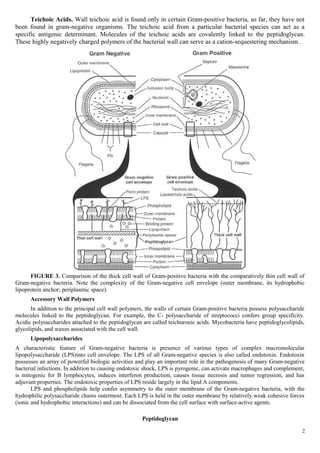
This document discusses the structure of prokaryotic cell walls and Gram staining methods. It begins by describing the key components of bacterial cell walls, including peptidoglycan, teichoic acids, lipopolysaccharides, and outer membranes. It then compares and contrasts the structures of Gram-positive and Gram-negative cell walls. Gram's staining method is introduced as a way to distinguish between the two types based on their ability to retain or release crystal violet dye. The document provides detailed steps for performing Gram staining and explains how it can be used to classify bacteria based on cell wall structure.