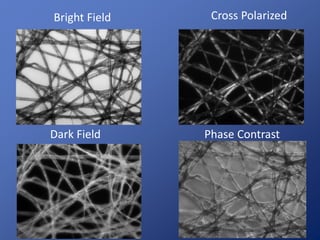
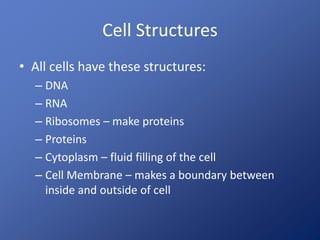
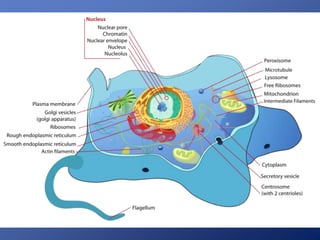
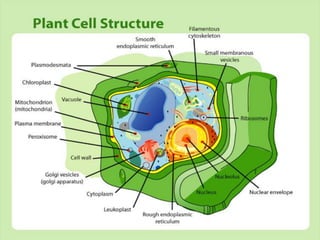
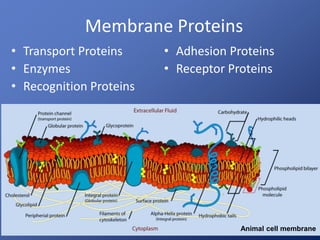
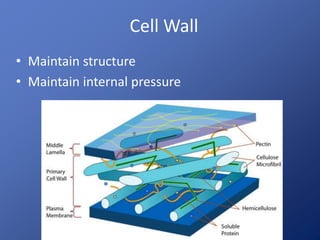
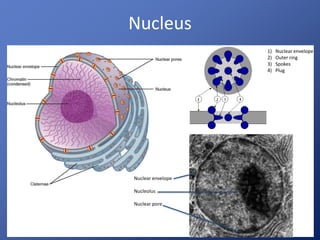
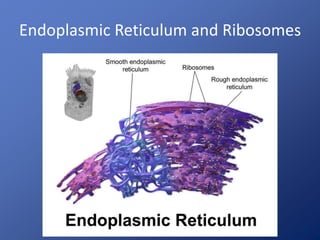
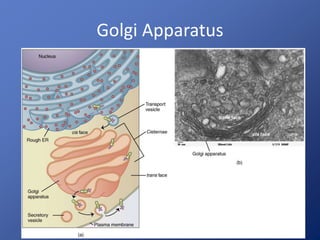
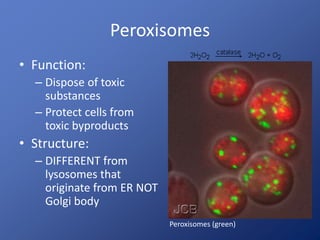
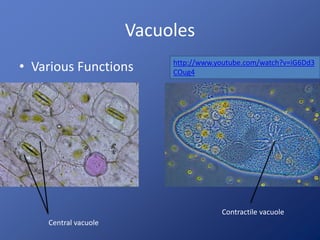
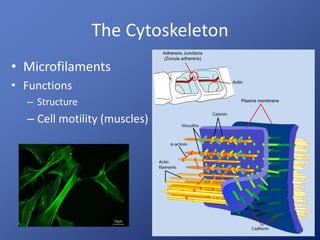
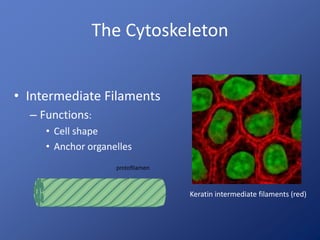
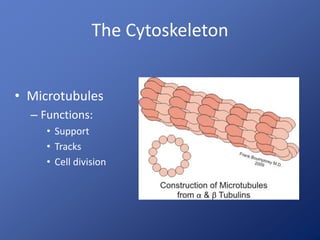
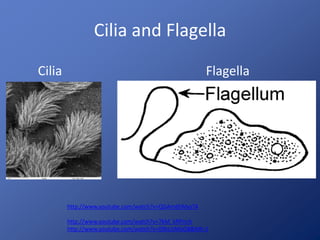
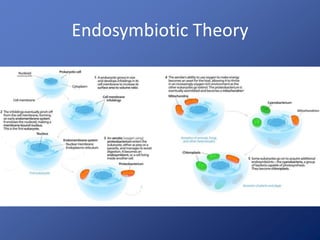
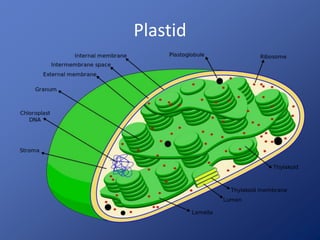
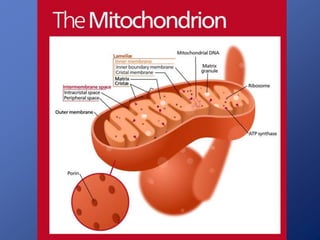
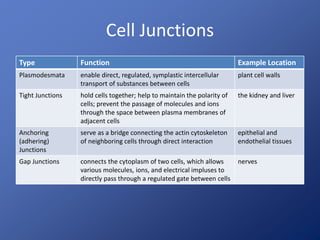
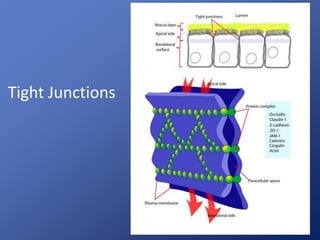
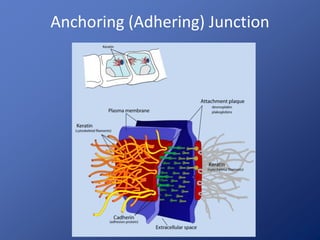
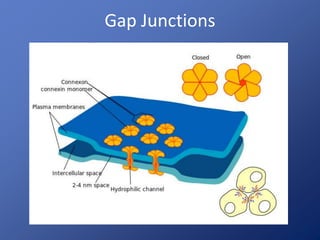
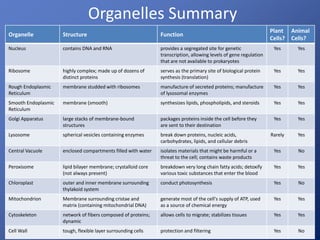
Cells are the basic unit of life. Robert Hooke first observed cells in 1665 using a microscope he invented. The cell theory states that all living things are made of cells and cells are the fundamental unit of life. Key structures of cells include the nucleus, which contains DNA; organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts; and a cell membrane that encloses the cell. Organelles perform specialized functions like carrying out photosynthesis in chloroplasts or producing energy in mitochondria.