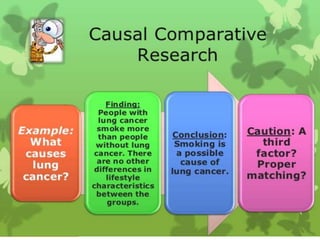
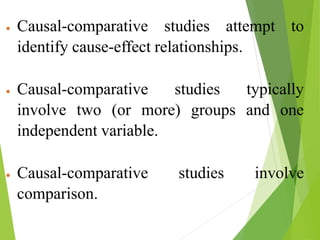
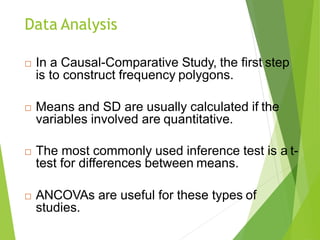
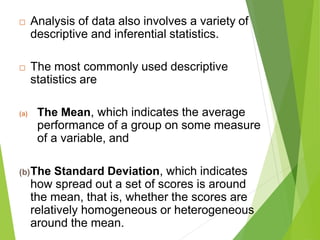
Causal-comparative research attempts to identify potential cause-and-effect relationships by comparing two or more groups that differ on some independent variable. Researchers select naturally occurring groups that vary on the independent variable, rather than manipulating the variable through experimentation. There are three types: exploration of effects, causes, and consequences. Threats to internal validity include lack of randomization and control. Analysis involves comparing means and frequencies between groups using t-tests, ANCOVA, or other inferential statistics.