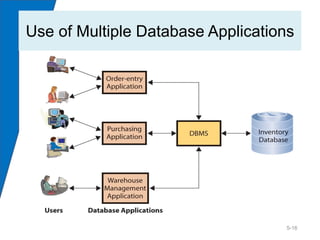
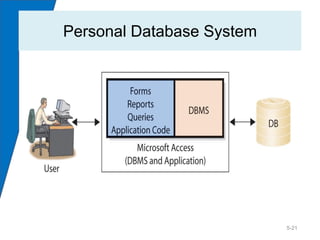
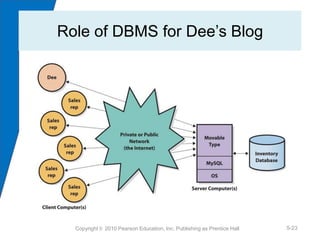
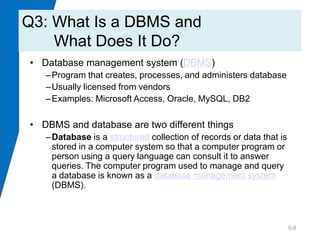
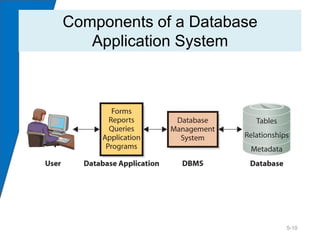
This chapter discusses databases and database management systems (DBMS). It explains that a database is a structured collection of records or data that is stored so it can be easily accessed, managed, and updated. A DBMS is a program that creates and maintains databases. The chapter compares enterprise and personal DBMS and describes how forms, reports, queries and other applications interface with databases. It also provides an example of how this information could help Dee explain her need for a database to her network administrators.





![Processing the Database
• Four DBMS operations
1. Read data
2. Insert data
3. Modify data
4. Delete data
• Structured Query Language
INSERT INTO Student
([Student Number], [Student Name], HW1, HW2,
MidTerm)
VALUES
(1000, ‘Franklin, Benjamin’, 90, 95, 100)
5-13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/casemisch05-120409010642-phpapp02/85/Case-mis-ch05-13-320.jpg)