[
ln
]
A
[
]
A
[
ln
1
]
A
[
]
A
[
ln
1
]
A
[
]
A
[
]
A
[
]
A
[
]
A
[
]
B
][
A
[
]
A
[
0
0
36.5 Integrated Rate Law Expressions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-23-2048.jpg)

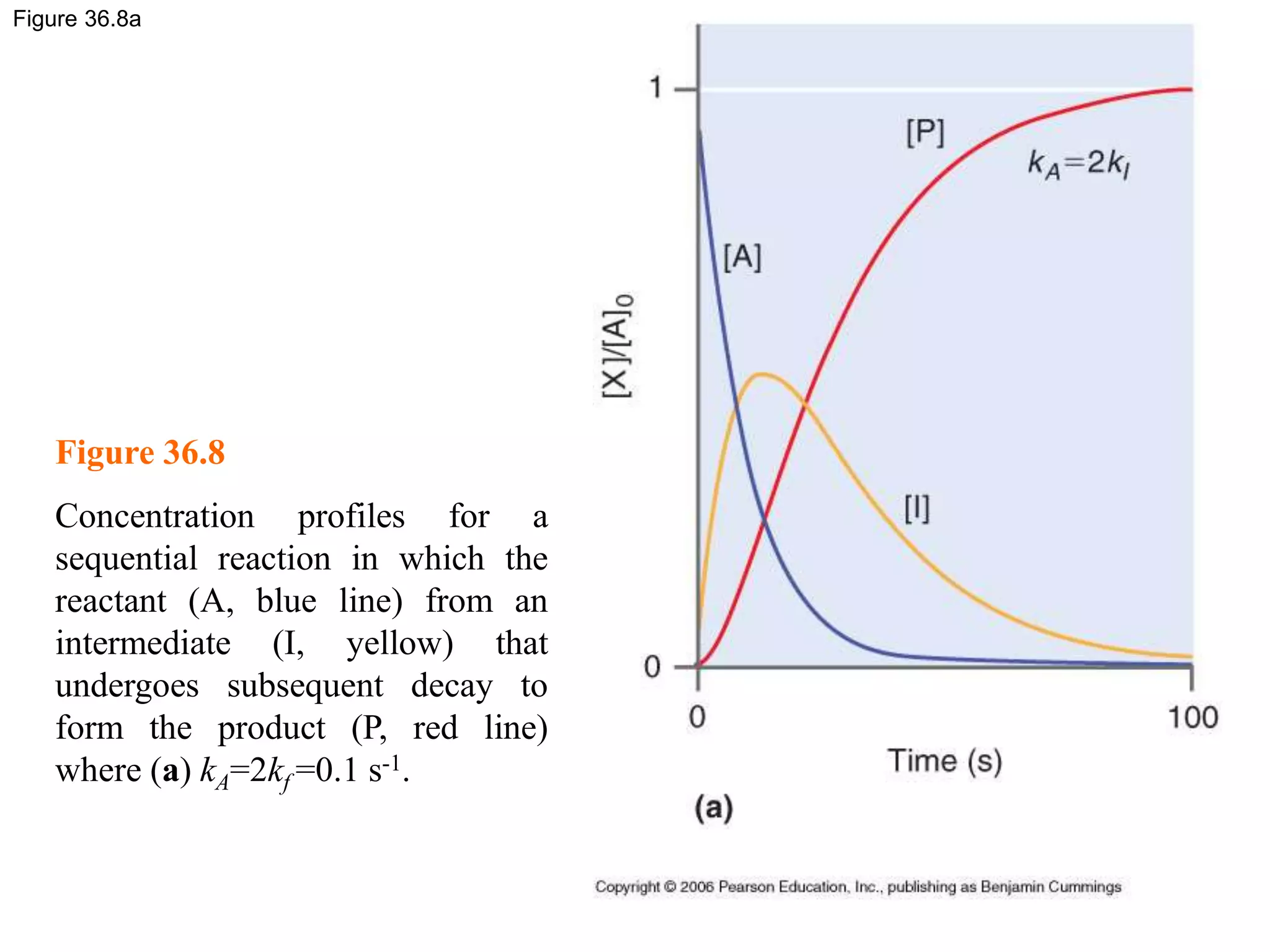
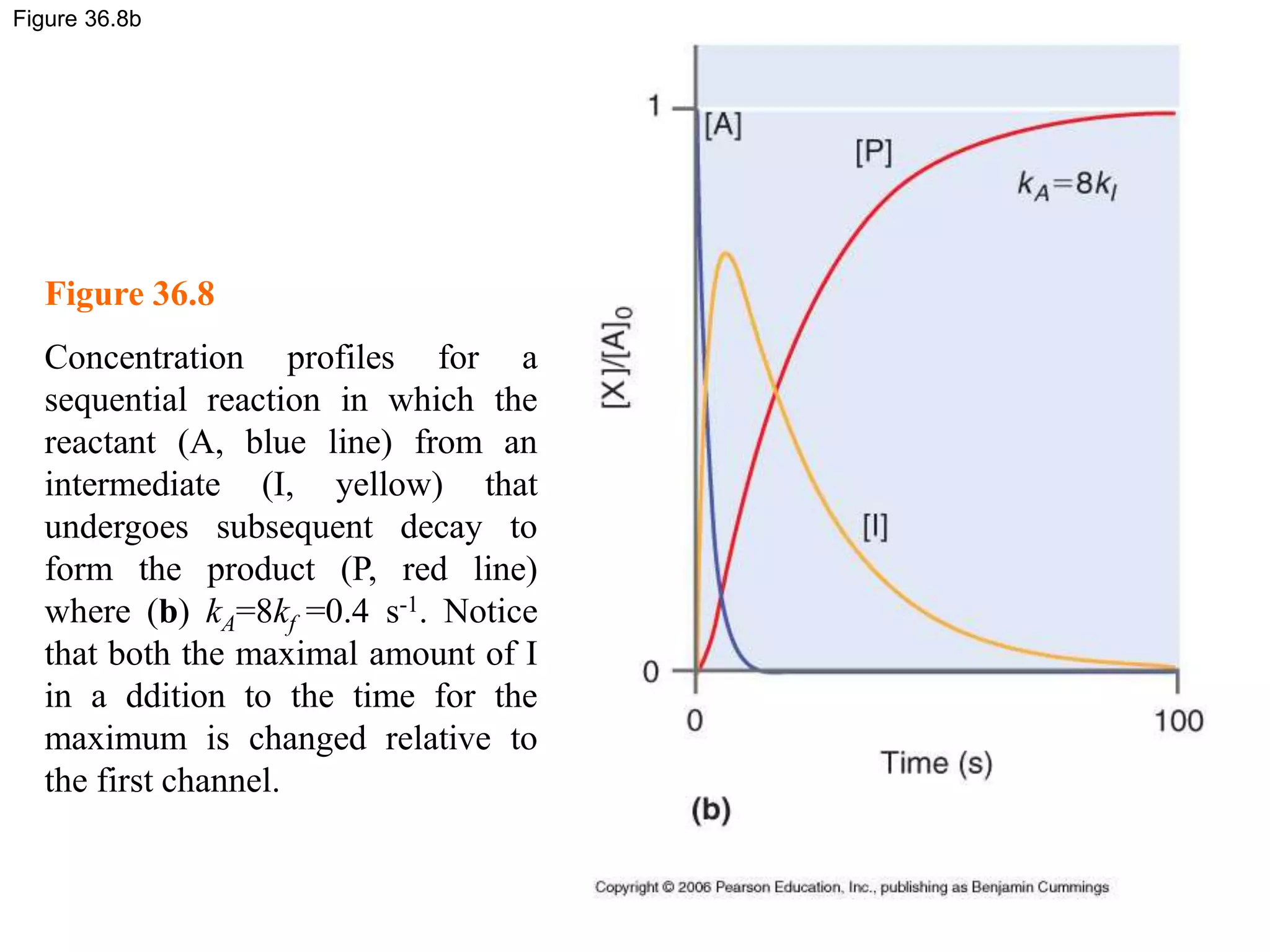
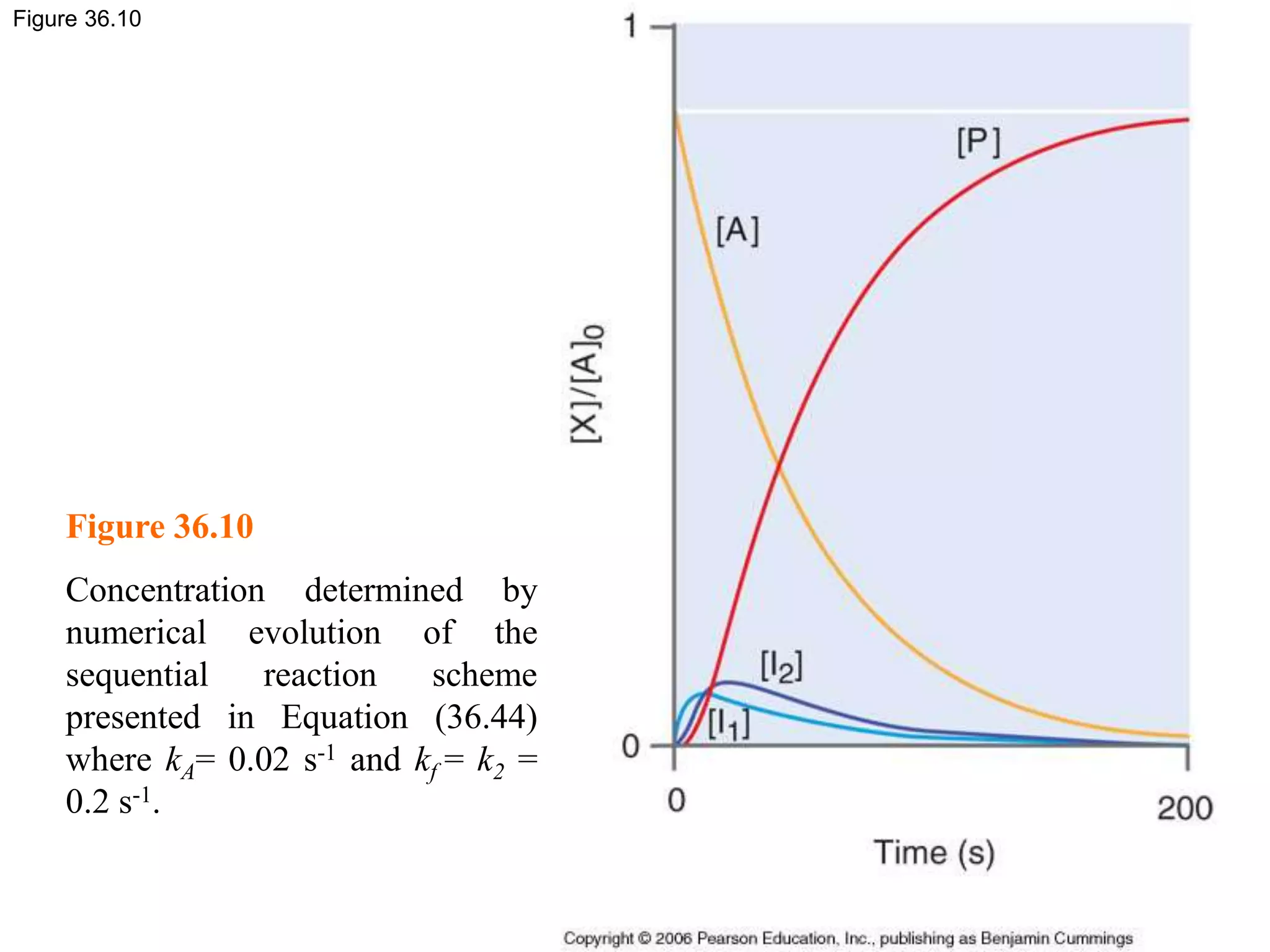
![Figure 36.8c
Figure 36.8
Concentration profiles for a
sequential reaction in which the
reactant (A, blue line) from an
intermediate (I, yellow) that
undergoes subsequent decay to
form the product (P, red line)
where (c) kA=0.025kf=0.0125 s-1.
In this case, very little
intermediate is formed, and the
maximum in [I] is delayed relative
to the first two examples.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-29-2048.jpg)
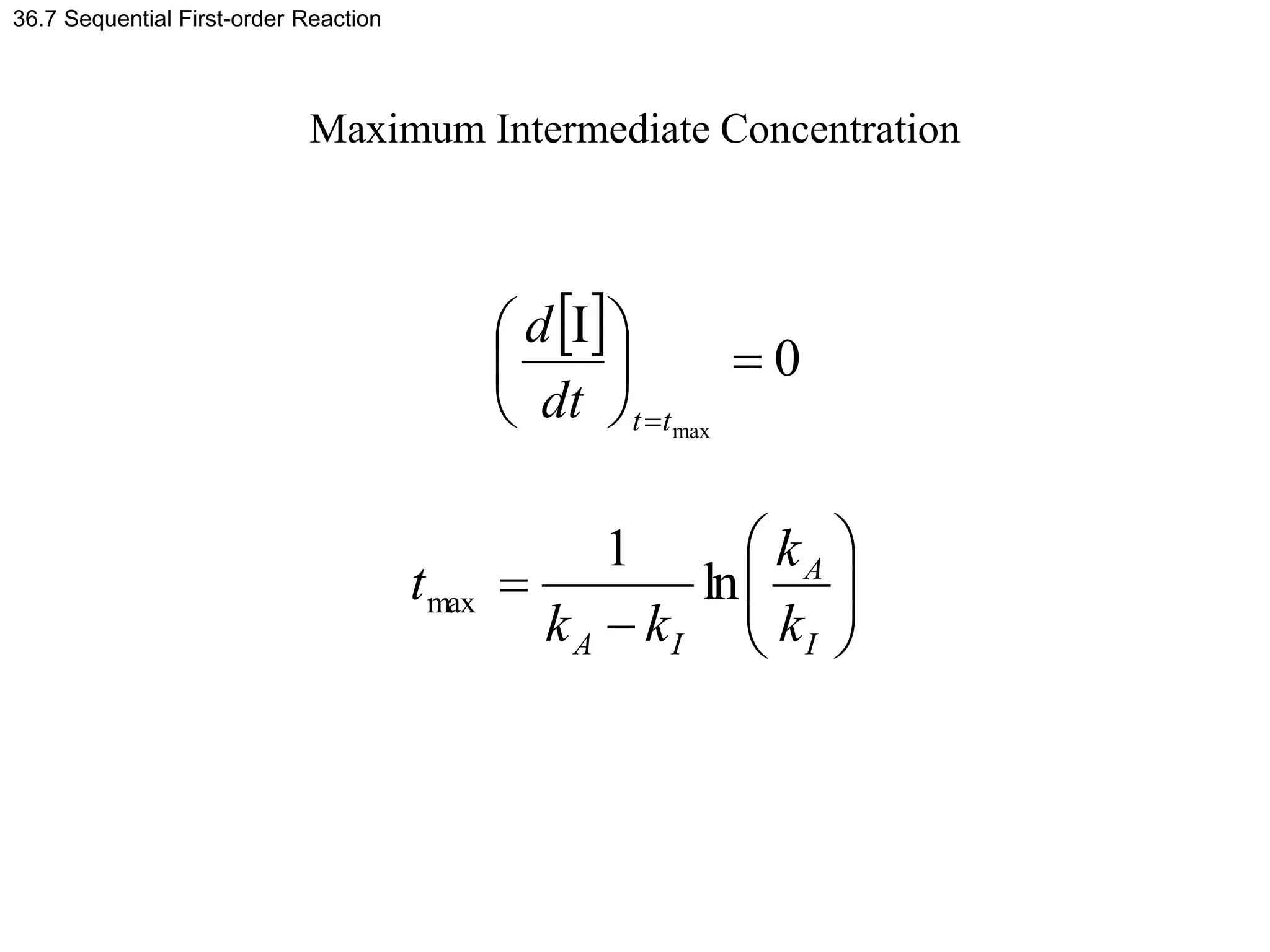
![Example problem 36.5
Example Problem 36.5
Determine the time at which [I] is at a maximum for
kA = 2kI = 0.1 s-1.
Solution
s
9
.
13
s
05
.
0
s
1
.
0
ln
s
05
.
0
s
1
.
0
1
ln
1
1
-
-1
1
-
1
-
max
I
A
I
A k
k
k
k
t](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-31-2048.jpg)

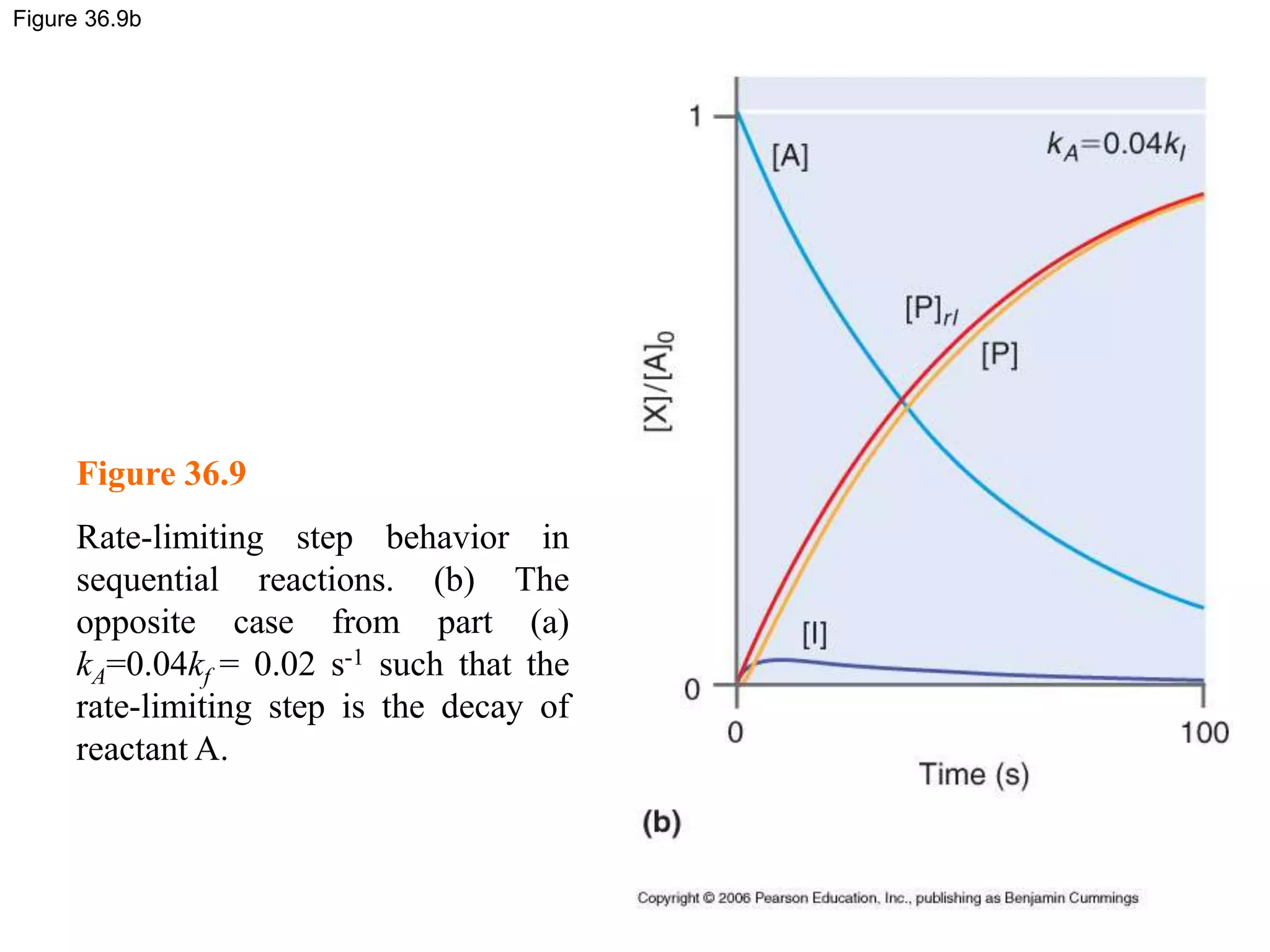
![Figure 36.9a
Figure 36.9
Rate-limiting step behavior in
sequential reactions. (a) kA=20kf
=1 s-1 such that the rate-limiting
step is the decay of intermediate I.
In this case, the reduction in [I] is
reflected by the appearances of [P].
The time evolution of [P]
predicted by the sequential
mechanism is given by the yellow
line, and the corresponding
evolution assuming rate-limiting
step behavior, [P]rl, is given by the
red curve.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-33-2048.jpg)











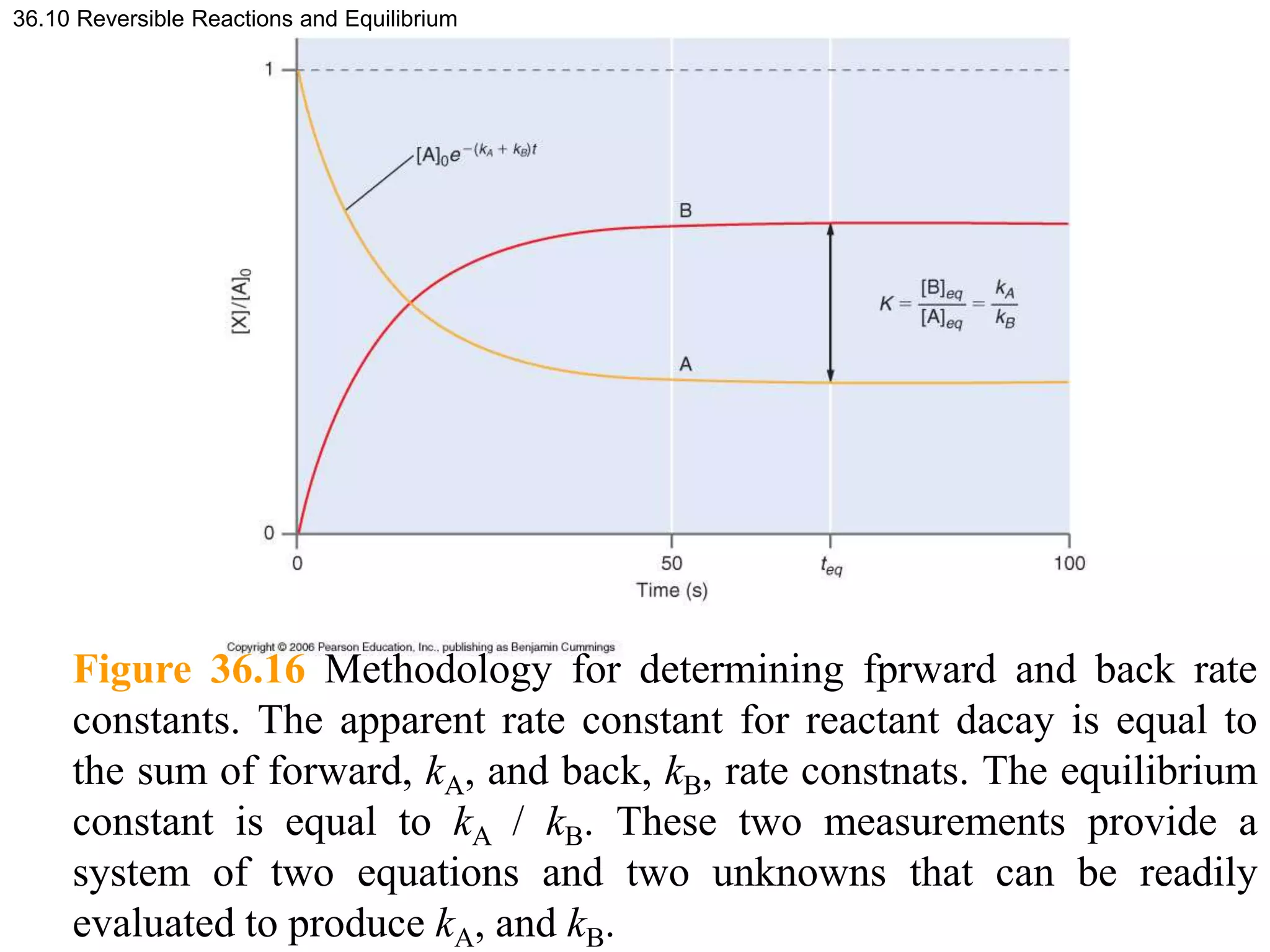


![Figure 36.17
Figure 36.17 Example of a temperature-jump experiment for a reaction in which
the forward and back rate pocesses are first order. The yellow and blue portions of
the graph indicate times before and after the temperature jump, respectively. After
the temperature jump, [A] decrease with a time constant related to the sum of he
forward and back rate constants. The change between the pre-jump and post-jump
equilibrium concentrations is given by 0](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch36-230127095600-a515efba/75/Ch36-ppt-54-2048.jpg)