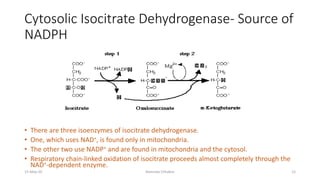
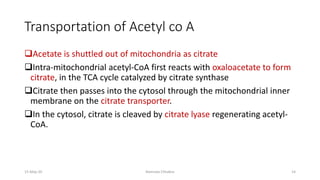
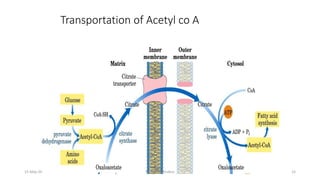
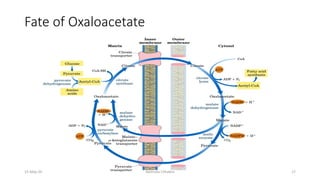
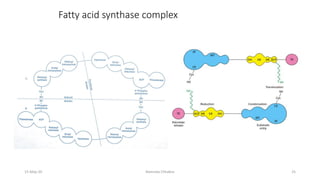
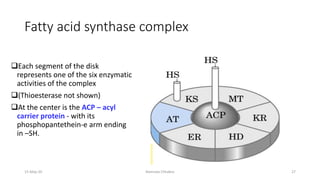
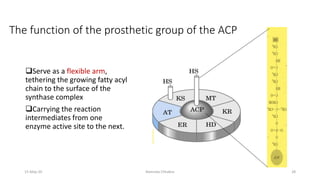
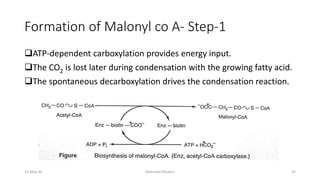
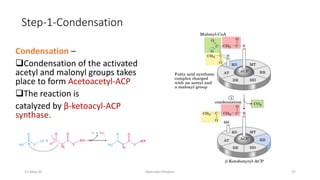
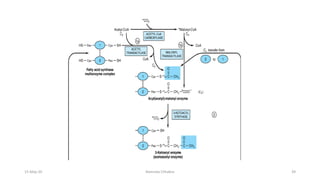
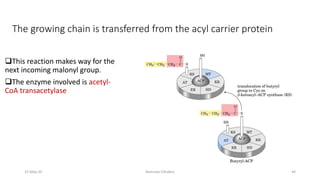
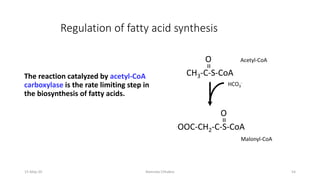
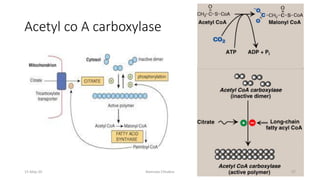
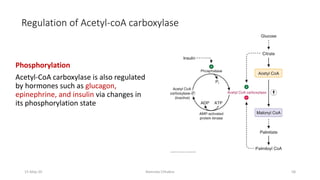
Fatty acids are synthesized through a cyclic process in the cytosol. Acetyl-CoA is carboxylated to form malonyl-CoA by the enzyme acetyl-CoA carboxylase, initiating fatty acid synthesis. The fatty acid synthase complex then catalyzes the remaining steps - condensation of acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA, followed by reduction, dehydration, and reduction to form a fatty acid. This cycle of condensation, reduction, dehydration, and reduction is repeated until a 16-carbon palmitate is synthesized. NADPH provides reducing equivalents and the acyl carrier protein transports intermediates between active sites of the fatty acid synthase