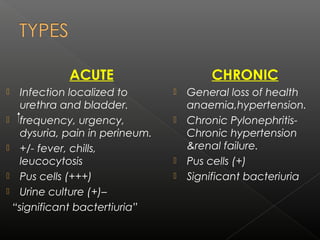
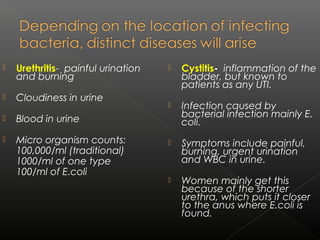
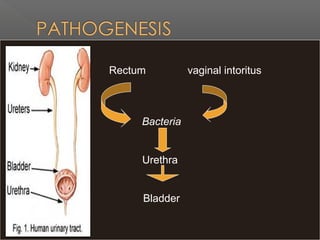
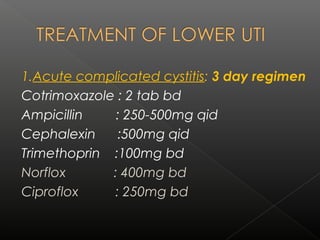
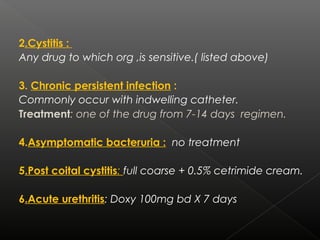
UTIs are caused by bacterial infections in the urinary tract. They range from cystitis, an infection of the bladder, to pyelonephritis, a serious infection of the kidneys. The most common pathogen is E. coli. Treatment depends on the severity and location of the infection, with acute uncomplicated cystitis usually treated with a 3 day course of antibiotics like cotrimoxazole or cephalexin. More serious or complicated infections may require 7-14 days of treatment with intravenous antibiotics such as gentamicin and third generation cephalosporins. Chronic infections necessitate long term suppressive antibiotic therapy after identifying and addressing any underlying causes.