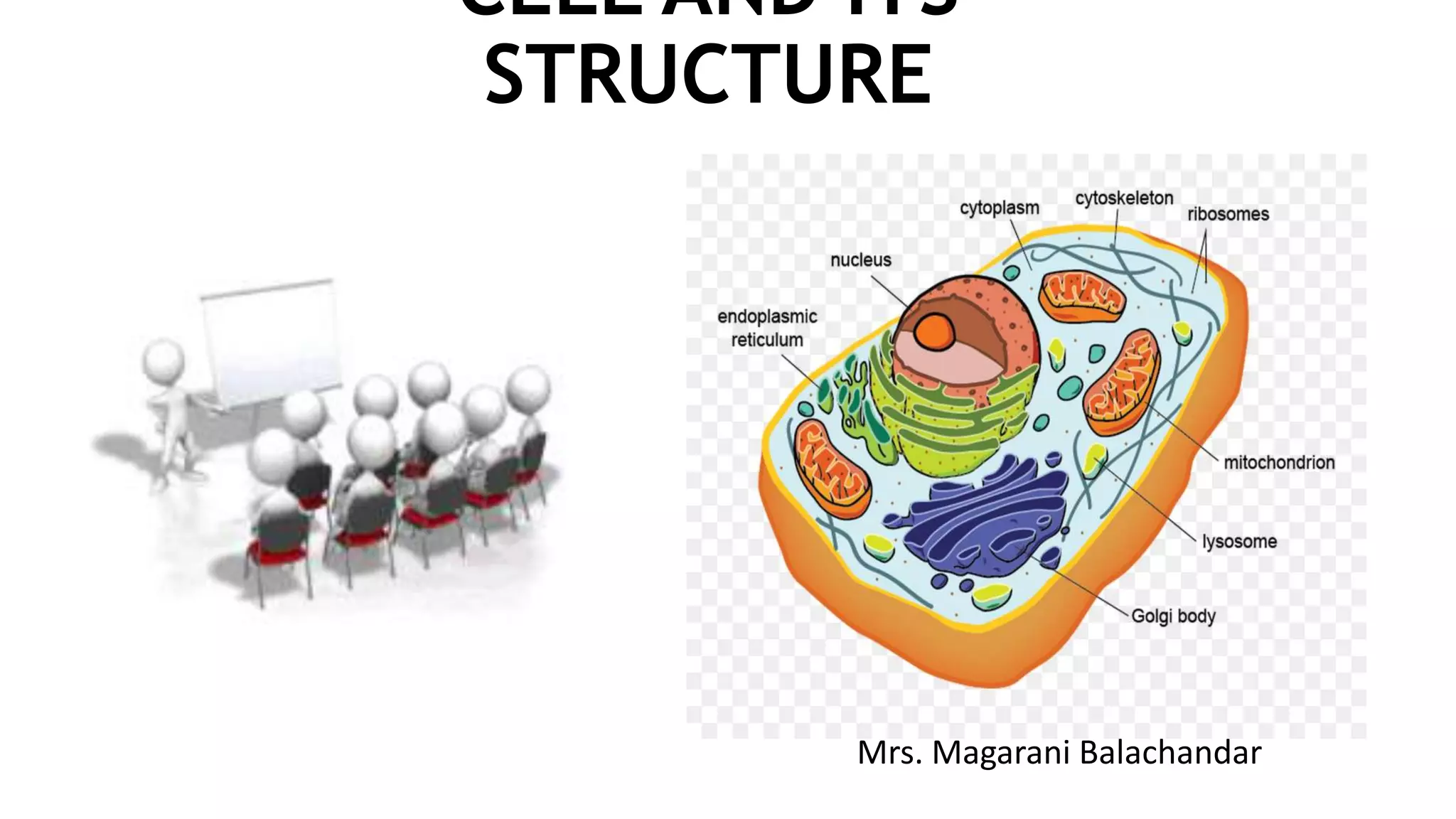
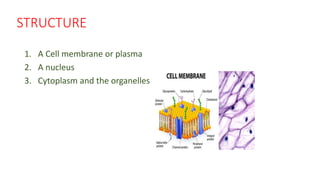
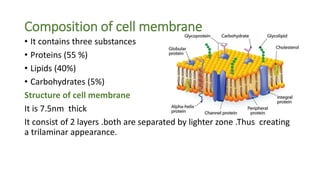
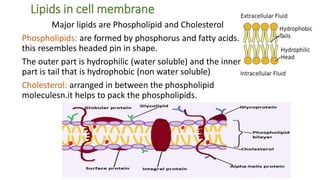
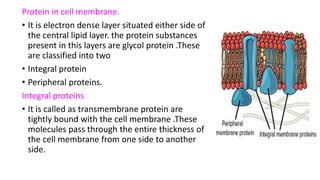
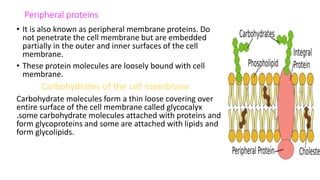
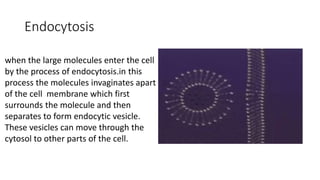
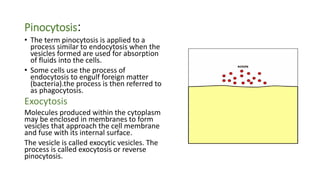
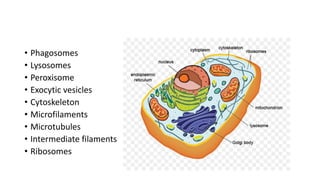
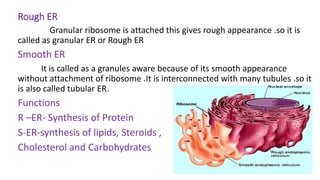
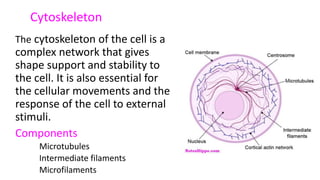
The document summarizes the structure of a cell. It discusses the key components of a cell including the cell membrane, cytoplasm, organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, and cytoskeleton. The cell membrane forms the protective outer layer of the cell and is semi-permeable, regulating what passes in and out. The cytoplasm contains organelles suspended in cytosol. The nucleus houses genetic material and controls cell activities. Other organelles carry out important functions like energy production, protein transport, and maintaining cell shape.