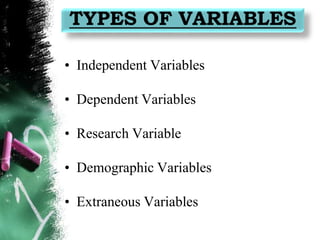
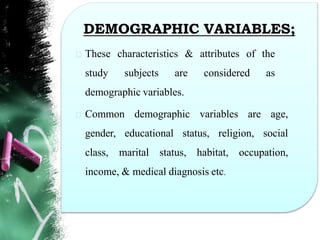
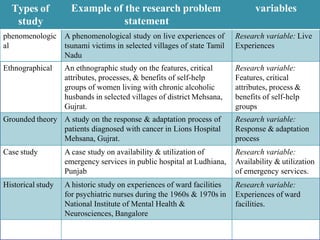
This document discusses different types of variables that may be studied in quantitative and qualitative research, including independent, dependent, research, demographic, and extraneous variables. It provides examples of how these variables are used in descriptive, exploratory, correlational, comparative, experimental, quasi-experimental, phenomenological, ethnographic, grounded theory, case study, and historical research studies. The document emphasizes that variables must be clearly defined in research to allow for measurement and analysis.