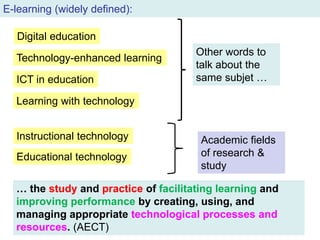
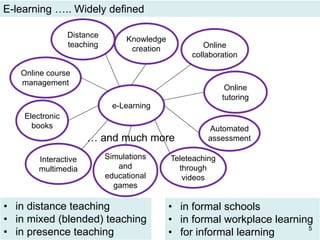
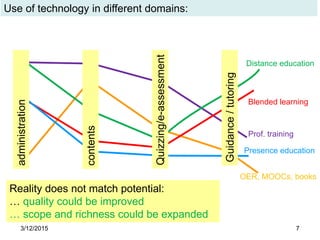
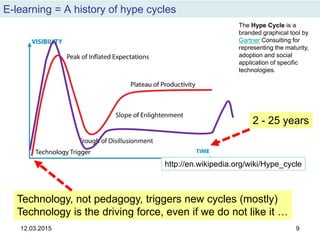
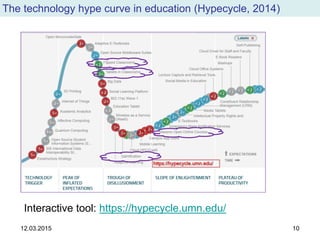
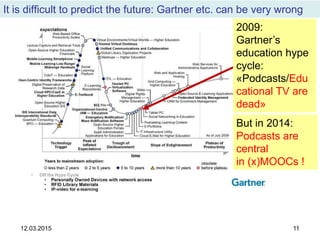
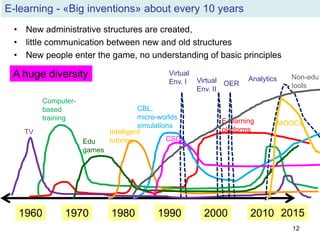
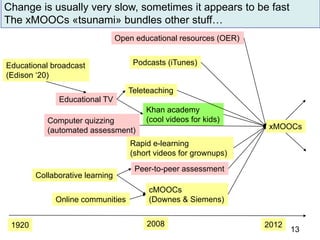
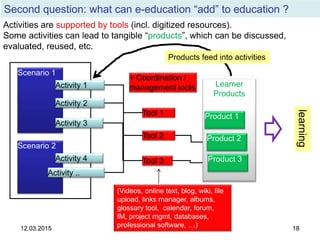
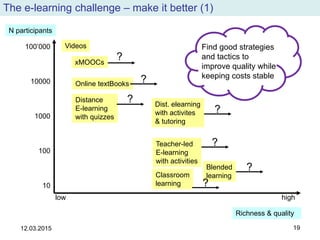
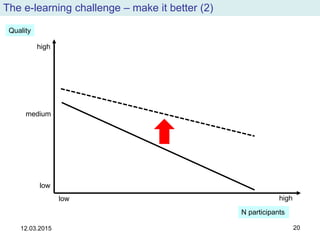
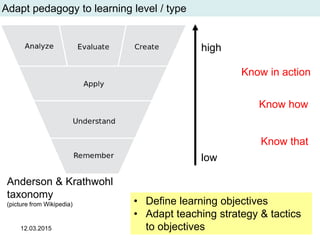
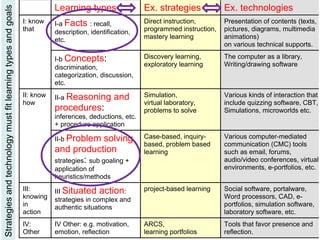
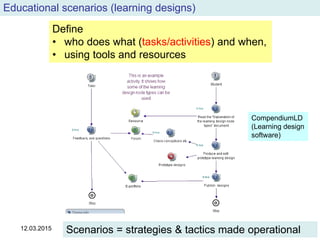
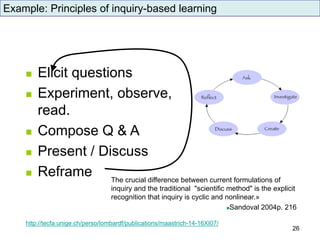
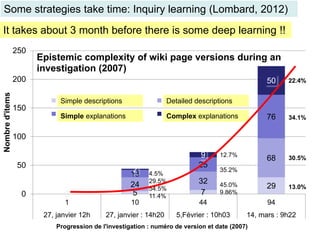
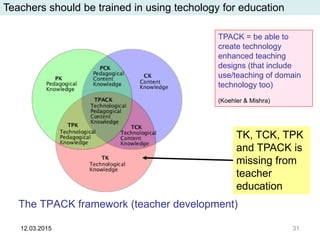
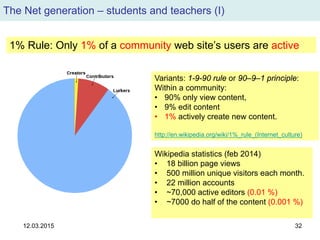
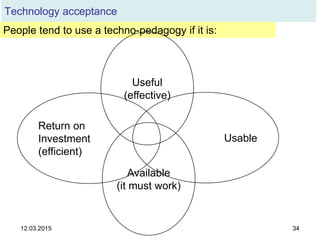
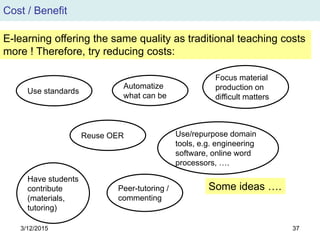
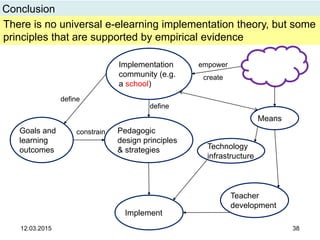
The document discusses the evolution and implementation of e-learning, emphasizing the importance of aligning technology with pedagogical principles to enhance educational quality. It highlights various e-learning methodologies, the challenges of integrating technology effectively, and the need for teacher training in technology-enhanced teaching strategies. The conclusion stresses that while there is no one-size-fits-all approach to e-learning, certain evidence-backed principles can guide successful implementation.