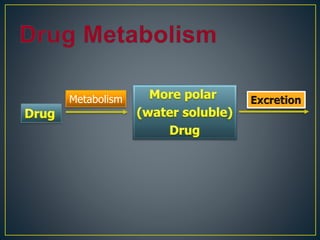
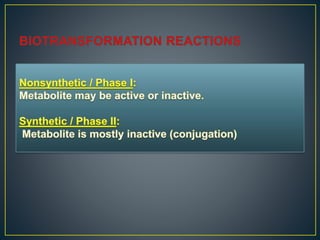
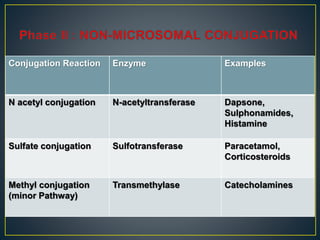
1. Drug metabolism involves enzymatic modification of drugs by the body with the goal of making them more water soluble and easier to excrete.
2. Metabolism can occur in many tissues like the liver, kidneys, lungs, and intestines and is primarily carried out by the cytochrome P450 enzyme system.
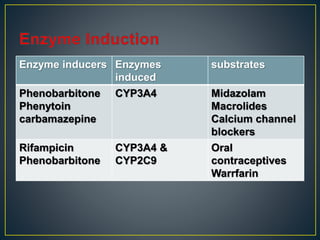
3. Metabolism can result in inactive, active, or more active drug metabolites and influences the drug's pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. Certain drugs are able to induce or inhibit the cytochrome P450 enzyme system, altering metabolism of other drugs metabolized by the same enzymes.