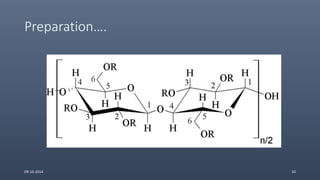
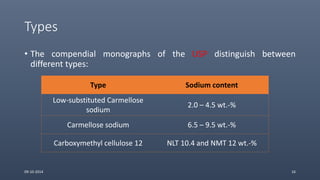
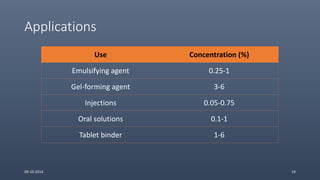
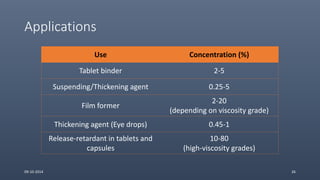
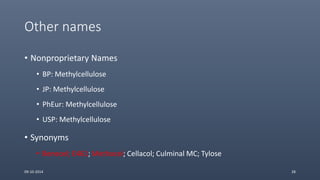
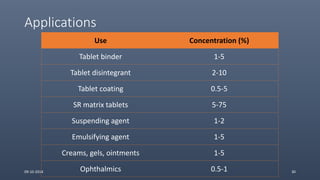
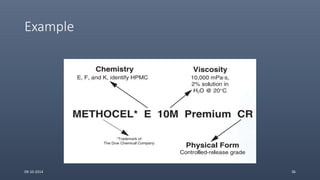
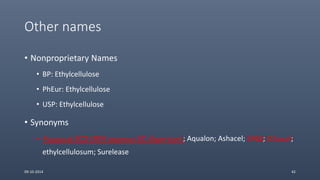
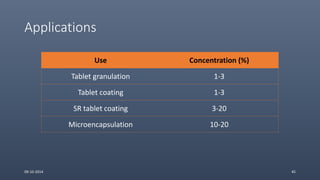
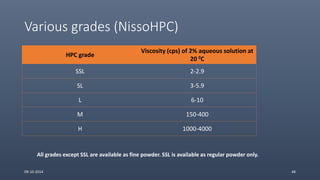
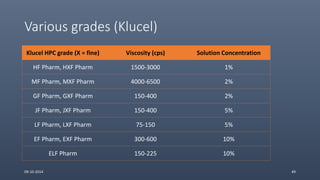
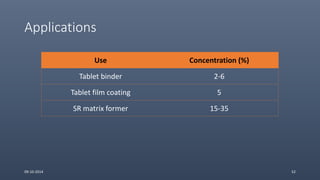
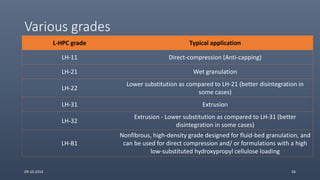
Cellulose ethers are versatile pharmaceutical excipients derived from cellulose. They include sodium carboxymethylcellulose (SCMC), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), methylcellulose, croscarmellose sodium, and ethylcellulose. SCMC is widely used as a coating agent, stabilizing agent, and suspending agent. HPMC is used as a bioadhesive, coating agent, and release-modifying agent. Methylcellulose and croscarmellose sodium are commonly used as disintegrants. Ethylcellulose is employed as a coating agent and release modifier. These cellulose derivatives find applications in oral, topical and other dosage forms due to their safety and functionality.