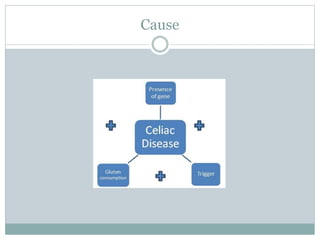
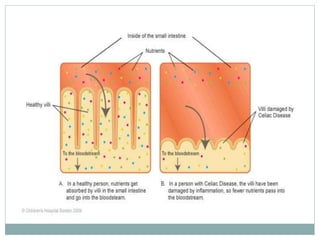
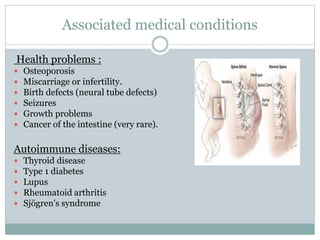
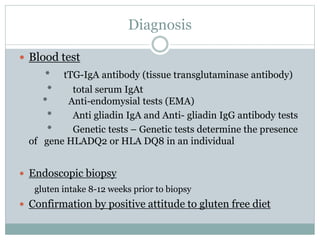
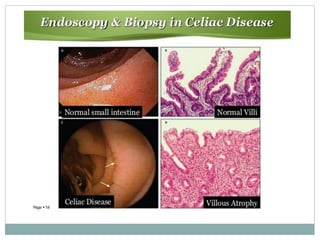
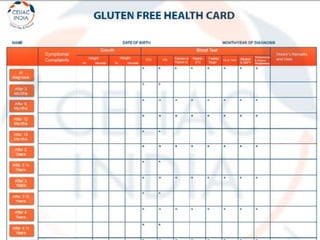
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder affecting the small intestine, with a prevalence of about 1% globally, particularly impacting populations in North India. Symptoms vary significantly between children and adults, including gastrointestinal issues in children and often atypical symptoms like fatigue and joint pain in adults. Diagnosis is primarily through blood tests and endoscopic biopsy, with treatment focused on a strict gluten-free diet, as there is currently no cure.