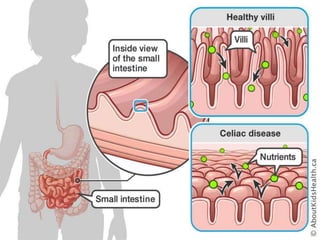
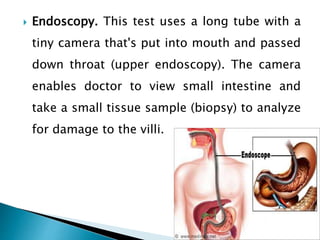
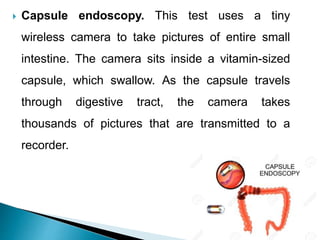
Celiac disease is an immune reaction to eating gluten, which is found in wheat, barley, and rye. It damages the lining of the small intestine and interferes with nutrient absorption. Symptoms include abdominal pain, diarrhea, weight loss, fatigue, and bone or joint pain. It is diagnosed through blood tests detecting antibodies and genetic testing, and confirmation with an intestinal biopsy. The only treatment is a strict lifelong gluten-free diet, which allows the intestinal lining to heal and symptoms to improve.