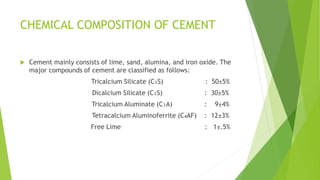
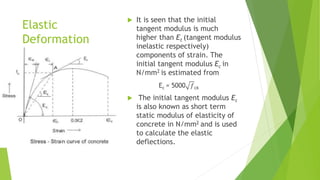
The document discusses different types of cement and concrete used in construction. It describes cement as the binding agent in concrete which is composed of aggregates, cement, and water. Several types of cement are listed including Portland cement and high alumina cement. The properties and chemical composition of concrete are also summarized. Different types of concrete for pavement construction are defined such as high strength concrete, fiber reinforced concrete, and self-compacting concrete.