Embed presentation
Downloaded 70 times



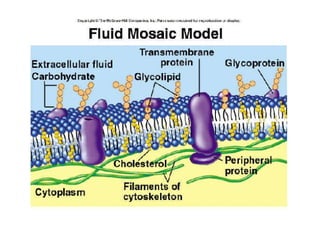













The document discusses various processes of cell transport, including passive transport mechanisms like diffusion and osmosis that move materials across the cell membrane towards equilibrium without energy usage, as well as active transport processes like endocytosis, exocytosis, and facilitated diffusion that move materials against concentration gradients by using energy. It introduces key terms related to cell transport and membrane structure, and outlines the different needs that must be met to maintain homeostasis within the cell.















