The document discusses cell membranes and the methods of transport across membranes. It covers four main methods:
1) Diffusion - the passive movement of molecules from high to low concentration without energy.
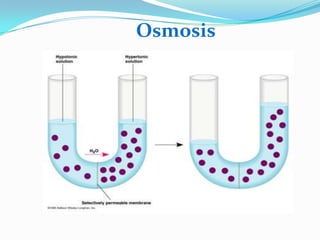
2) Osmosis - the passive movement of water across membranes.
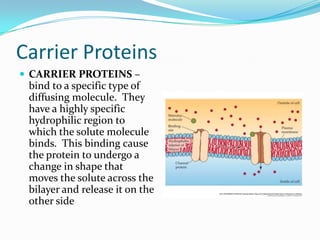
3) Facilitated diffusion - uses carrier proteins to transport molecules across membranes without energy.
4) Active transport - requires energy (ATP) to transport molecules against their concentration gradient using carrier proteins. The document provides examples and explanations of these transport methods.