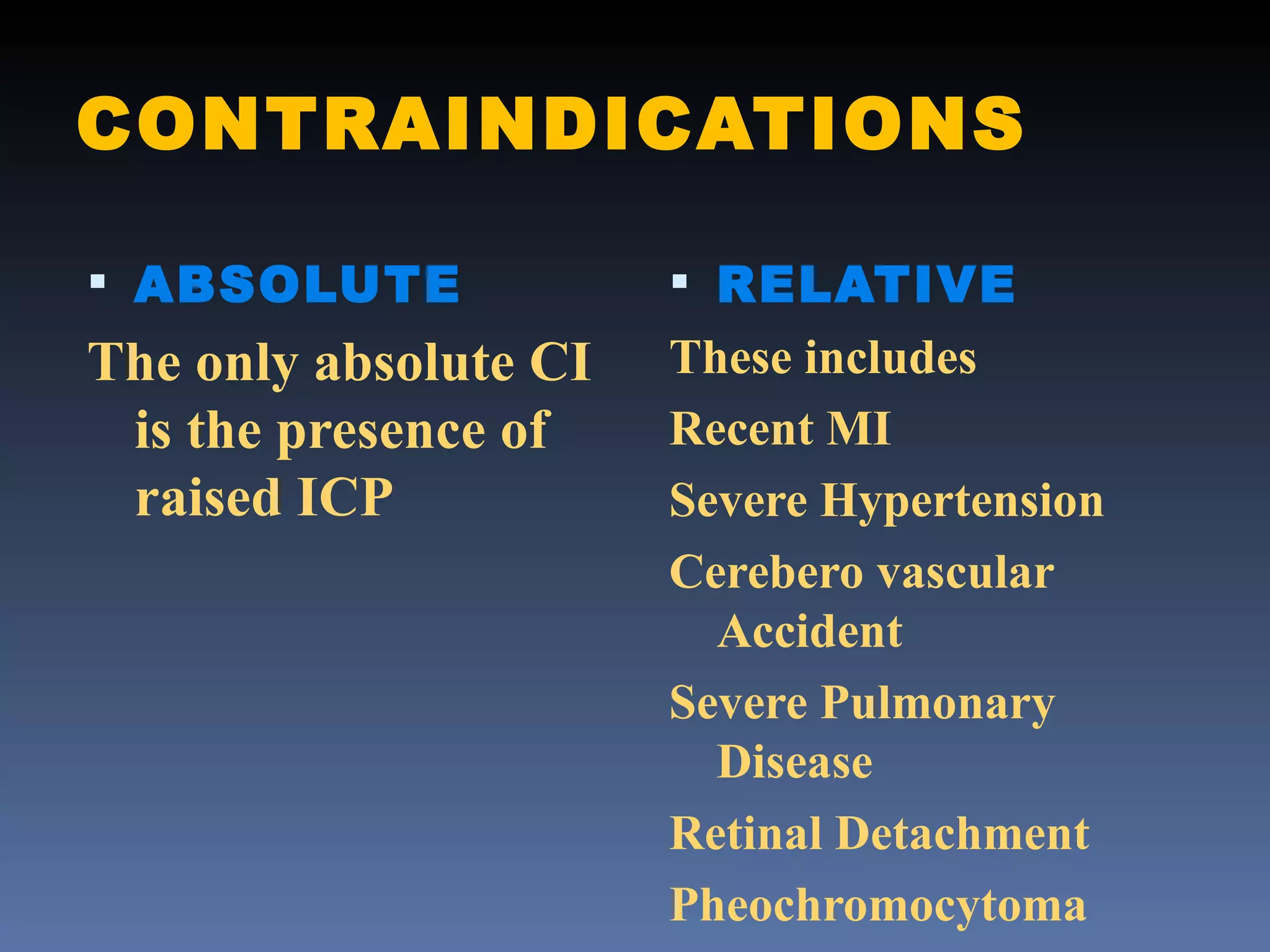
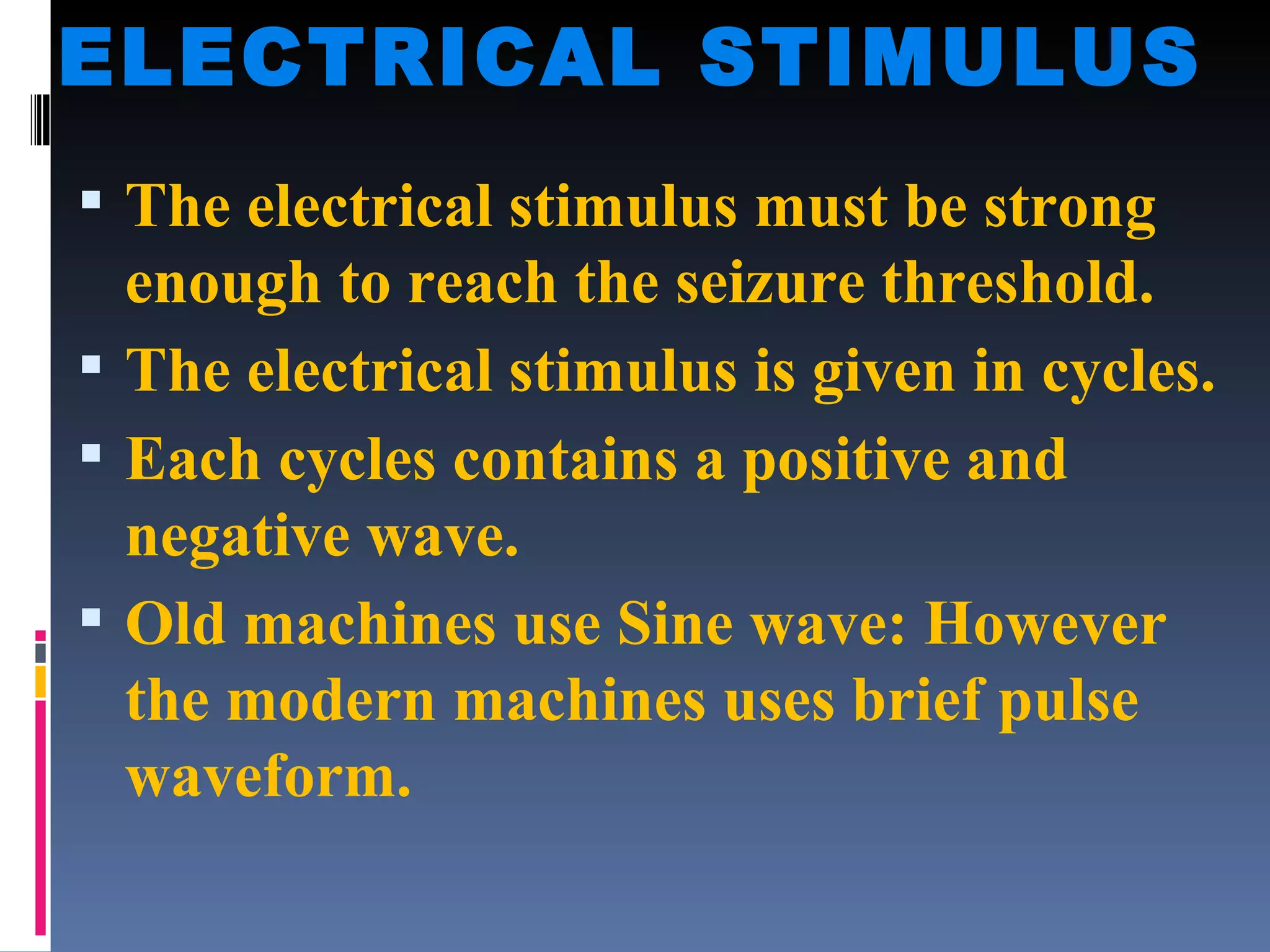
Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) involves applying electric current to the brain through electrodes placed on the head to induce seizures. It is used to treat severe depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia and other conditions. The document outlines the history, mechanism of action, administration process, monitoring, side effects and nurse's role in ECT. ECT remains an effective treatment for severe mental illnesses when other options have failed or cannot be used.