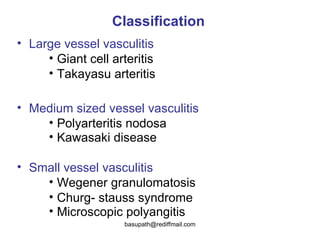
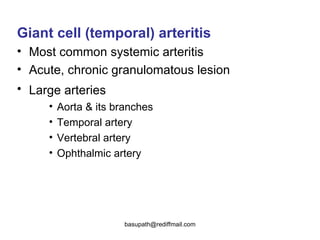
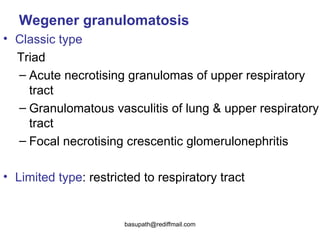
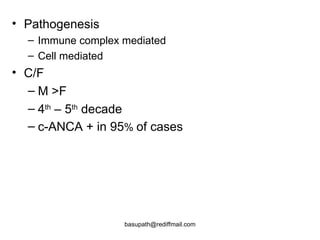
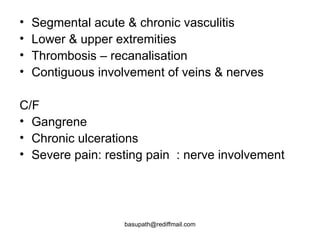
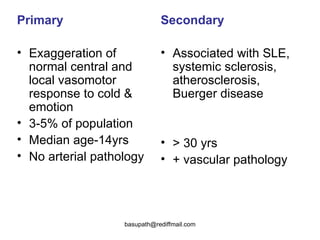
Vasculitis refers to inflammation of blood vessels. It can be caused by direct infection, immune complexes, or antibodies. Types include large vessel vasculitis like giant cell arteritis, medium vessel vasculitis like polyarteritis nodosa, and small vessel vasculitis like Wegener's granulomatosis. Giant cell arteritis most commonly affects those over 50 and causes headaches, vision loss, and temporal artery inflammation. Polyarteritis nodosa involves small and medium arteries and can cause fever, weight loss, and kidney involvement. Wegener's granulomatosis is characterized by lung and respiratory tract inflammation and kidney disease.