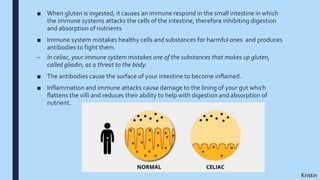
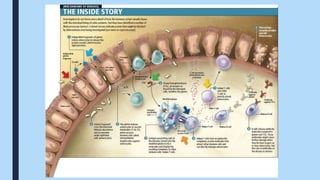
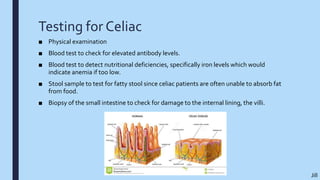
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder triggered by gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley and rye. It affects about 1% of the population and causes damage to the lining of the small intestine, inhibiting nutrient absorption. Genetic and environmental factors can increase risk. Symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, and nutrient deficiencies. Treatment requires a lifelong gluten-free diet to avoid immune system attacks on intestinal cells. While challenging, following a gluten-free diet can help manage the disease and prevent further complications.