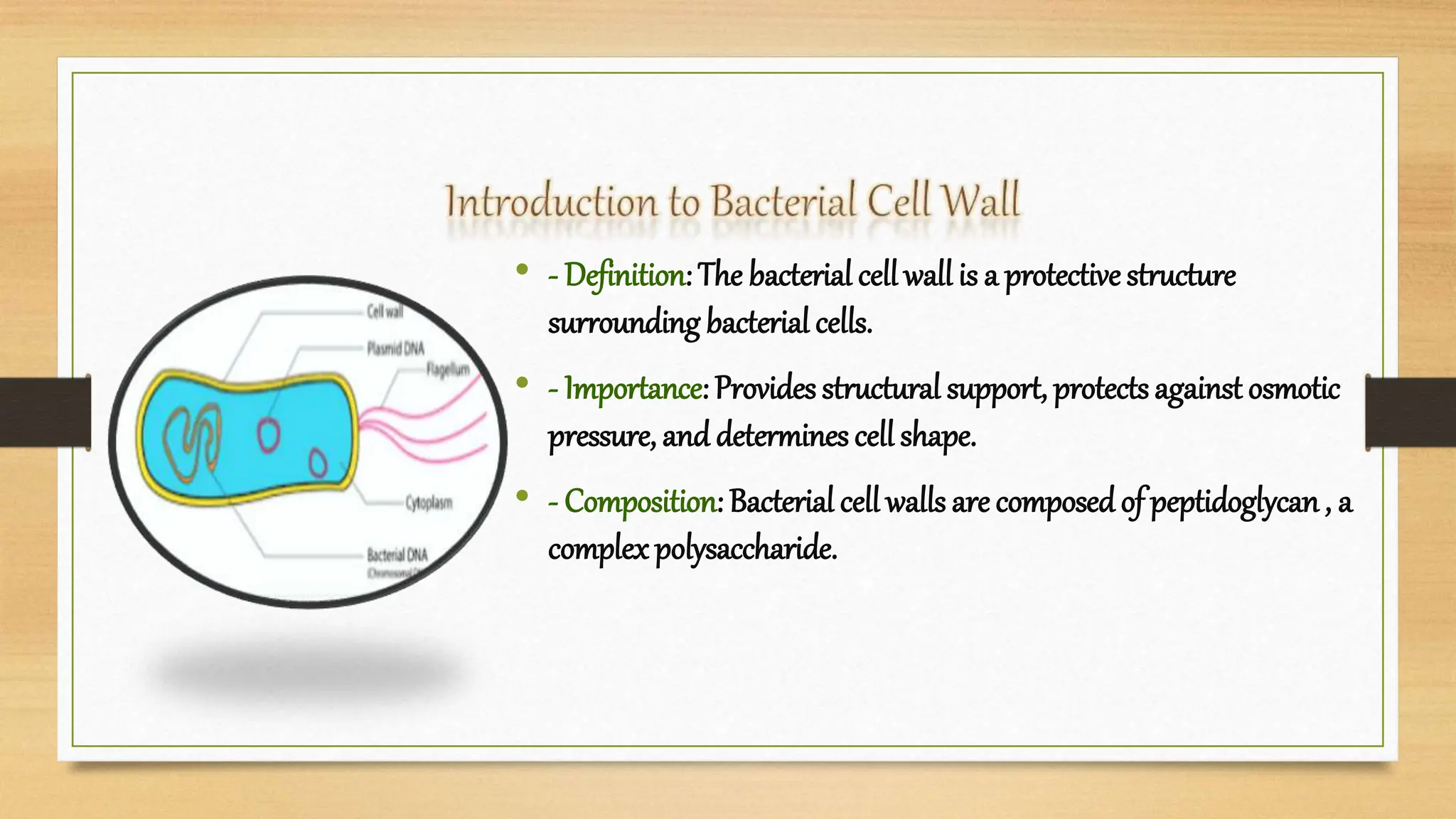
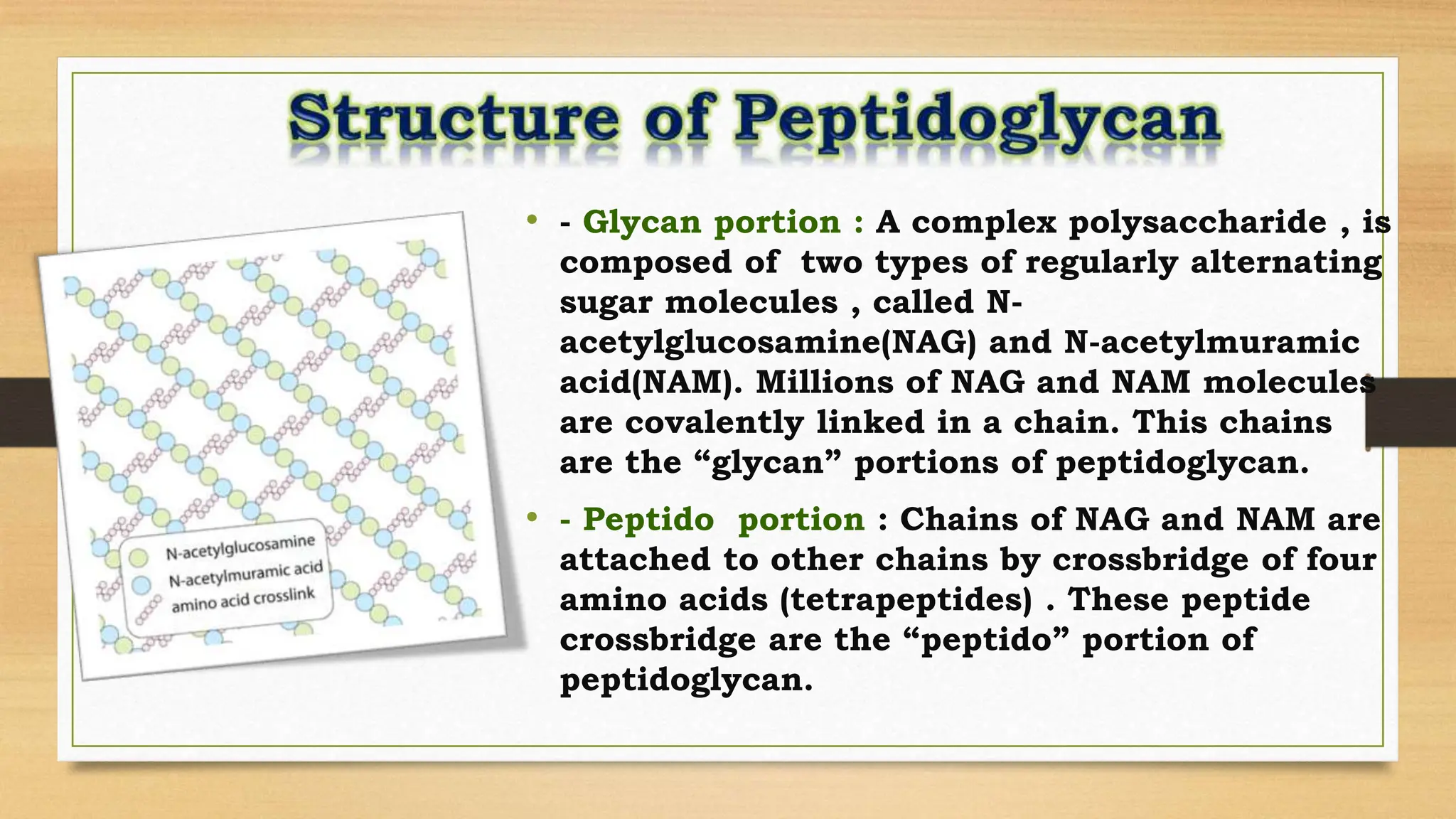
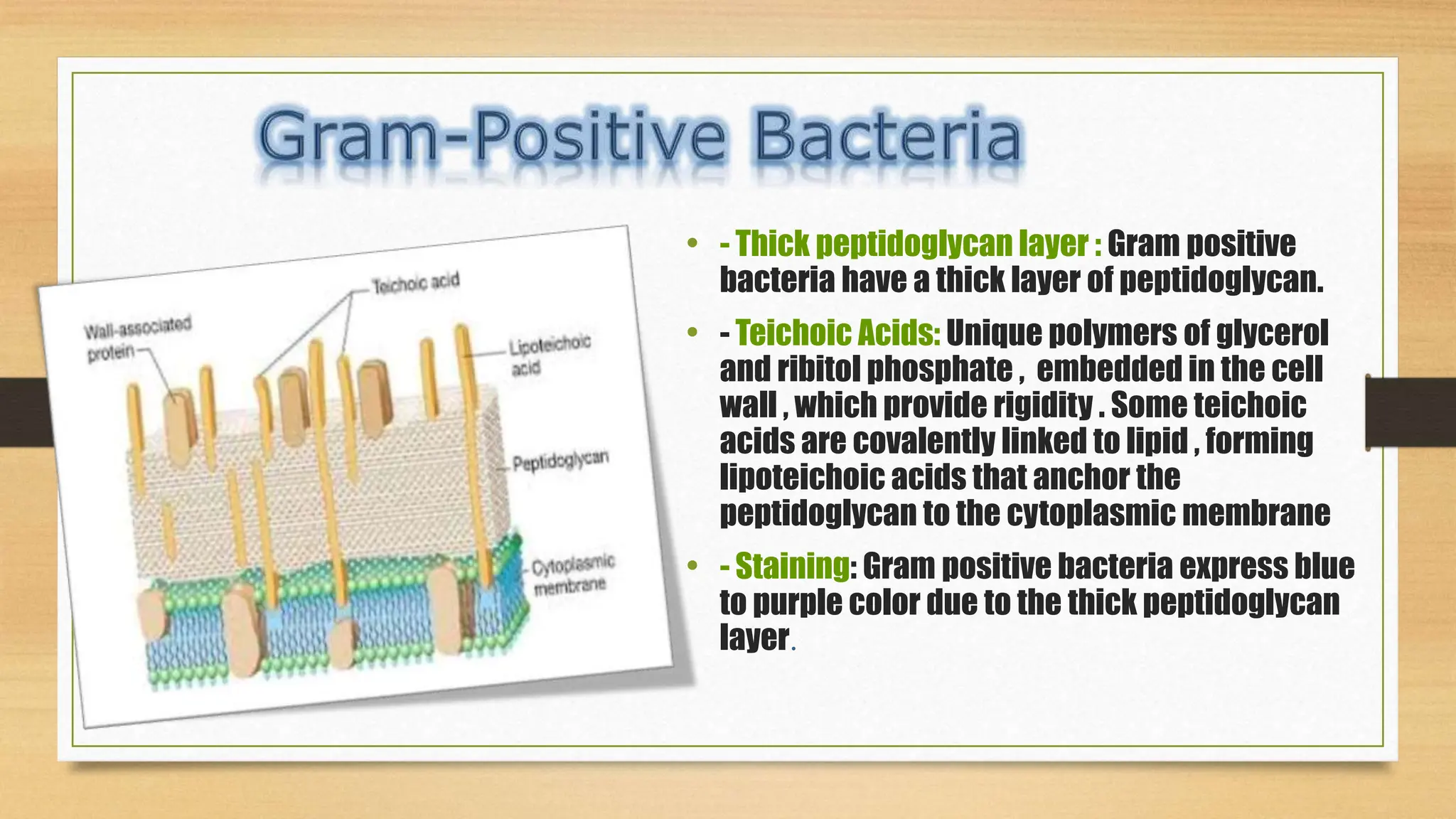
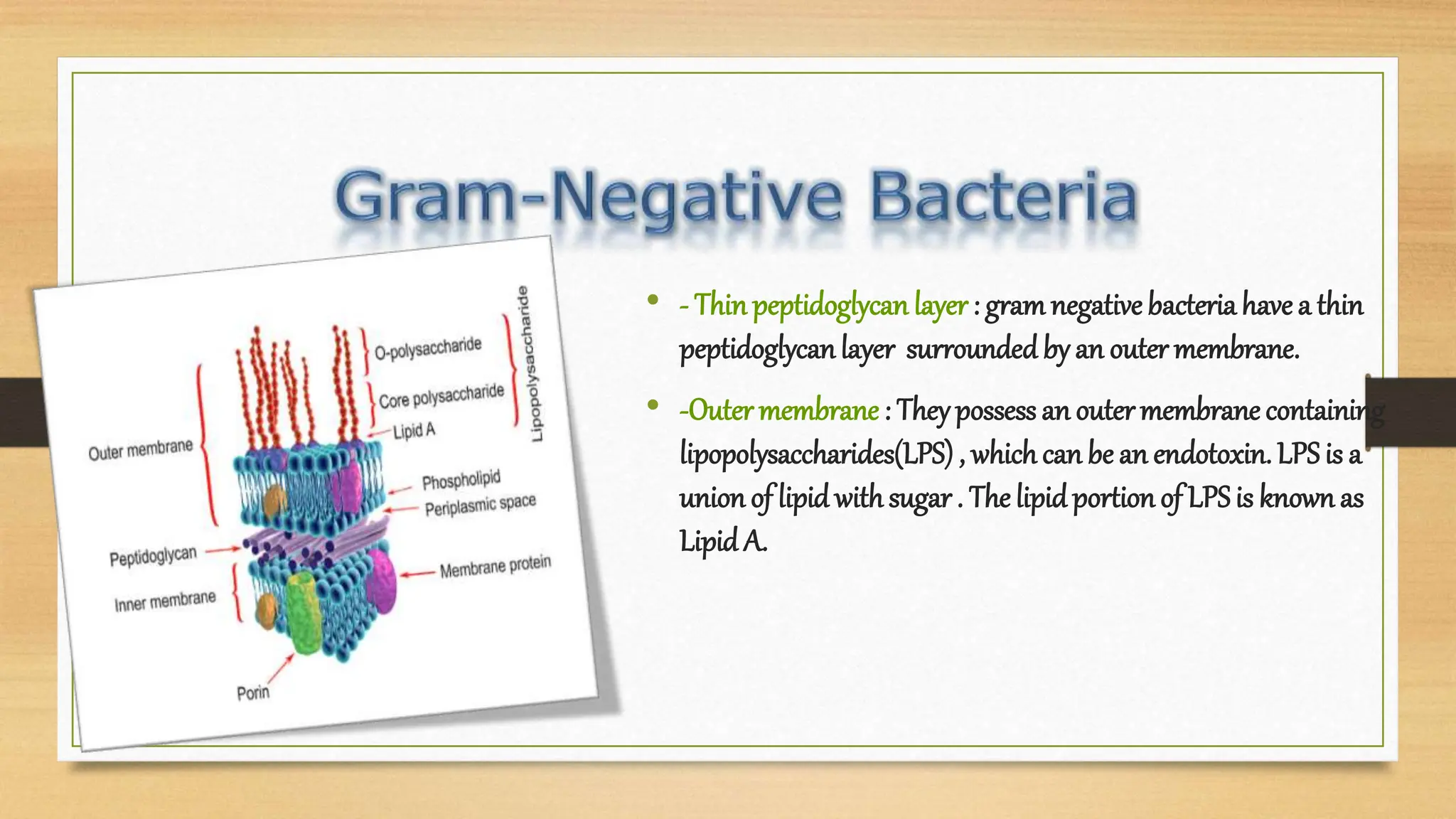
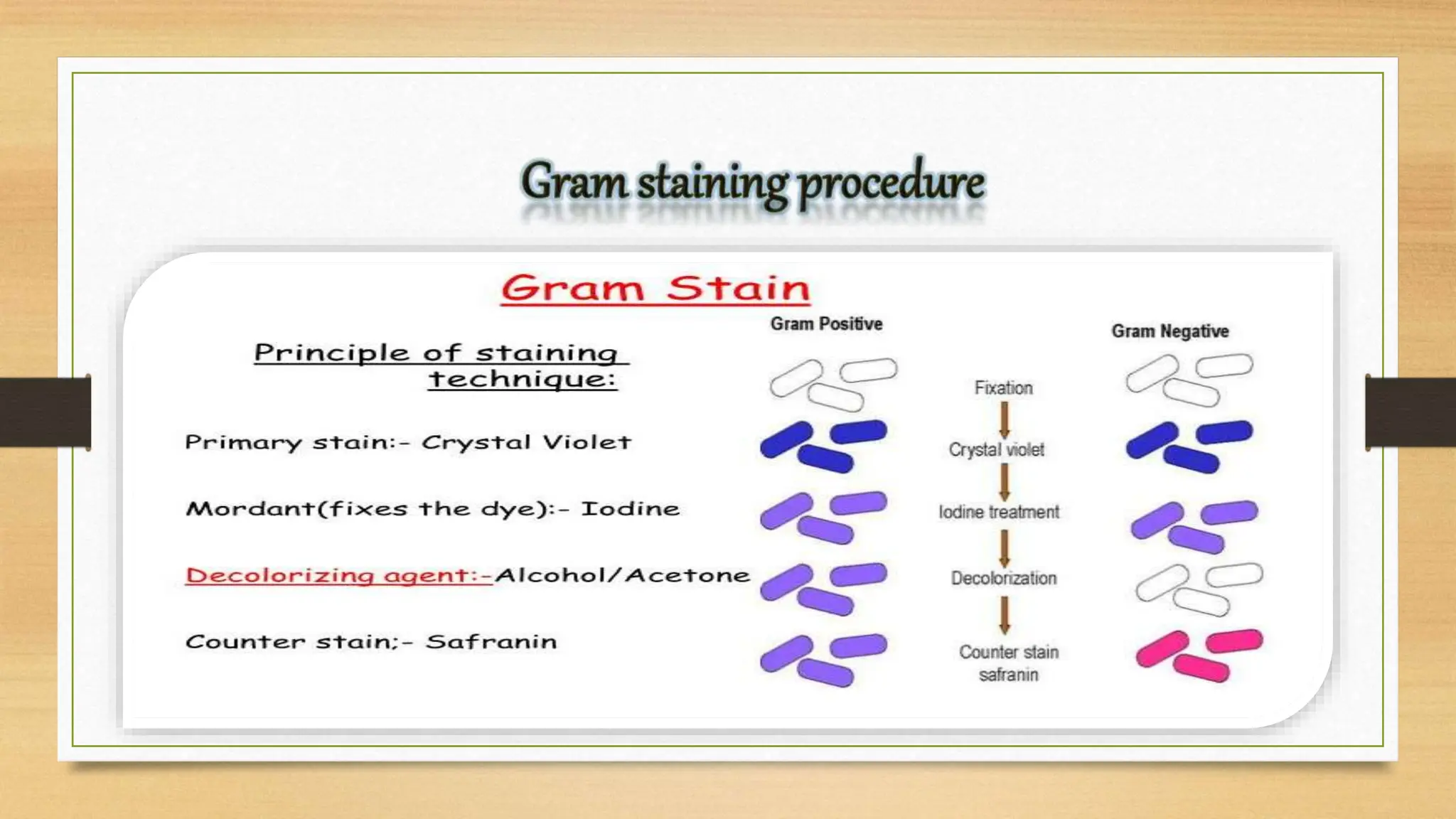
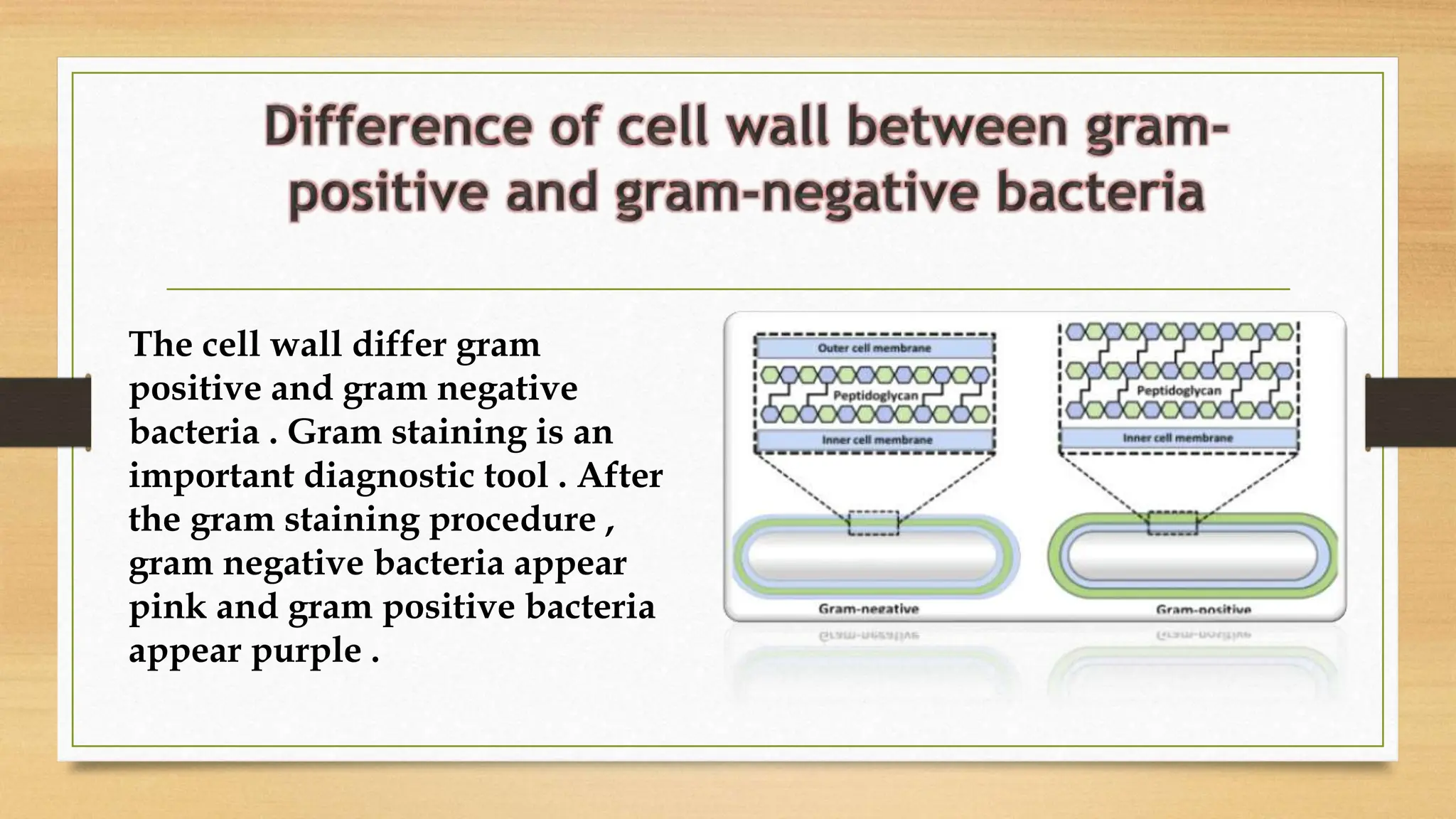
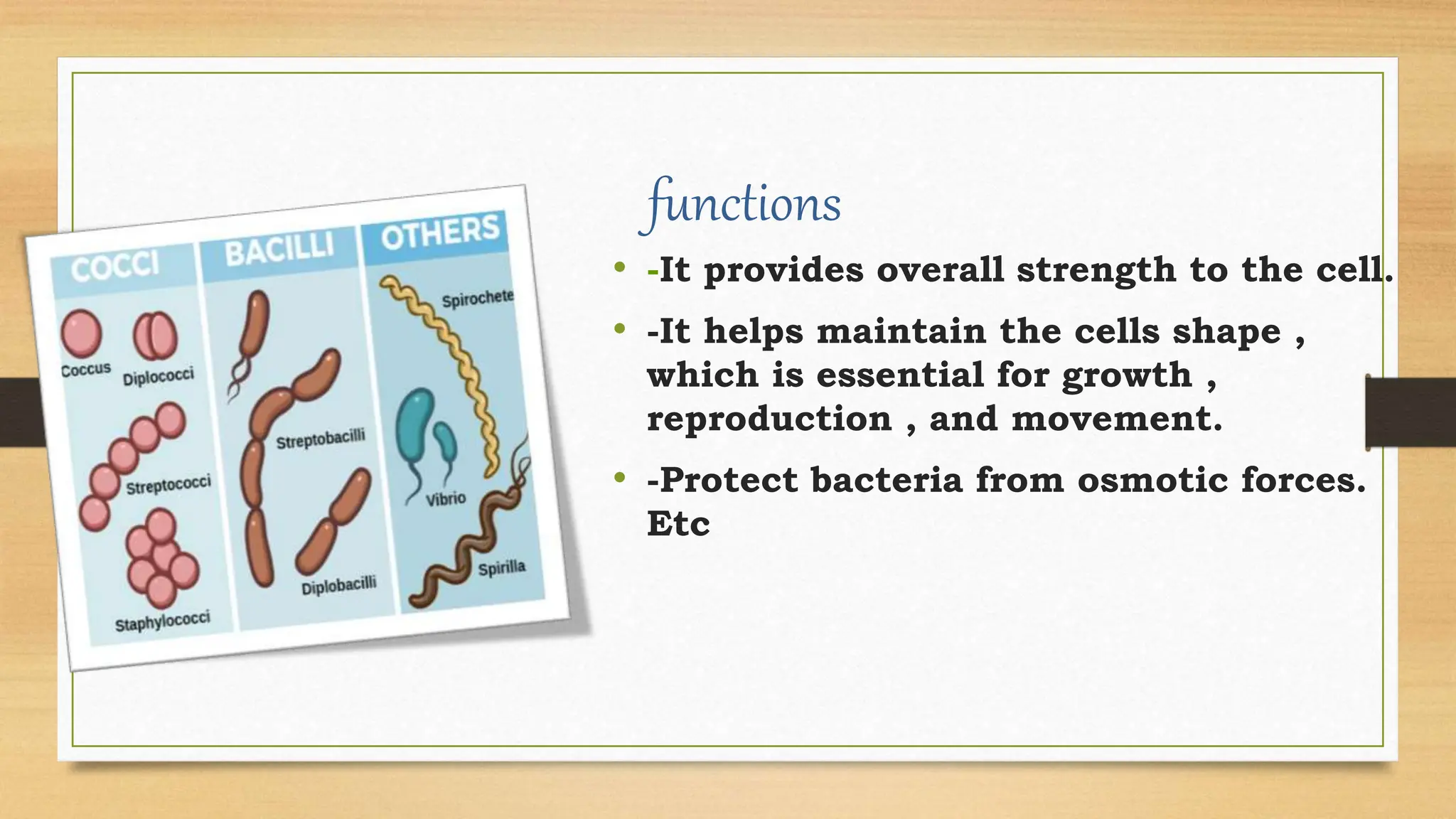
The bacterial cell wall is a protective structure critical for maintaining cell shape, protecting against osmotic pressure, and providing structural support. It is primarily composed of peptidoglycan, which includes glycan and peptido portions, differing between gram-positive (thick layer) and gram-negative (thin layer with outer membrane). Gram staining distinguishes these bacteria based on their cell wall characteristics, leading to different color expressions that aid in diagnostics.