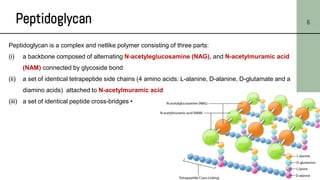
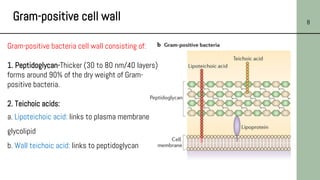
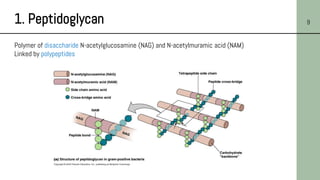
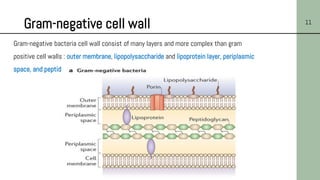
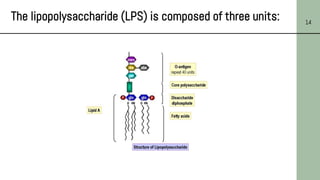
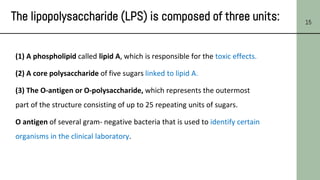
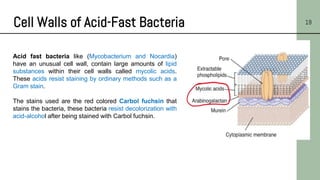
This document discusses the structure of bacterial cells, focusing on differences in cell walls between gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It notes that gram-positive bacteria have a thicker peptidoglycan layer and contain teichoic acids, while gram-negative bacteria have a thinner peptidoglycan layer surrounded by an outer membrane containing lipopolysaccharides. It also describes the roles of these cell wall components and how they help bacteria survive in different environments.