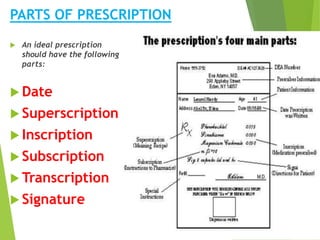
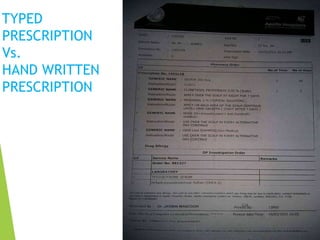
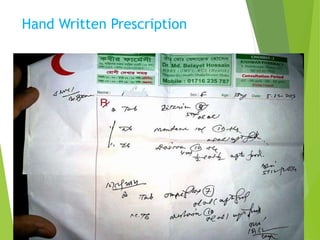
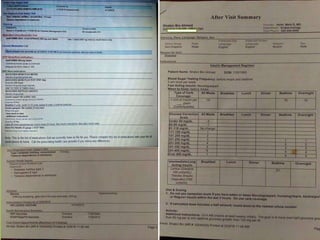
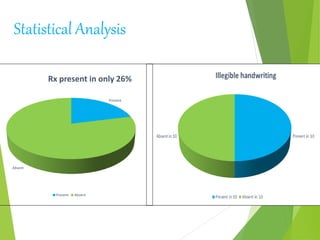
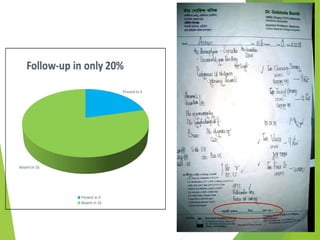
The document discusses the definition and types of prescriptions, detailing components like date, superscription, inscription, subscription, transcription, and signature. It highlights the differences between pre-compounding and extemporaneous prescriptions and emphasizes the importance of minimizing prescription errors through various steps. The document also mentions a study conducted on prescriptions in Dhaka, identifying common problems and comparing typed versus handwritten prescriptions.