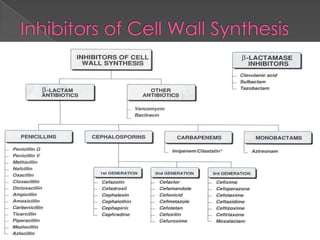
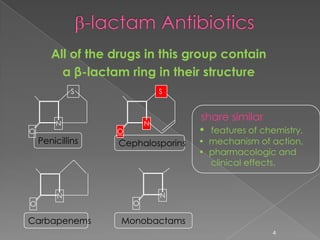
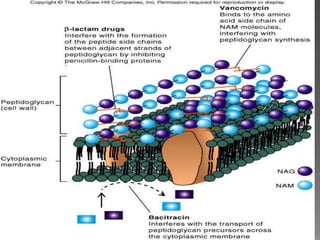
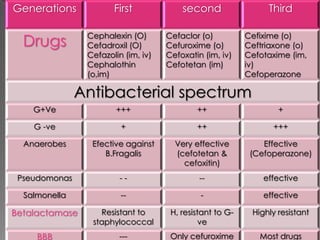
This document discusses different classes of beta-lactam antibiotics including penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems, and monobactams. It describes the key features and differences between generations of cephalosporins, including their antimicrobial spectra, stability to beta-lactamases, nephrotoxicity, and examples of commonly used drugs. It also summarizes the mechanisms of action, clinical uses, and adverse effects of vancomycin and beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations.