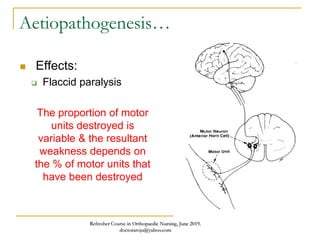
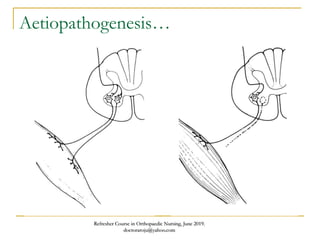
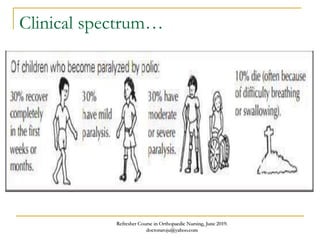
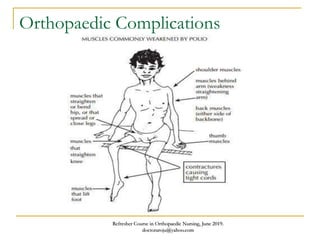
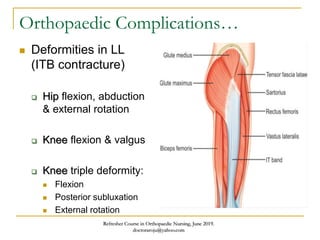
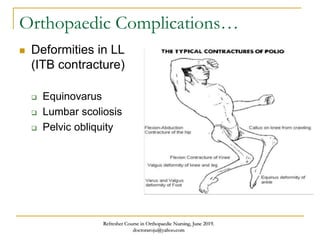
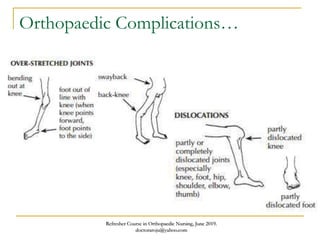
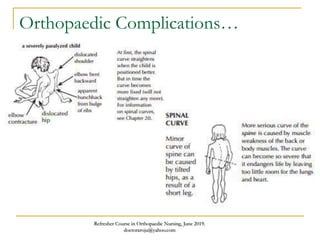
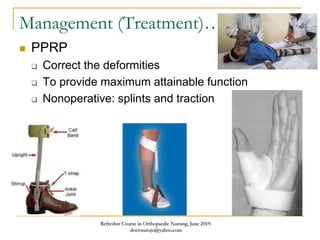
This document discusses poliomyelitis (polio), including its causes, clinical presentation, complications, management, and prognosis. Polio is caused by infection with the poliovirus, which destroys motor neurons and can cause flaccid paralysis. It primarily affects children under 5 years old and presents as aseptic meningitis or flaccid paralysis that is usually asymmetric. Long-term complications include deformities of the limbs from muscle imbalances. Management involves vaccination to prevent transmission and treatment of complications through bracing, therapy, or surgery. Prognosis depends on the initial severity and extent of paralysis.