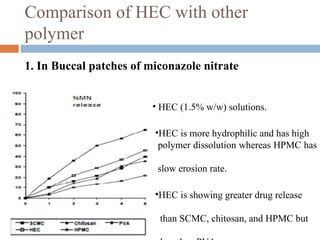
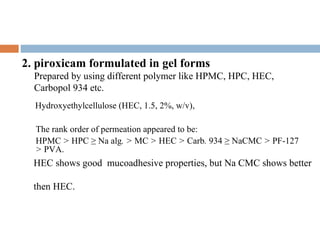
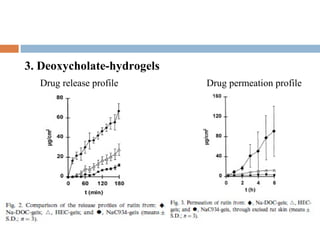
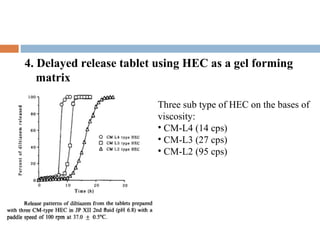
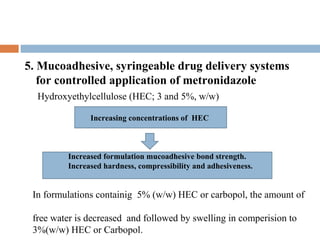
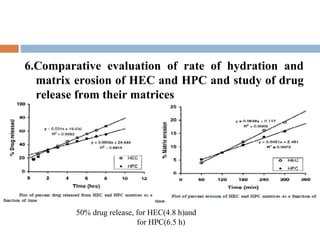
This document provides a review of hydroxyethyl celluloses. It describes hydroxyethyl cellulose as a white powder that is odorless, tasteless and hygroscopic. It is used as a thickening agent, suspending agent, tablet binder and viscosity-increasing agent. The document compares hydroxyethyl cellulose to other polymers, finding it has high polymer dissolution and drug release capability. Hydroxyethyl cellulose shows good mucoadhesive properties compared to other polymers like sodium carboxymethyl cellulose. The conclusion is that hydroxyethyl cellulose is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations between concentrations of 1.5-3% weight/weight.
![5. Structural Formula
R is H or [—CH2CH2O—]mH where m is a common integral
number of cellulose derivatives.
6. Functional Category
Coating agent; Thickening agent;
Suspending agent; Tablet binder;
Viscosity-increasing agent.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/areviewonhydroxyethylcellulose-120321030811-phpapp02/85/A-review-on_hydroxyethyl_cellulose-3-320.jpg)