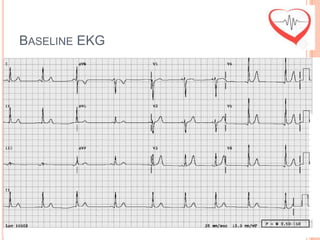
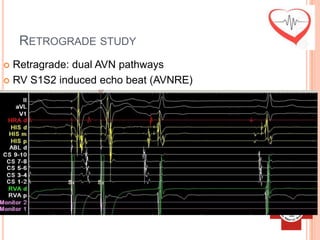
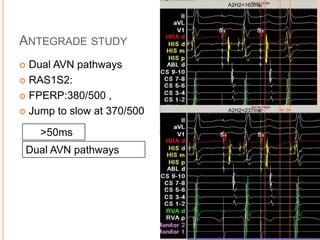
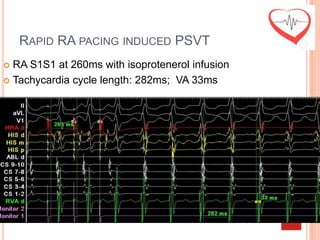
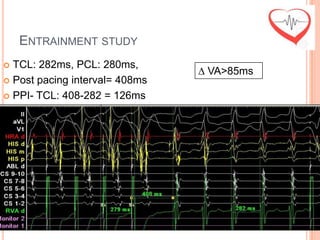
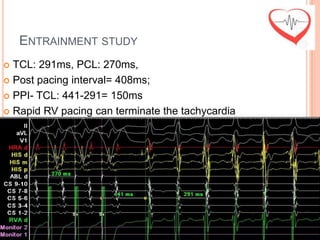
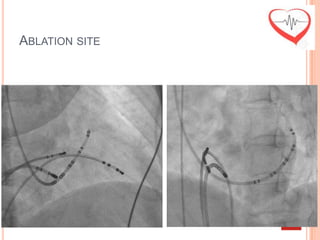
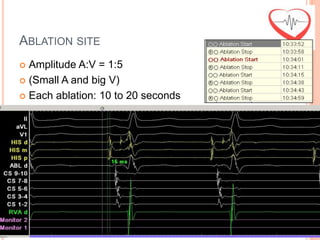
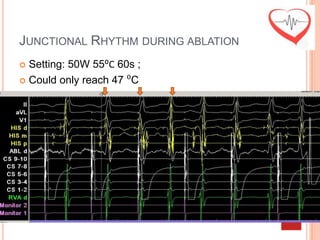
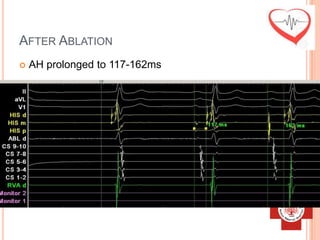
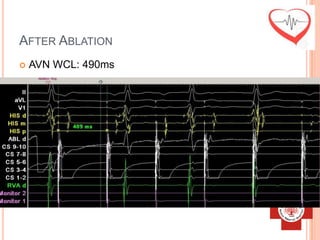
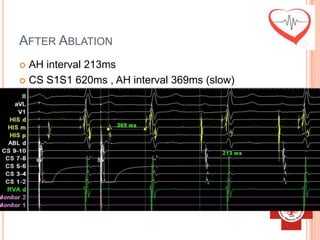
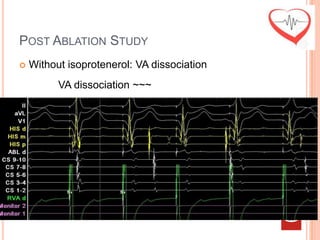
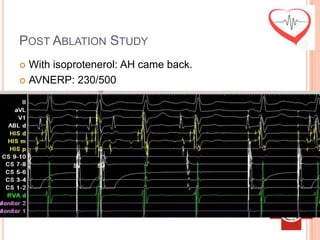
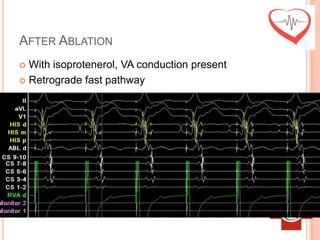
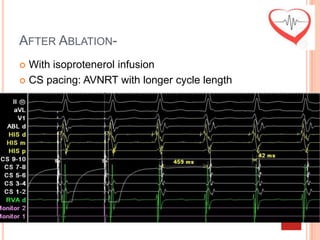
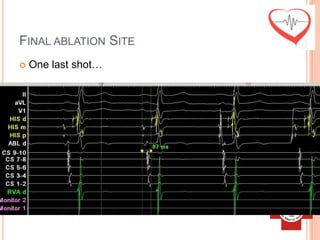
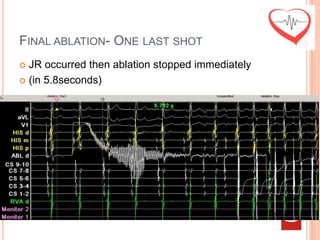
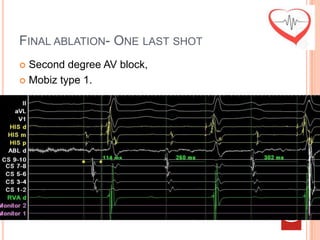
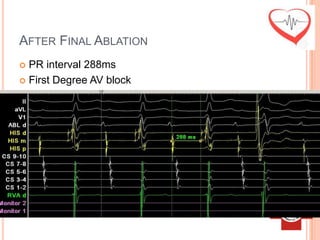
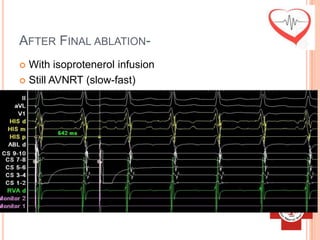
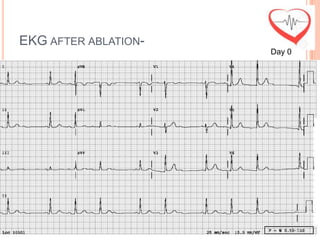
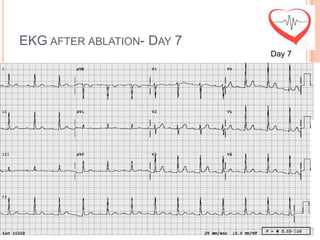
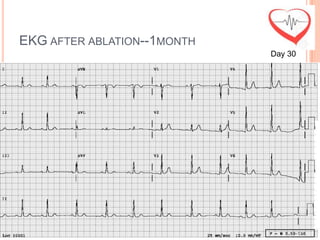
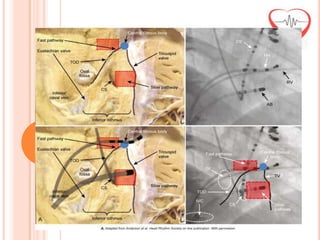
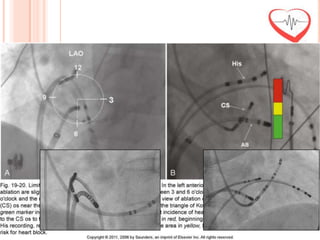
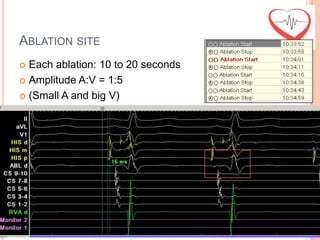
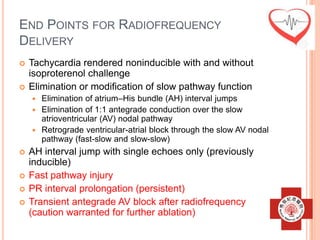
This document presents a case study of a 51-year-old female patient who suffered from chest pain, palpitations, and dizziness. She was previously diagnosed with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia. An electrophysiology study revealed dual atrioventricular nodal pathways. Radiofrequency ablation was performed and initially failed to eliminate the tachycardia. After further ablation attempts, junctional rhythm occurred and ablation was stopped. This resulted in second-degree atrioventricular block. Follow-up EKGs showed first-degree AV block initially and normal sinus rhythm later. The document discusses endpoints for successful radiofrequency ablation and techniques for preventing AV block.



![PREVENTING ATRIOVENTRICULAR BLOCK
Method Description Comment
Ablation sites below triangle of Koch Inferior to level of CS roof Standard practice
Discontinue RF for loss of 1:1 retrograde
Monitor retrograde junctional conduction Standard practice
conduction
Discontinue RF for junctional rhythm <
Monitor for rapid junctional rhythm[87] Not prospectively tested
350msec
Difference timing between AEGM His and
Δ A-A timing His and ablation recordings[112] Not prospectively tested
AEGM ablation site > 20msec
Identify site on septum producing shortest
Pace mapping triangle of Koch[113] Not prospectively tested
stimulus to His time and avoid ablation there
Pace atrium faster than junctional rate to
Overdrive atrial pacing Not prospectively tested
monitor antegrade conduction
Start at 5W and increase power by 5W
Gradual power titration[114] every 5sec until junctional rhythm, then Not prospectively tested
increase power by 10W for total RF 120sec
Cryoablation 6 or 4mm tip](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/0415psvt-120430024018-phpapp01/85/Case-Presentataion-psvt-32-320.jpg)
