Embed presentation
Downloaded 37 times
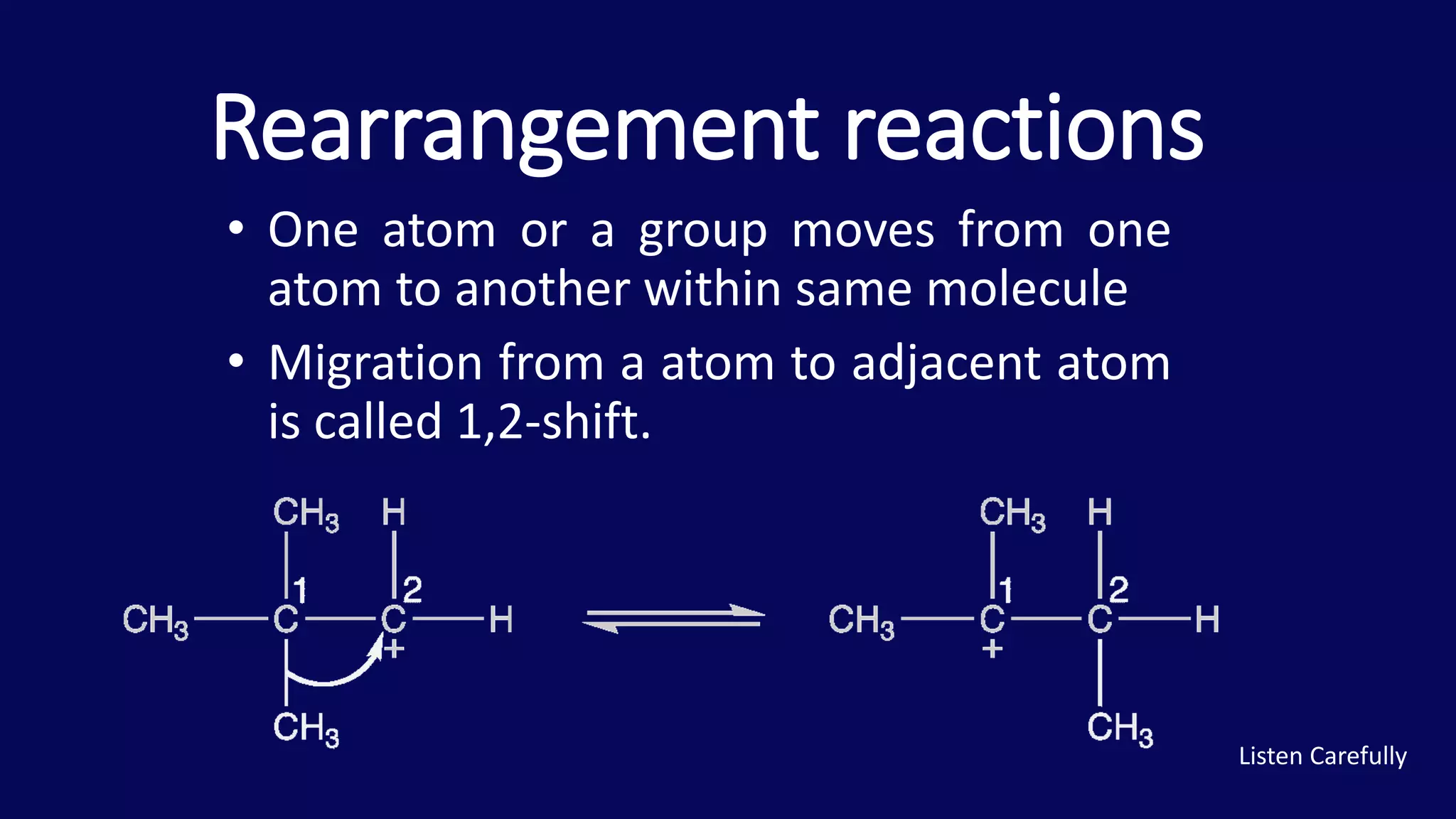

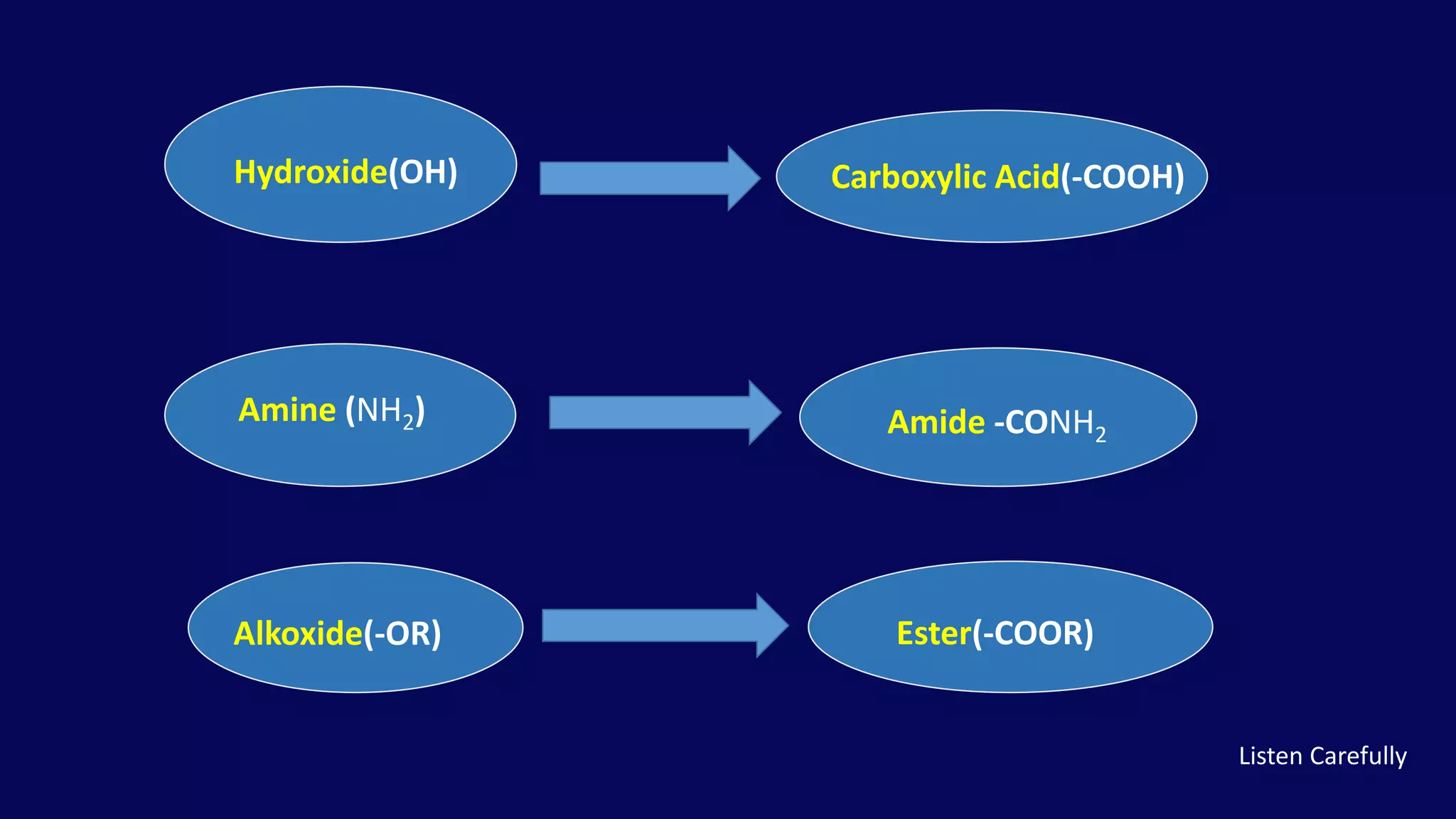
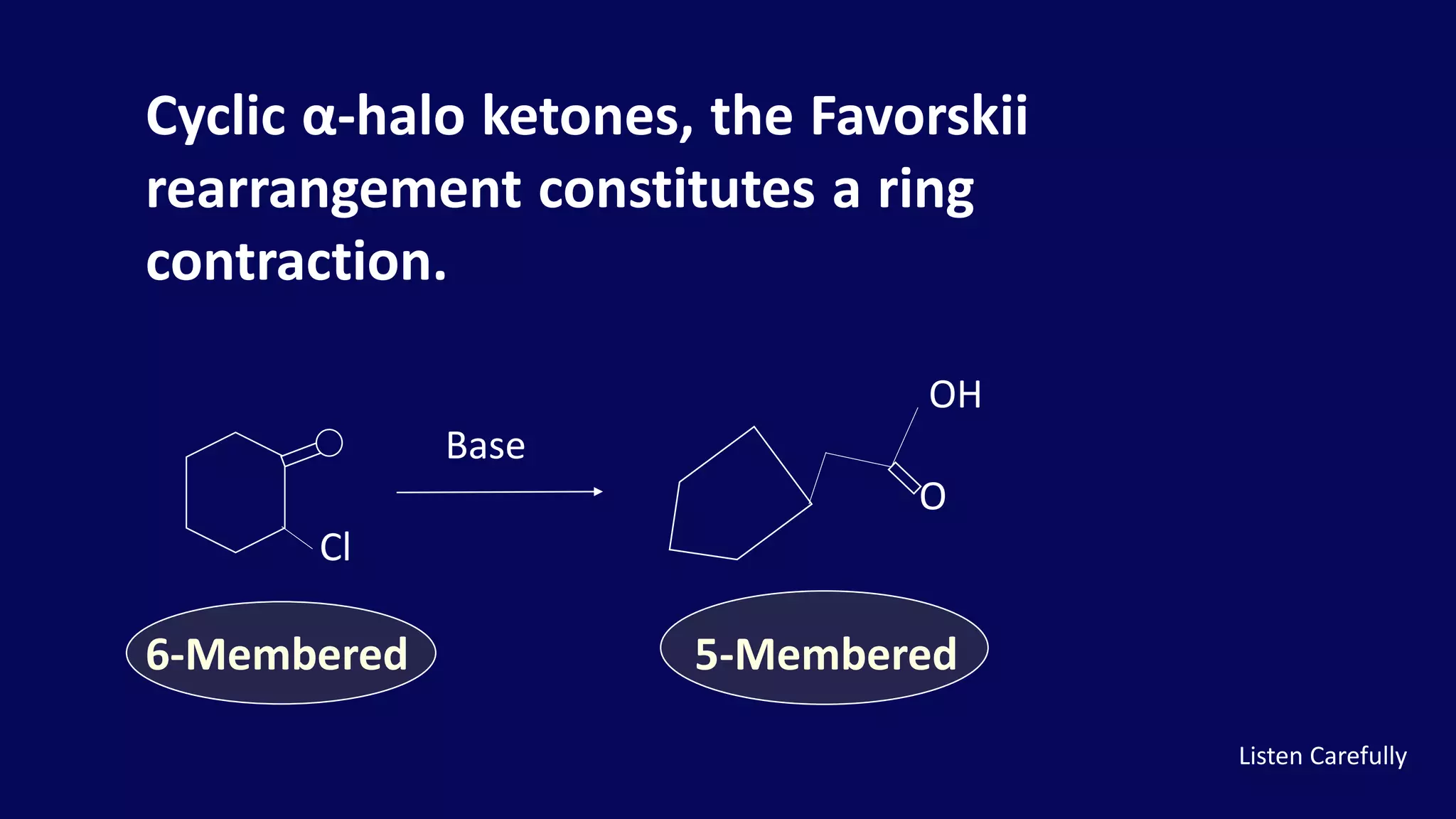
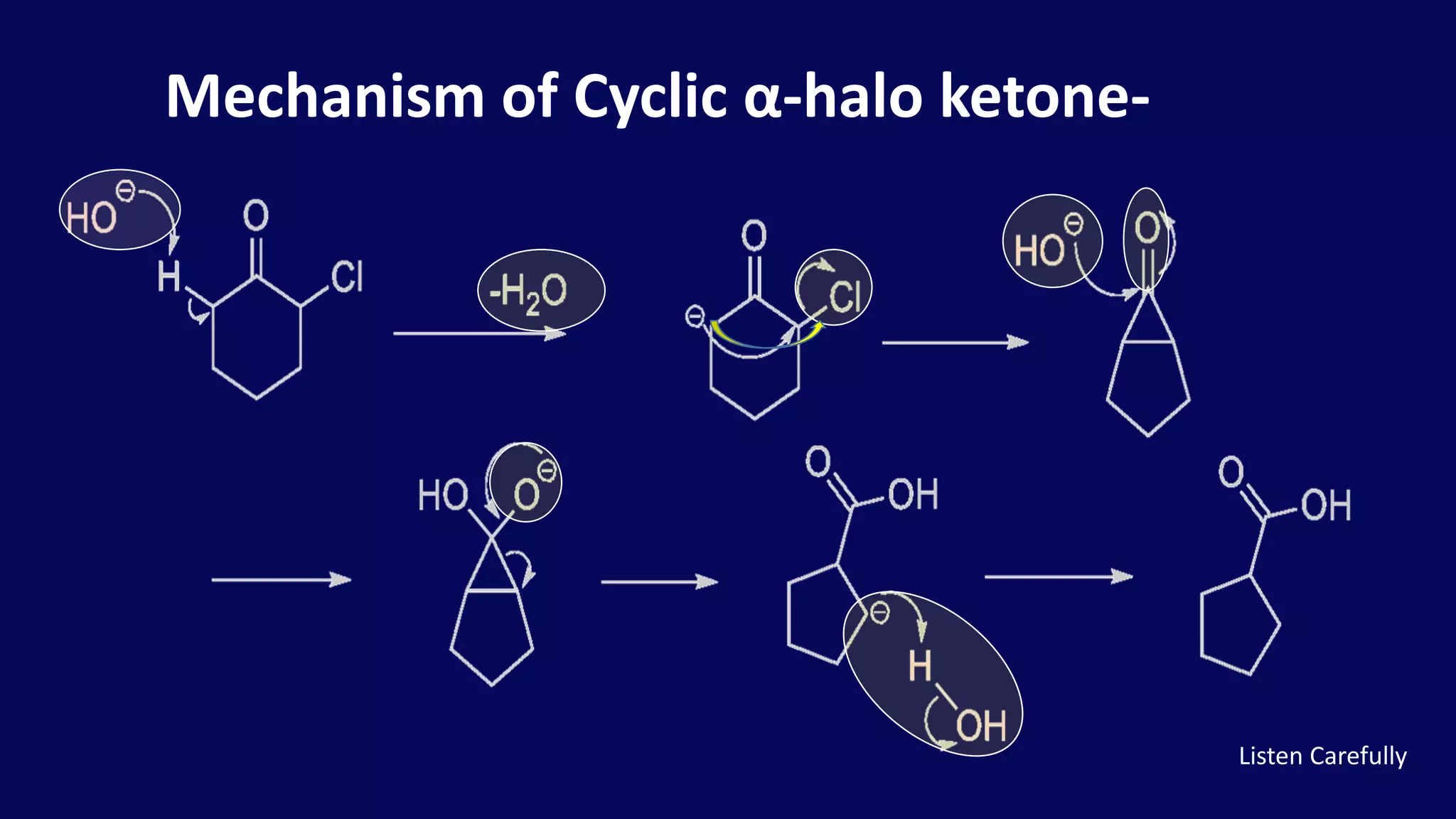
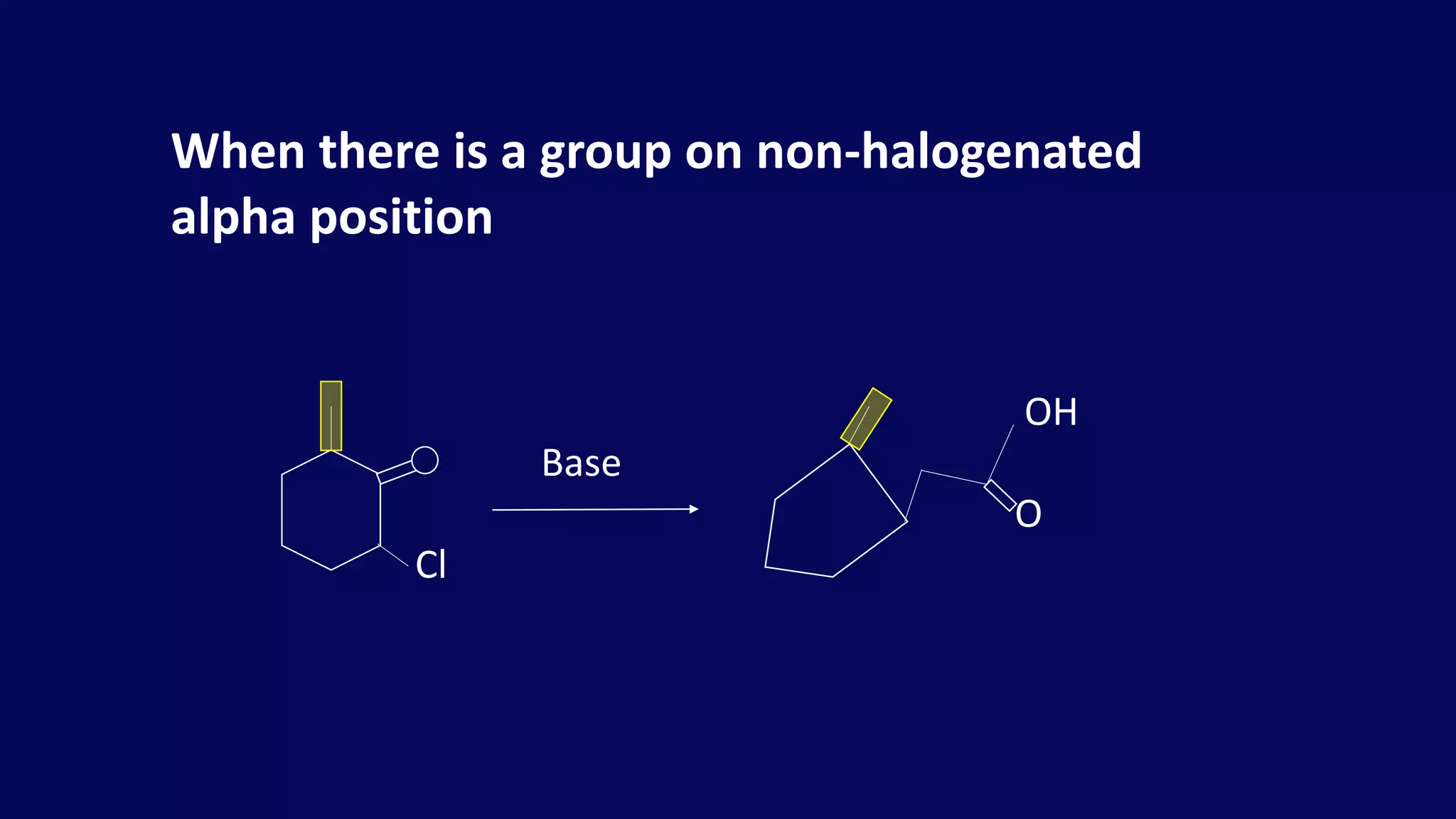
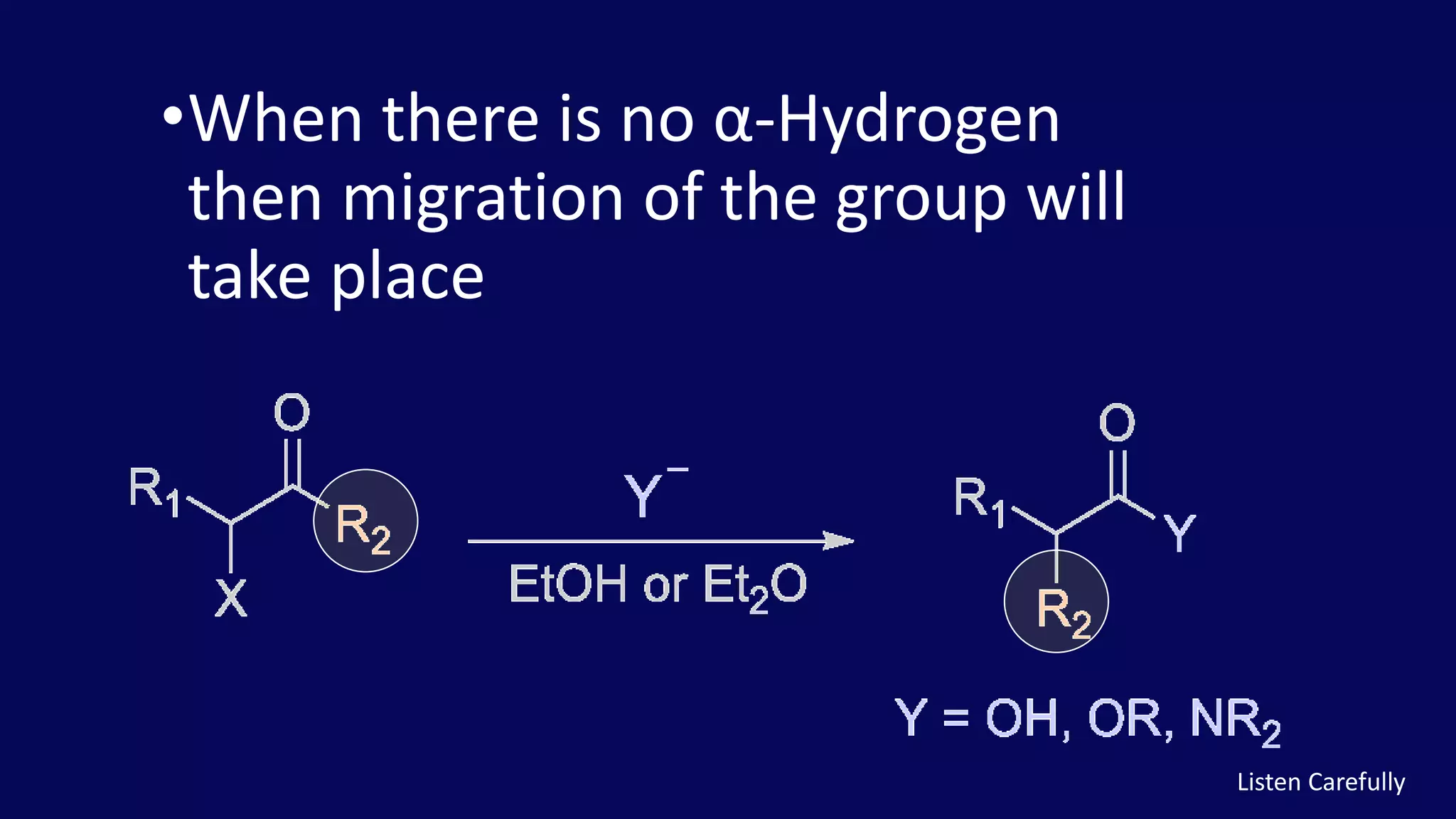
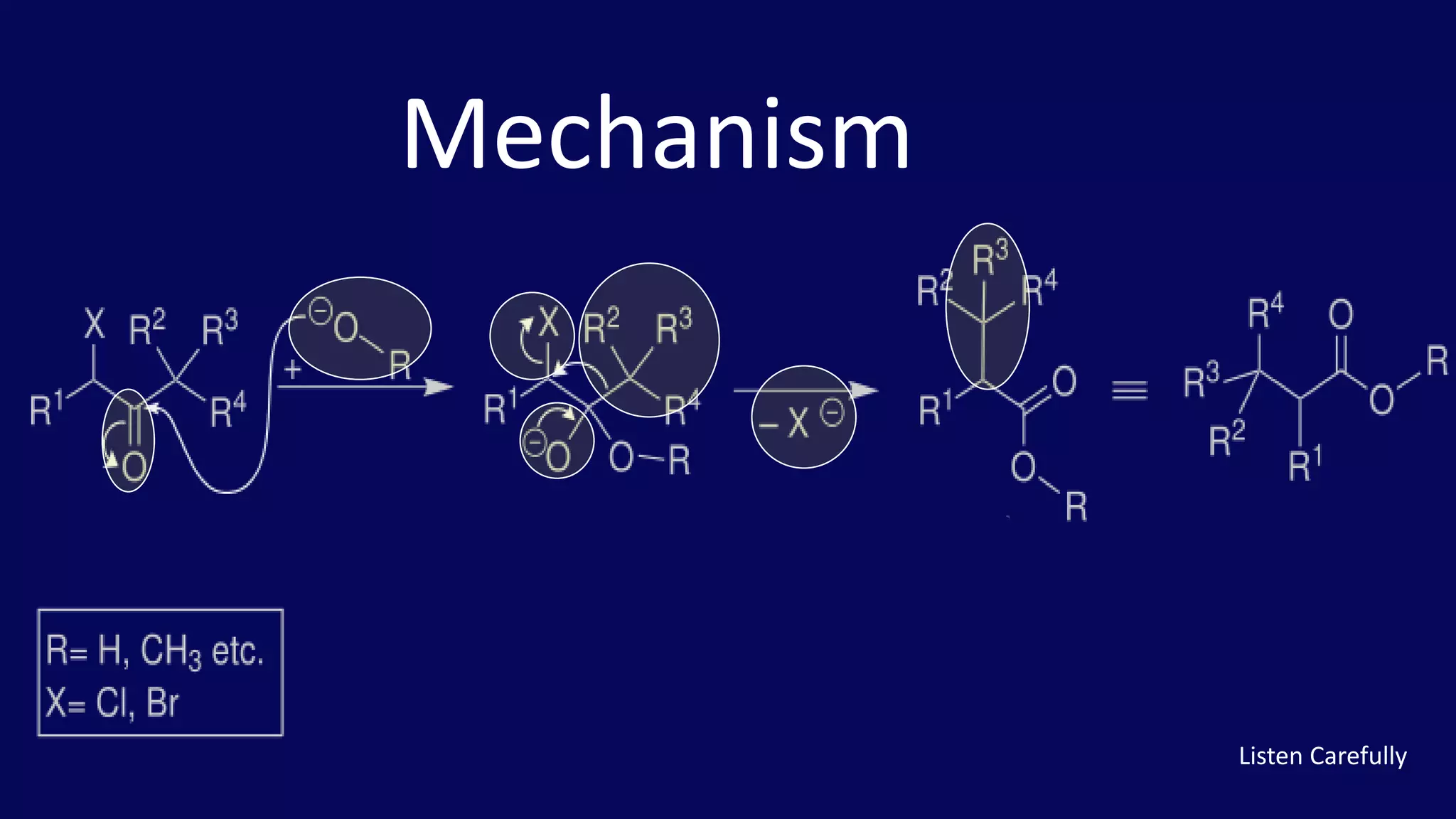
Rearrangement reactions involve the migration of an atom or group within the same molecule. A 1,2-shift is a migration from one atom to an adjacent atom. The Favorskii rearrangement involves the rearrangement of cyclopropanones and α-halo ketones in the presence of a base, forming carboxylic acids or derivatives. For cyclic α-halo ketones, the Favorskii rearrangement causes a ring contraction from a 6-membered to a 5-membered ring.







