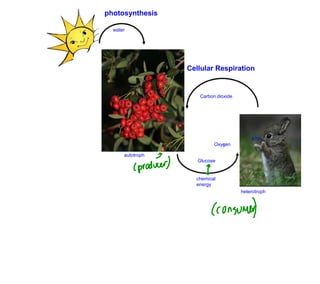
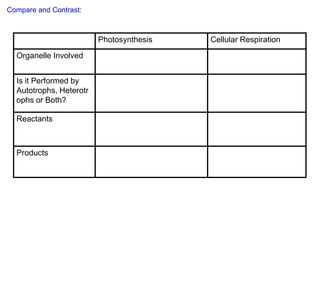
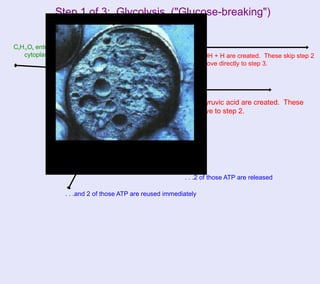
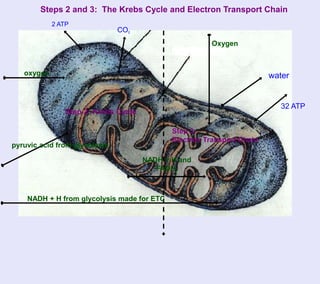
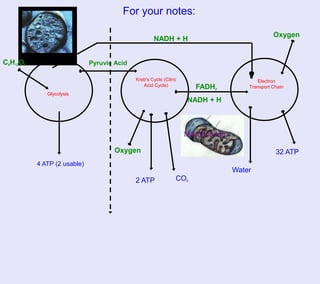
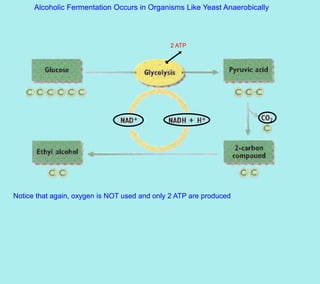
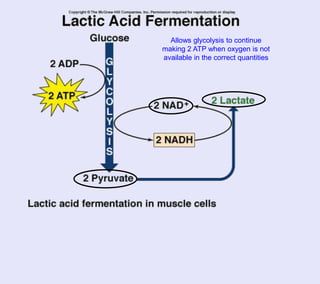
The document provides information about cellular respiration. It defines cellular respiration as the 3-step process by which glucose molecules are broken down to release usable energy. The three steps are glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain. Cellular respiration occurs in all cells and produces 32 ATP molecules from one glucose molecule with oxygen as the final electron acceptor. Fermentation is discussed as cellular respiration that can occur without oxygen to produce a small amount of ATP.