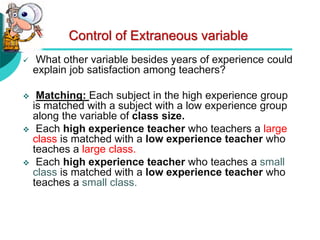
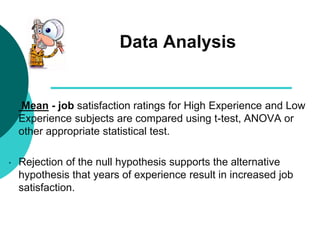
Causal-comparative research involves comparing two or more groups that differ on some independent variable to determine the cause or reason for pre-existing differences between the groups. It attempts to identify cause-and-effect relationships. The researcher does not manipulate the independent variable because it has already occurred or cannot be manipulated. Causal-comparative research involves selecting groups that differ on the independent variable, making comparisons between the groups on a dependent variable, and attempting to determine the cause for any differences found. An example is comparing job satisfaction between teachers with high experience versus low experience.