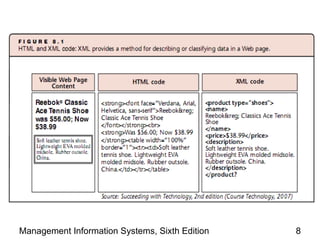
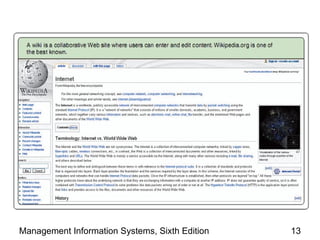
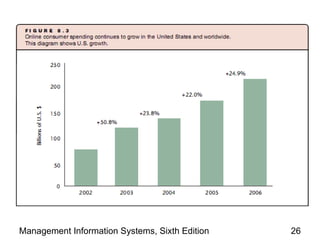
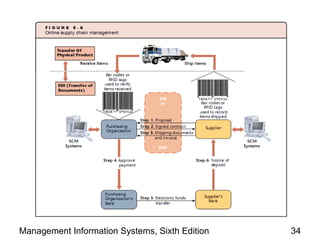
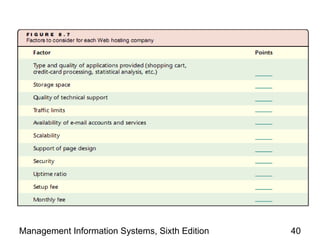
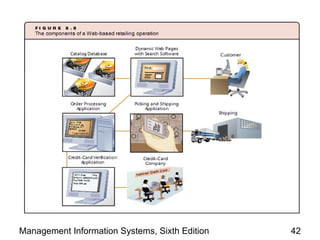
The document discusses how the web and internet technologies are changing business operations. It covers topics like HTTP, HTML, XML, blogs, wikis, cookies and how they enable web technologies. It also compares options for web servers and hosting. Different models of business-to-business and business-to-consumer practices on the web are explained. The relationship between web technologies and supply chain management is discussed. Examples of features successful business websites offer and considerations for online security are provided.
[/SUMMARY]