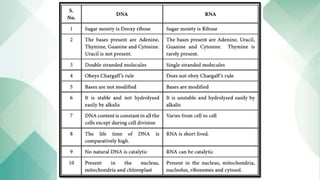
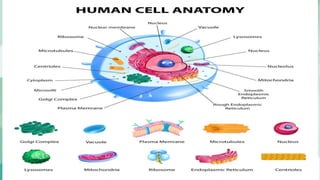
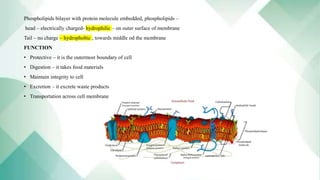
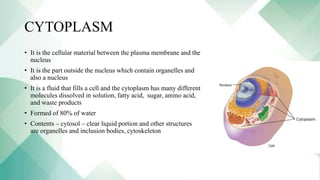
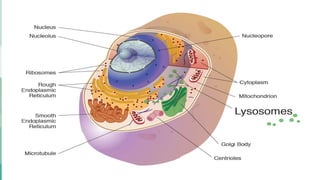
Human cells contain various organelles that carry out essential functions. The basic components of a cell include the cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, and organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and cytoskeleton. The cell membrane forms the boundary of the cell and regulates what enters and exits. The nucleus contains genetic material and influences cell activities. Mitochondria generate energy for cell processes through ATP production. Other organelles are involved in protein synthesis, modification and transport, waste breakdown, and maintaining cell structure.





![Mitochondria
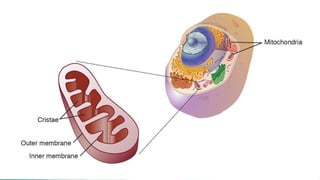
• Power house of cell
• Double membrane bounded
• Sausage shaped structure in cytoplasm
• Converts oxygen and nutrients into adenosine triphosphate(ATP)-provide energy for various biochemical
processes in the body
• Mitochondria contains outer and inner membrane
1. The outer layer which is smooth
2. An inner layer folded into sheet of tubules called cristae
• Both these cavities are enclosed a central cavity called matrix
• Mitochondria are made up of protein, phospholipids and RNA [they also contain some important
enzymes ]
• They are metabolically active cells [ muscle cells , liver cells have more mitochondria]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basiccell-231014065110-0974bbf2/85/basic-cell-pptx-10-320.jpg)

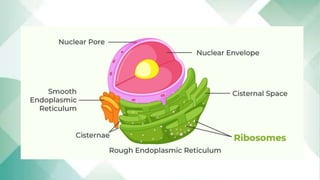
![Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
• The smooth endoplasmic reticulum functions in
many metabolic processes.[ change food into
energy]
• It synthesizes lipids, phospholipids as in plasma
membranes, and steroids. Cells that secrete these
products, such as cells of the testes, ovaries, and
skin oil glands, have an excess of smooth
endoplasmic reticulum.
• The smooth endoplasmic reticulum also carries out
the metabolism of carbohydrates and steroids. In
muscle cells, the smooth endoplasmic reticulum
regulates calcium ion storage.
• Develops from Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum.
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
• it is the part of endoplasmic reticulum to which
granular ribosomes are attached . This part is called
granular ER. It is concerned with protein synthesis
• It possesses ribosomes attached to its membrane.
• It might develop from the nuclear envelope
• The RER is also located near the Golgi apparatus,
which transports, modifies, and packages proteins
for delivery to targeted destinations. Many proteins
that are synthesized in the RER are packaged into
vesicles and transported to the Golgi apparatus.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basiccell-231014065110-0974bbf2/85/basic-cell-pptx-13-320.jpg)

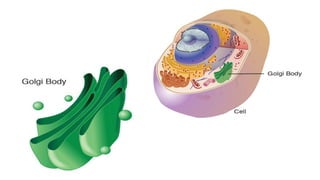
![Golgi apparatus
• Consist of stacks of closely folded flattened membrane set
• It consists of flattened membrane disc called saccule, a typical Golgi apparatus consists of five
saccules
• They lies near the nucleus and shows micro vesicles [ secretory glands ] on the surface
• They help in process of receiving and storing of secretory products [ protein]
• It is present in all cells but is larger in those that synthesize and export proteins
• It is cup like shape structure and contain vesicles
• A Golgi body, also known as a Golgi apparatus, is a cell organelle that helps process and package
proteins and lipid molecules, especially proteins destined to be exported from the cell.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basiccell-231014065110-0974bbf2/85/basic-cell-pptx-16-320.jpg)

![Nucleus
• Large oval body near the center of the cell
• The control center for all activity
• Nucleus is found in all cells except mature erythrocytes [ RBC] and platelets
• The shape is normally rounded and placed centrally
• Nucleus contain genetic material and influences the metabolic activities of cell
• Normally cells have one nucleus but some cells like osteoclast, skeletal muscle have 2 or more
nuclei
• Nucleus id surrounded by a nuclear membrane which the membrane have many pores called
nuclear pores which the substances can transport to the cytoplasm
• Cytoplasm of nucleus is nucleoplasm contain chromatin material [ gene carrier ] and nucleolus
which is rich in RNA and concerned with protein synthesis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/basiccell-231014065110-0974bbf2/85/basic-cell-pptx-20-320.jpg)