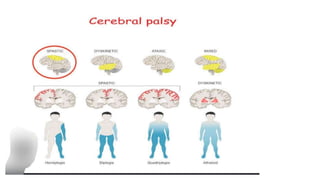
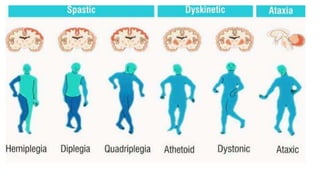
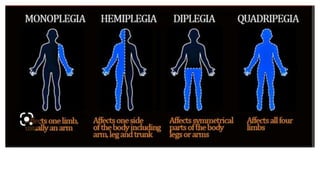
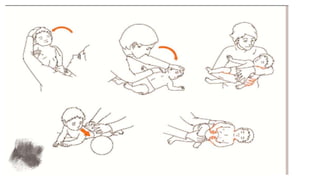
This document provides an overview of cerebral palsy (CP) including its definition, causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment. CP is a non-progressive motor disability caused by damage to the developing brain, usually before or during birth. It is classified based on clinical presentation (spastic, athetoid, ataxic, flaccid, mixed) and body location affected (quadriplegic, hemiplegic, etc.). Symptoms vary depending on the type but may include abnormal muscle tone, reflexes, movement, and development problems. Treatment involves physiotherapy, occupational therapy, medications, and exercise to manage symptoms and improve function.