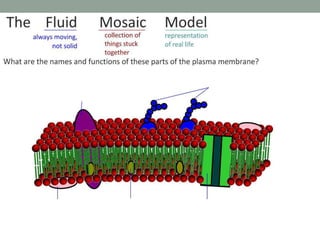
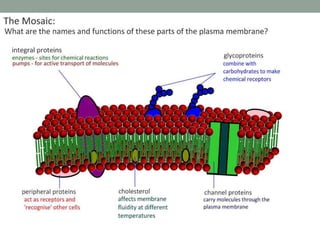
Membranes allow selective transport of molecules across them. There are three main types of transport:
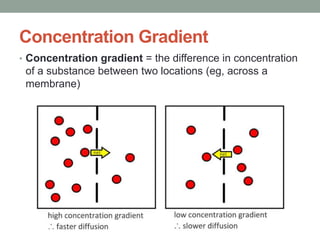
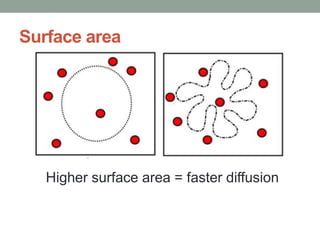
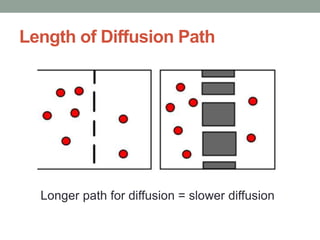
1) Diffusion is the passive movement of particles down a concentration gradient without needing energy. It occurs through the phospholipid bilayer or using carrier proteins.
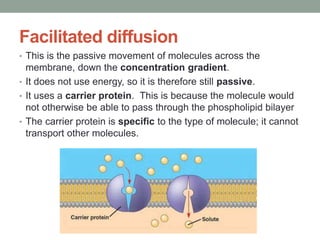
2) Facilitated diffusion also moves molecules passively down a concentration gradient but uses carrier proteins to transport molecules that cannot diffuse through the bilayer.
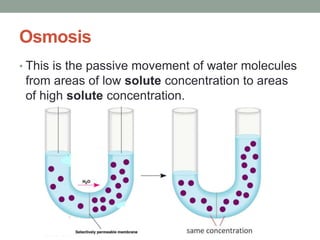
3) Osmosis is the passive movement of water molecules from low to high solute concentration areas since water can pass through membranes but solute particles cannot to equalize concentrations.