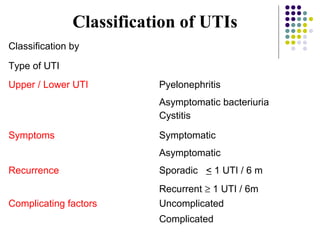
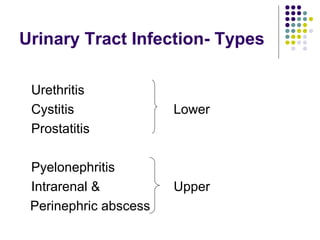
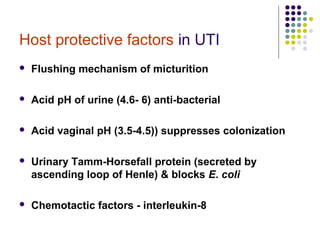
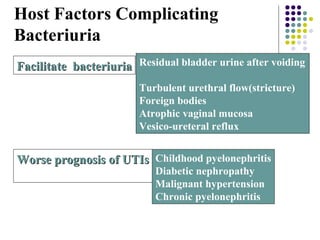
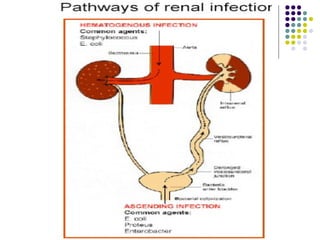
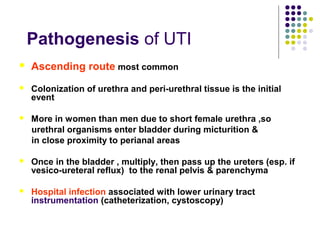
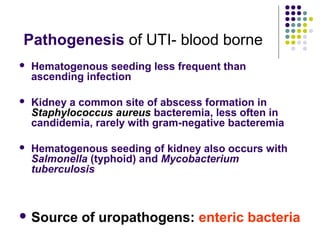
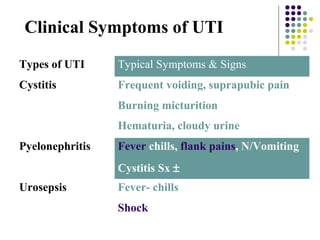
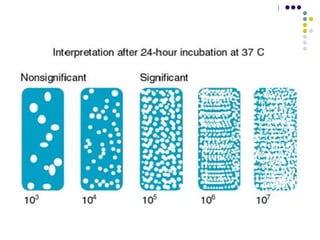
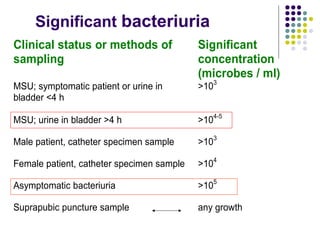
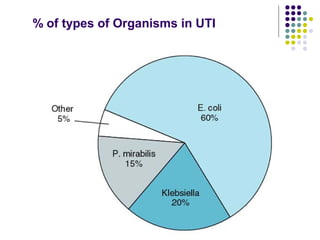
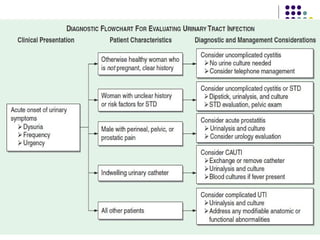
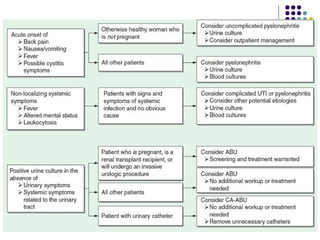
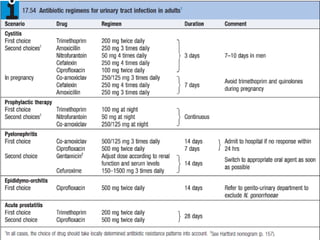
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are very common, affecting around 150 million people worldwide each year. The majority are cystitis, with a smaller percentage being pyelonephritis. Risk factors include being female, as well as factors like urinary catheters and anatomical abnormalities. Escherichia coli is the most frequent cause of community-acquired UTIs. Diagnosis involves urinalysis, urine culture and sensitivity testing. Treatment consists of antibiotics targeting the identified organism. Recurrent UTIs may be prevented with low dose antibiotic prophylaxis.