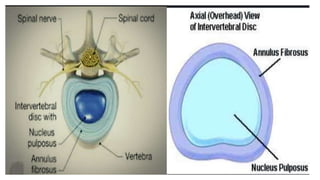
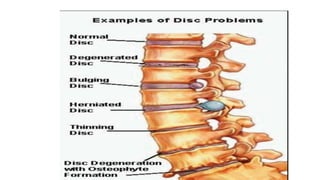
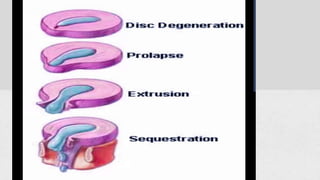
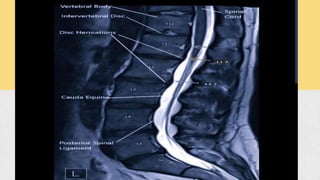
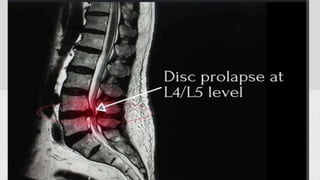
This document summarizes the components, pathology, diagnosis, clinical features, and treatment of a prolapsed intervertebral disc. It discusses the three components of the intervertebral disc - the cartilage end plates, nucleus pulposus, and annulus fibrosis. Pathology includes degeneration and displacement of the nucleus. Diagnosis involves imaging like CT and MRI. Clinical features commonly affect those aged 20-40 and include low back pain, sciatica, and neurological deficits. Treatment focuses on rest, medications, and physiotherapy including exercises and electrotherapy. Surgical options include fenestration, laminotomy, and laminectomy procedures.