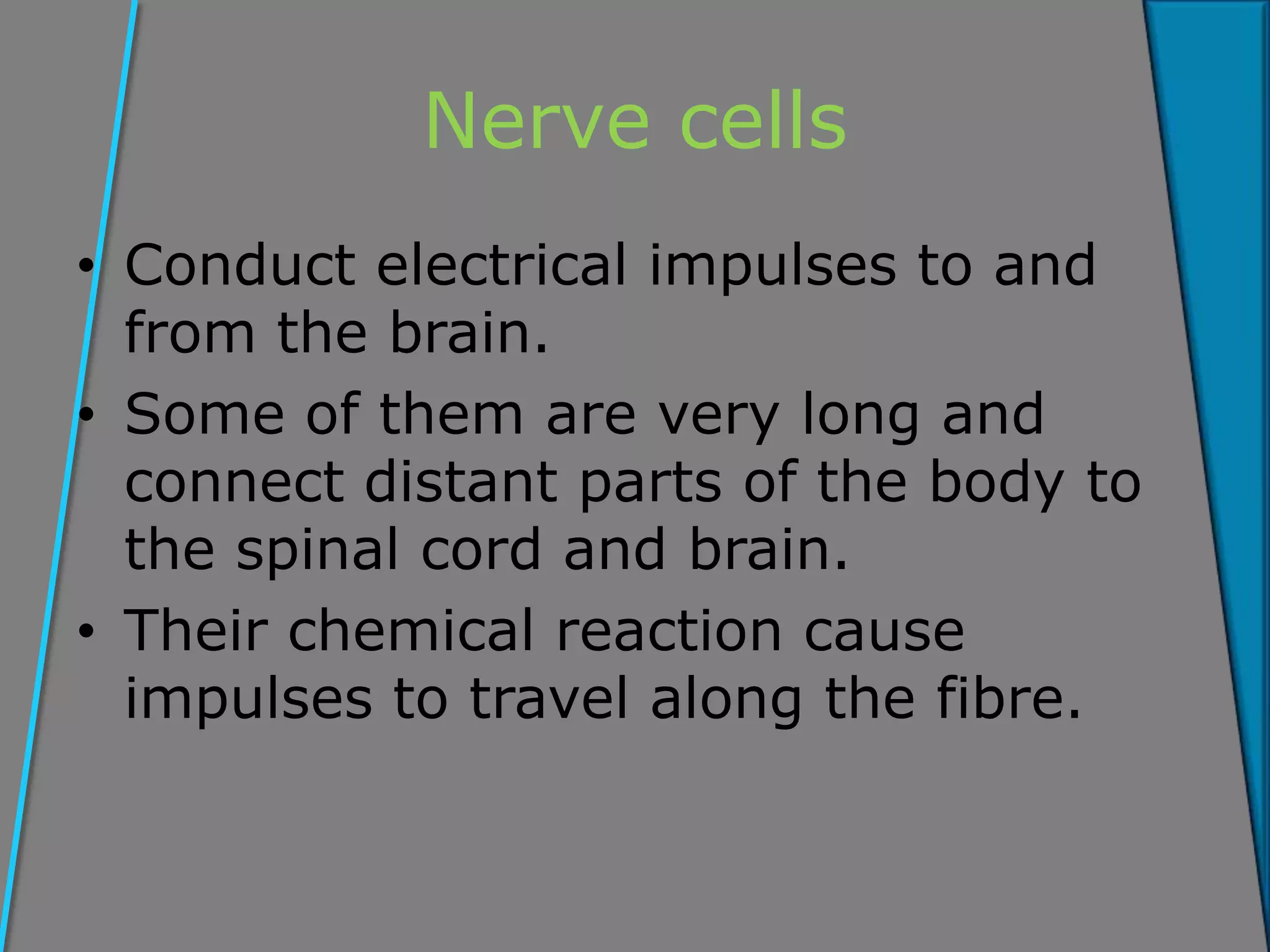
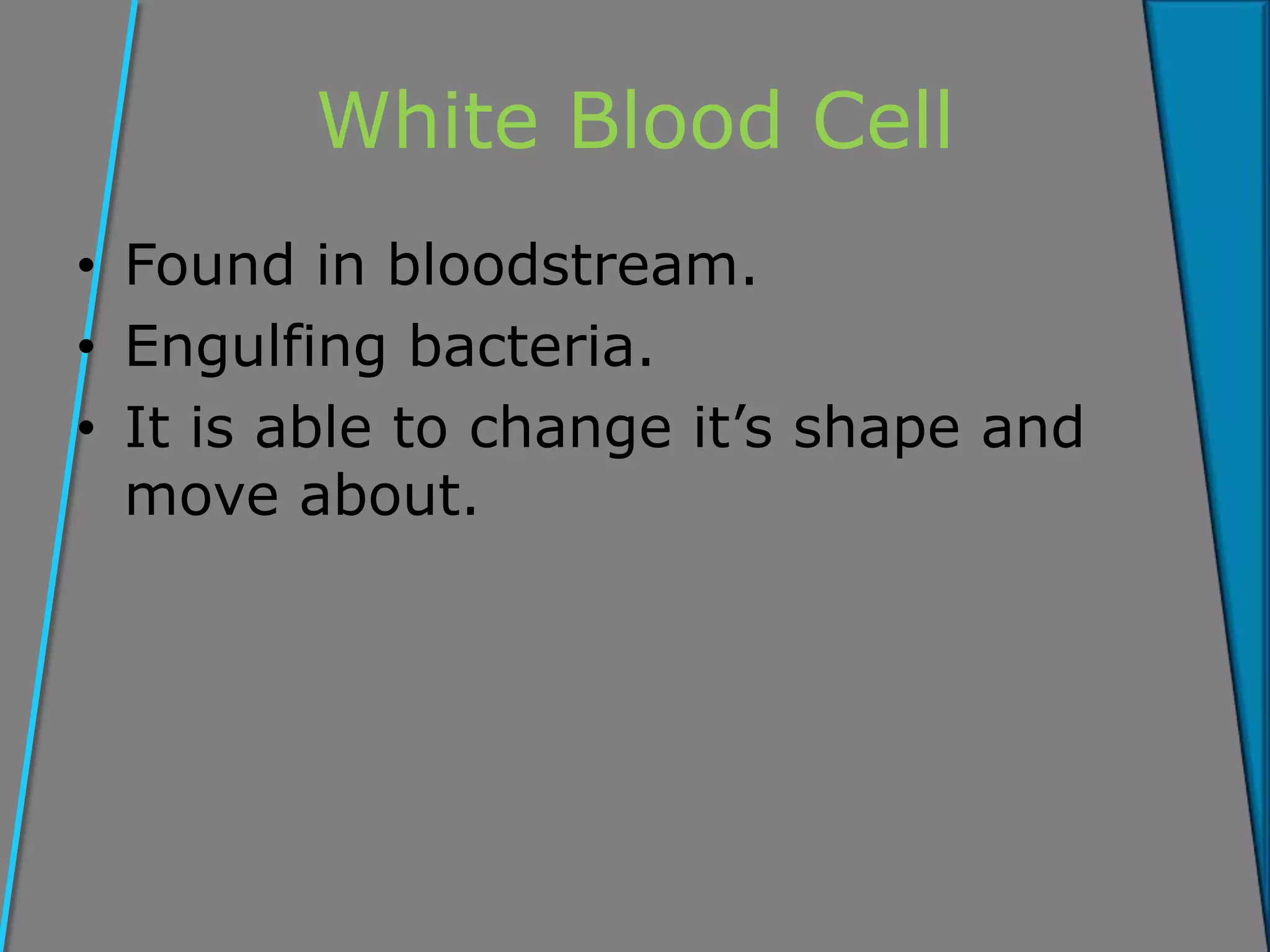
Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms. The key components of cells include the nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, and in plant cells cell walls, vacuoles, and plastids. Cells divide through mitosis to grow and reproduce. As cells become specialized through division of labor, they develop distinct shapes and chemical functions to perform roles like conducting nerve impulses, absorbing water and minerals in roots, moving mucus in the lungs, or transporting nutrients in plants. Tissues are groups of similar cells that work together, such as muscle or gland tissues. Organs are composed of multiple tissue types organized to perform a specific function, and organ systems integrate to keep the whole organism alive.