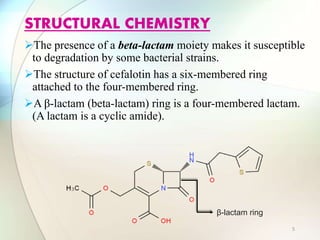
This document provides information about the antibiotic cefalotin. It discusses cefalotin's structural chemistry as a first generation cephalosporin antibiotic. The document outlines cefalotin's chemical and physical properties, dosage and administration, indications for use, pharmacokinetics, mechanism of action, interactions, side effects, and packaging/storage. The objectives are to describe cefalotin's properties and appropriate use as a parenterally administered antibiotic with activity against gram-positive bacteria.



![IUPAC Name: (6R,7R)-3-(acetyloxymethyl)-8-
oxo-7-[(2-thiophen-2-ylacetyl)amino]-5-thia-1-
azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid.
Chemical Names: Cephalothin; Cefalotin;
Cefalothin; Cephalotin; Cefalotine; Keflin.
Brand Names:
Averon-1®
Cemastin®
Coaxin®
Keflin®
Seffin®
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cefalotin-ppt-150526174828-lva1-app6892/85/Cefalotin-ppt-4-320.jpg)