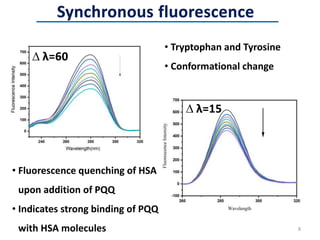
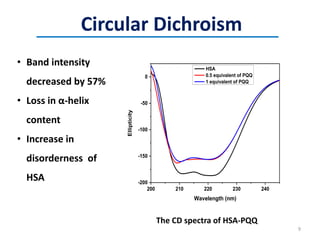
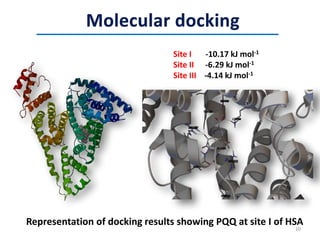
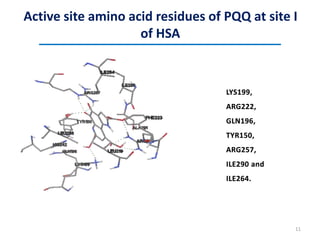
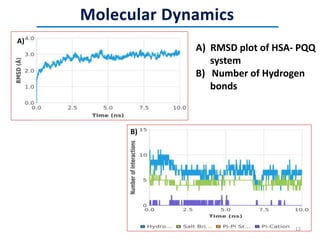
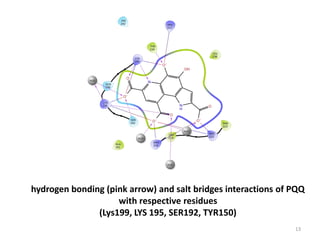
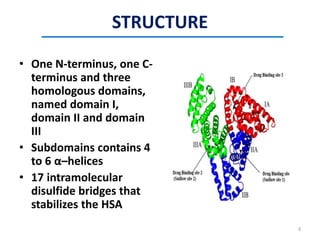
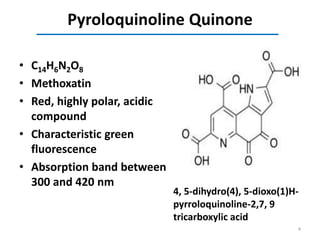
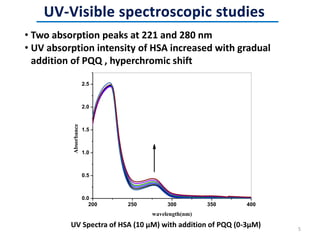
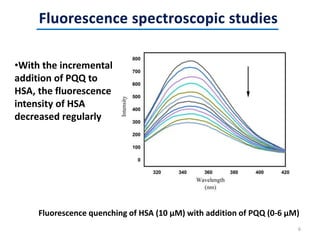
This document discusses the binding of Pyroloquinoline Quinone (PQQ) to Human Serum Albumin (HSA). UV-Vis spectroscopy shows the absorption of HSA increases with the addition of PQQ, indicating their binding. Fluorescence spectroscopy and quenching experiments determine the binding constant between PQQ and HSA is 2.194 × 107 M-1. Circular dichroism experiments reveal PQQ causes a loss of α-helical structure in HSA. Molecular docking simulations identify the highest affinity binding site of PQQ on HSA is site I, and hydrogen bonding stabilizes their complex formation.

![-6.0 -5.8 -5.6 -5.4 -5.2
-1.0
-0.8
-0.6
-0.4
-0.2
0.0
0.2
log
(Fo/F)
log(Q)
Logarithmic plots of HSA with addition of PQQ
Stern-Volmer equation is used to estimate the binding constant (K) and binding
number (n)
log (F0-F)/F = log Kb + nlog[Q]
Kb = 2.194 × 107 M-1
7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation3-230122133718-411273f5/85/Presentation3-pptx-7-320.jpg)