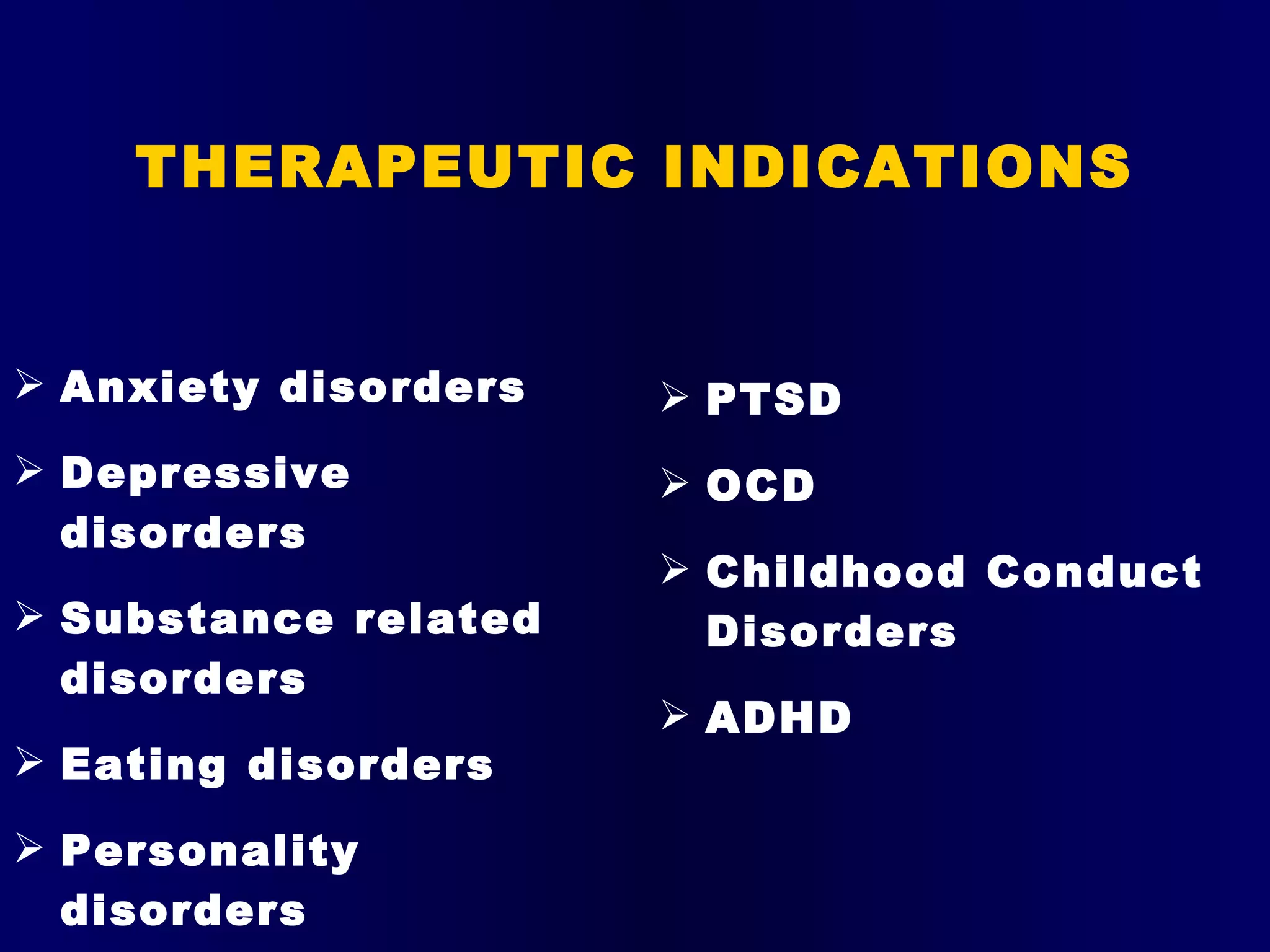
Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) is a type of psychotherapy that is based on changing patterns of thinking. CBT aims to challenge and change unhelpful thoughts and beliefs through cognitive and behavioral techniques. It is a collaborative process between the therapist and client that is goal-oriented and time-limited, usually lasting 12-16 weeks. CBT helps clients monitor thoughts, recognize connections between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors, and replace distorted thoughts with more realistic interpretations.