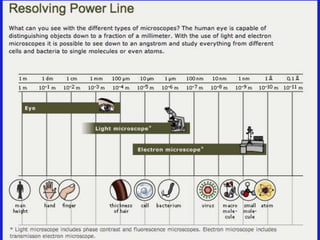
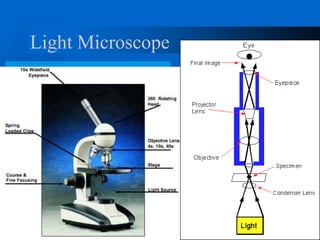
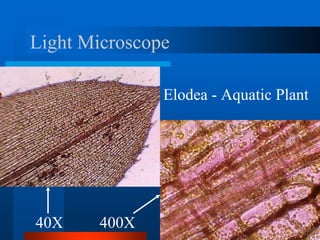
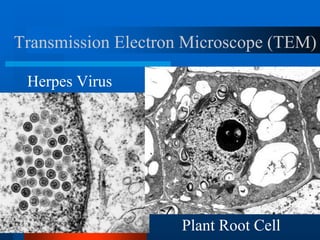
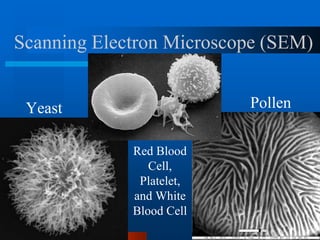
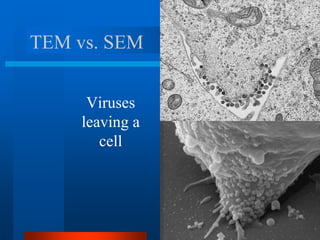
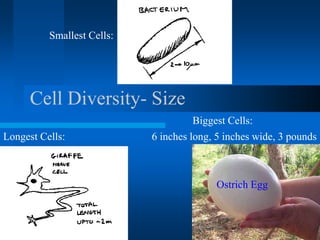
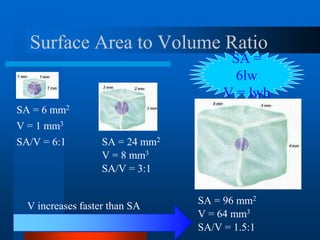
1. The document describes the history and development of cell theory, from early microscope observations of cells to the modern understanding that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function, and new cells are produced from existing cells.
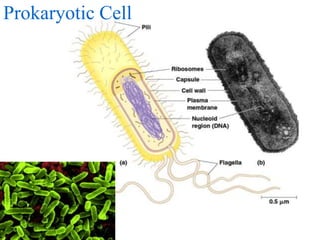
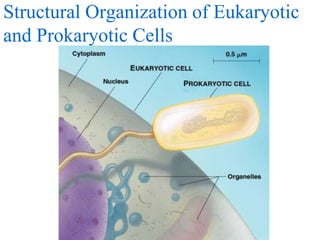
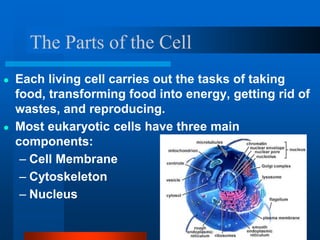
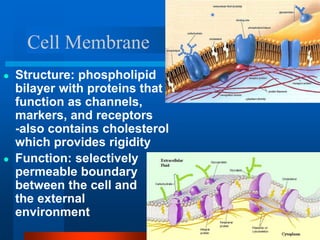
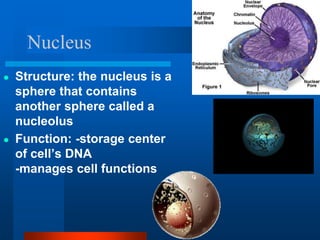
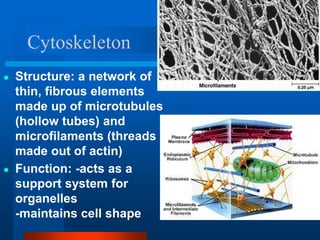
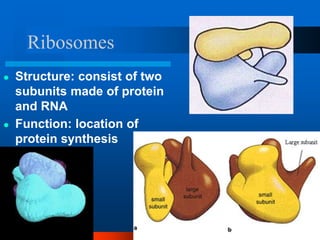
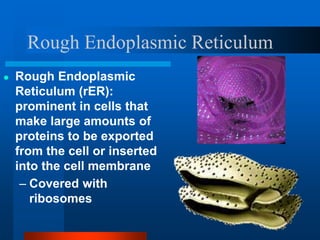
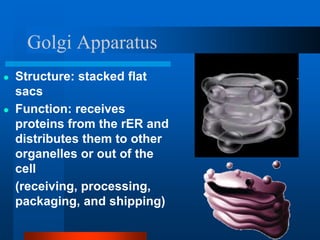
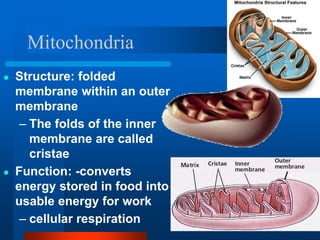
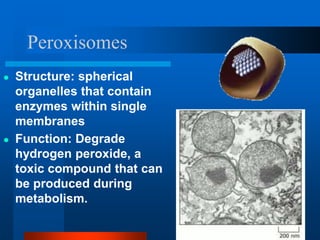
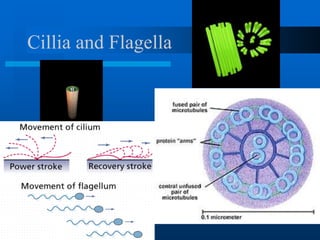
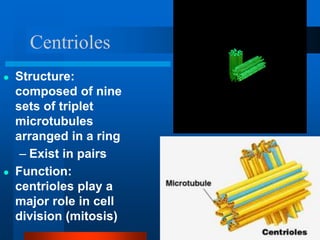
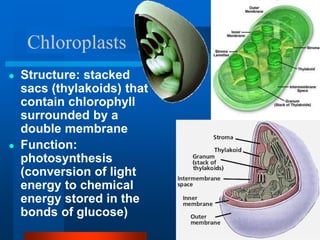
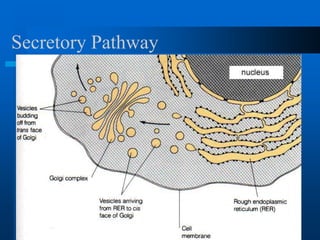
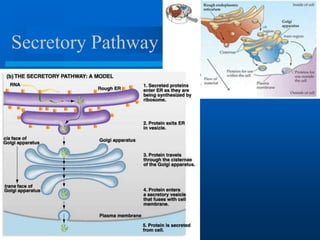
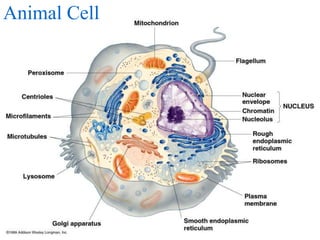
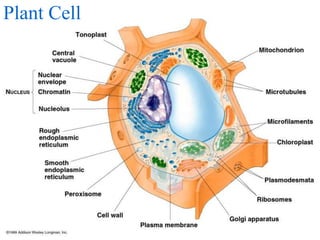
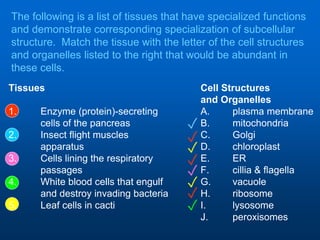
2. It discusses cell structures including organelles found in plant and animal cells like the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and describes their functions.
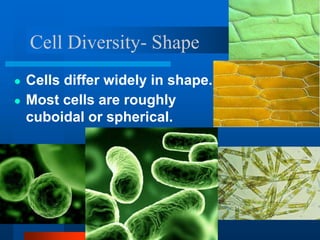
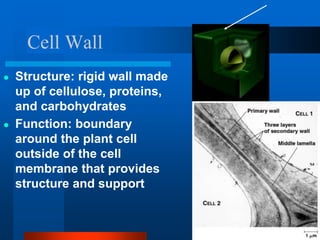
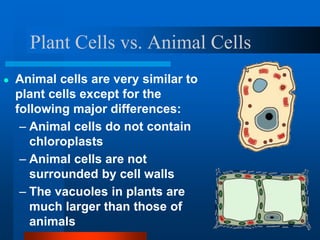
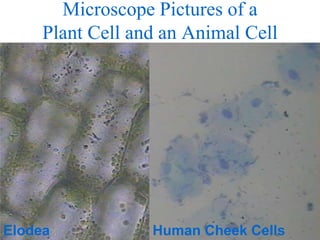
3. Key differences between plant and animal cells are highlighted such as plant cells having cell walls and chloroplasts while animal cells do not.