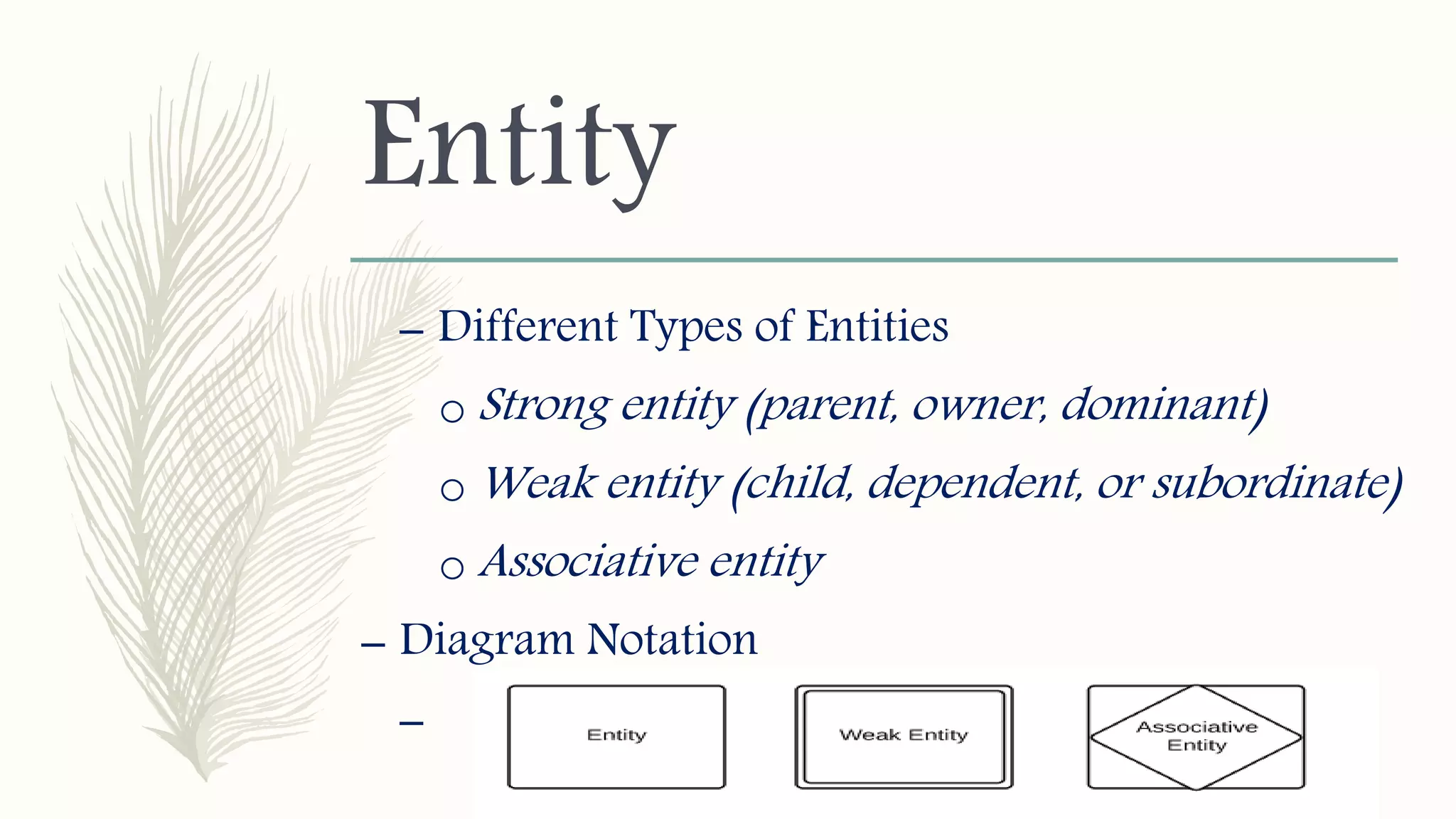
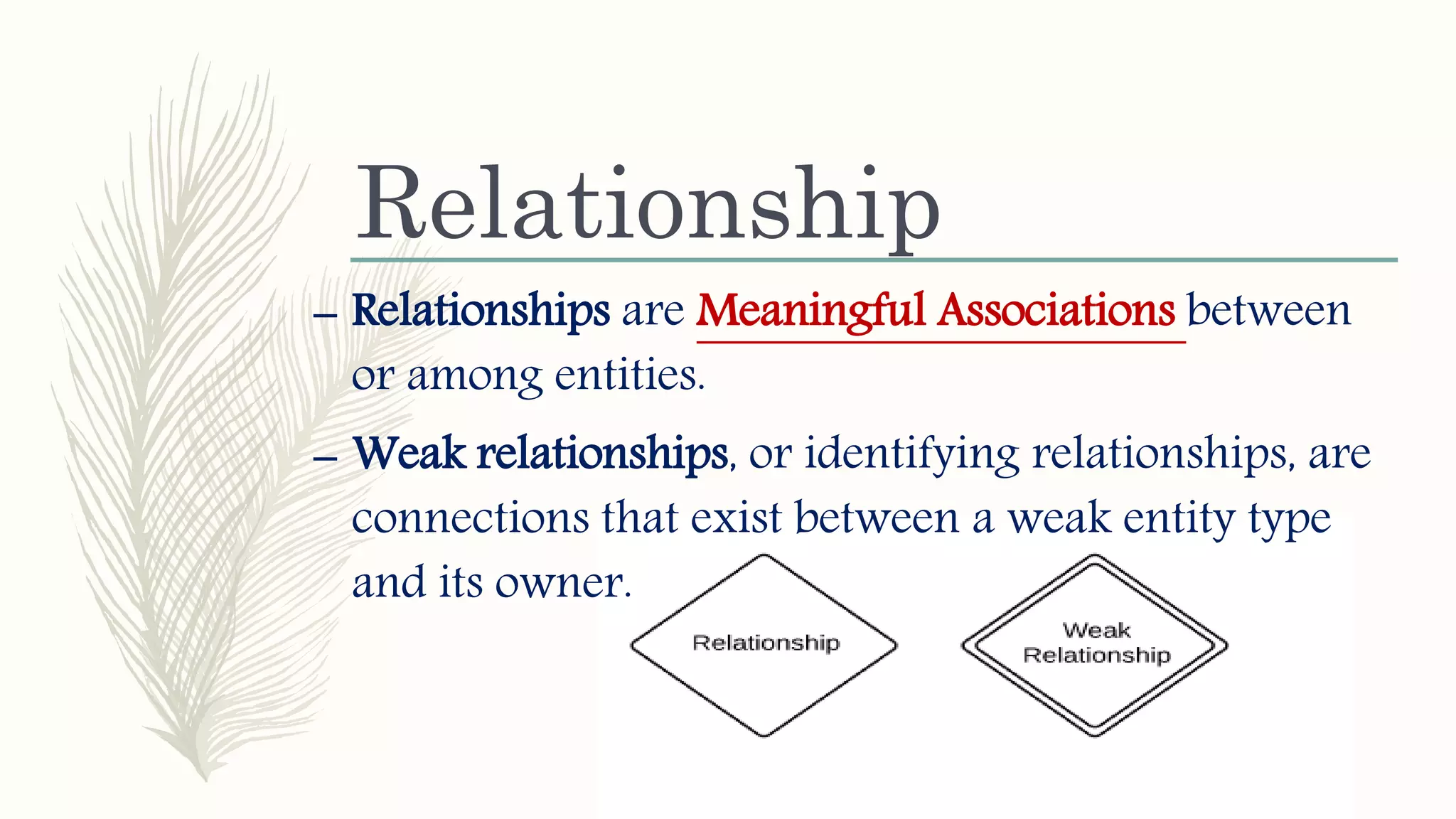
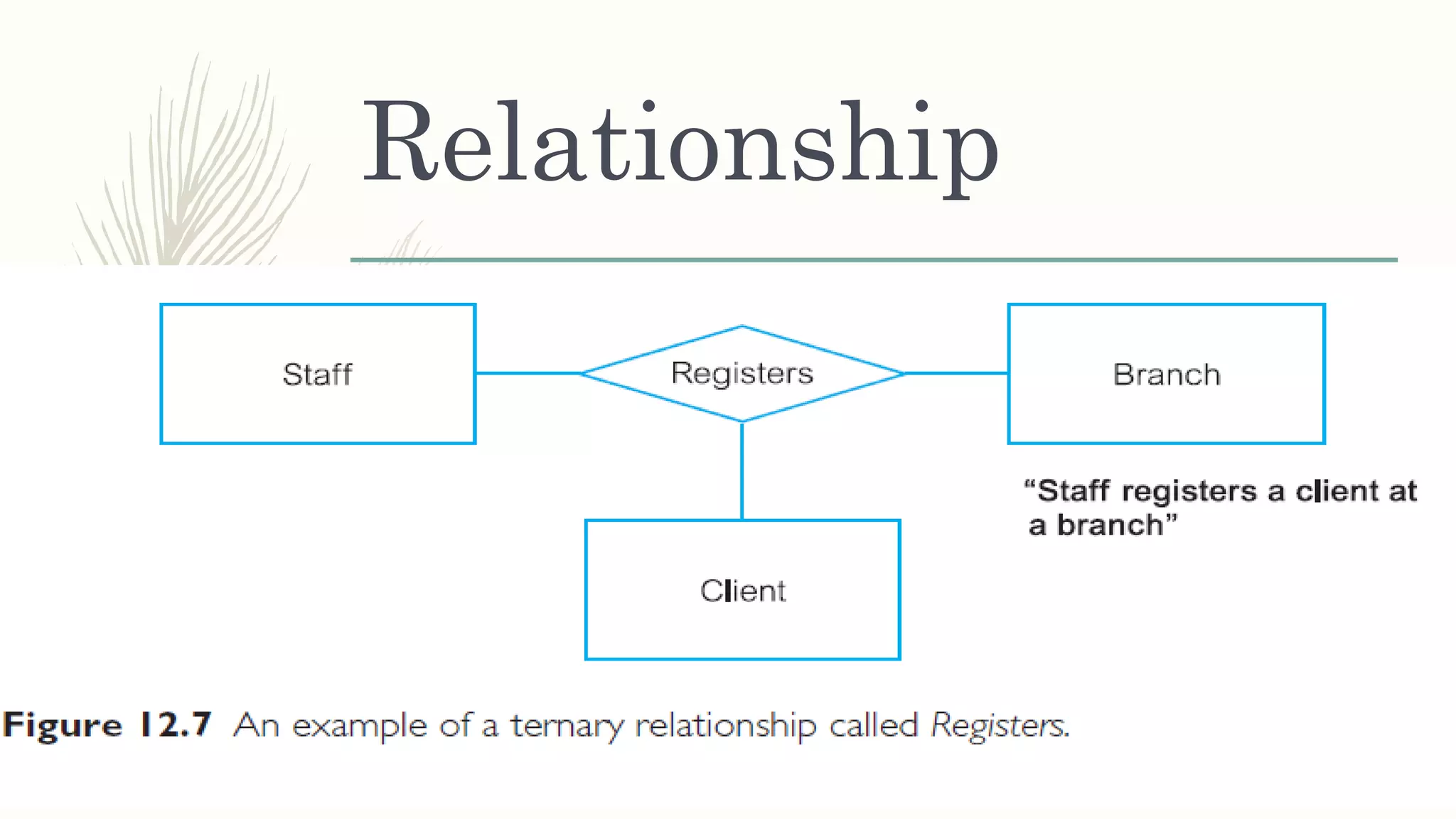
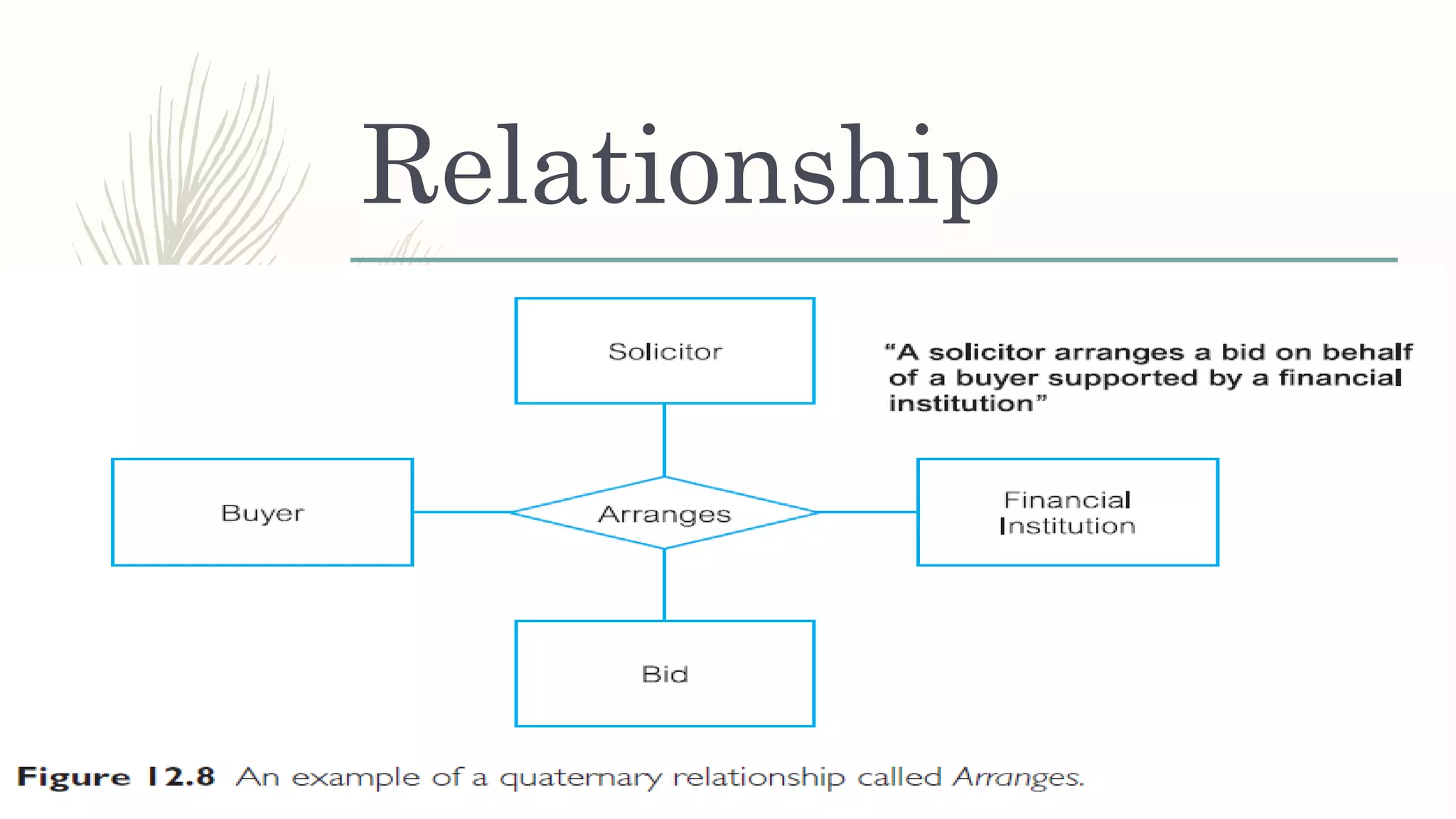
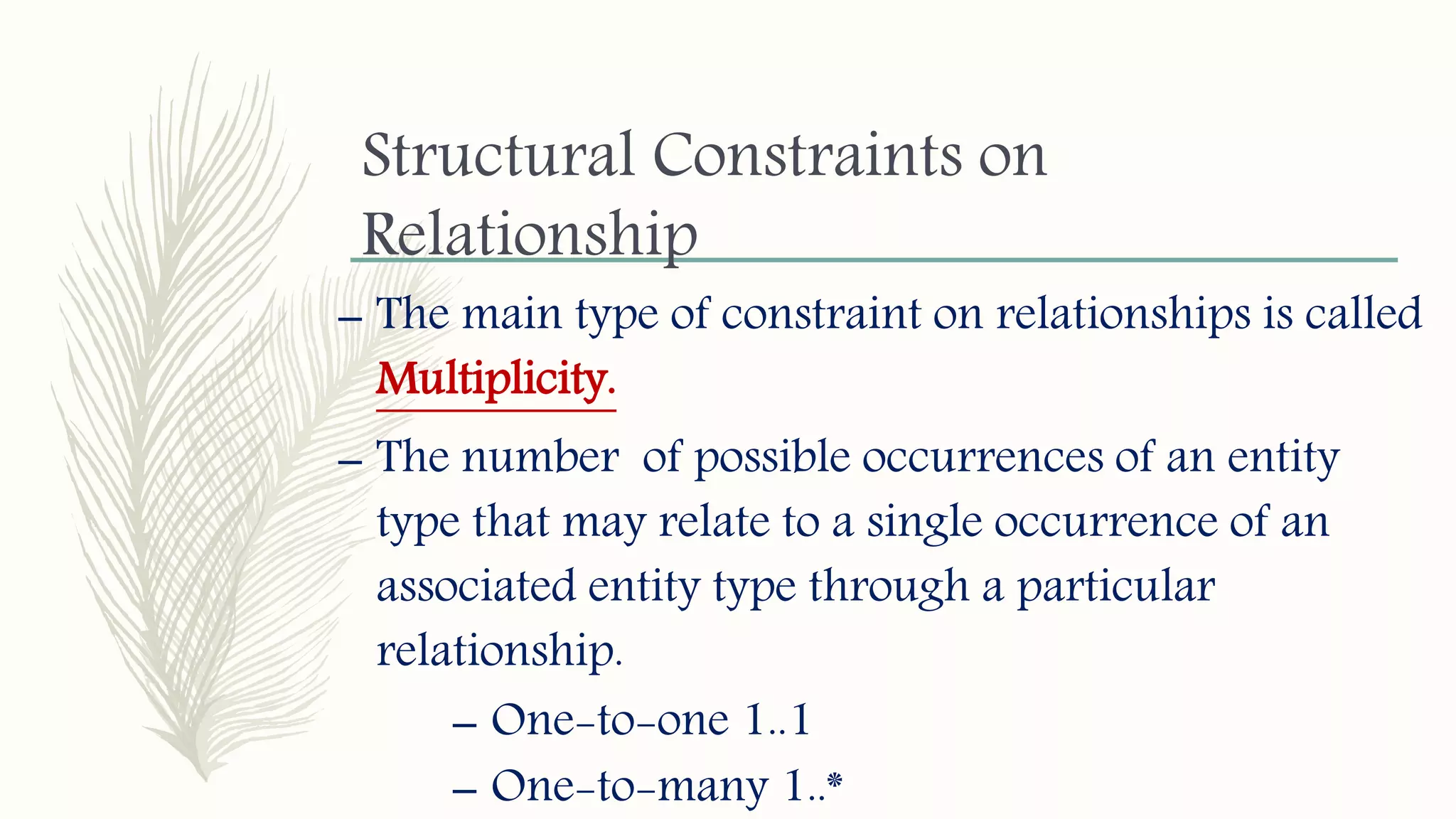
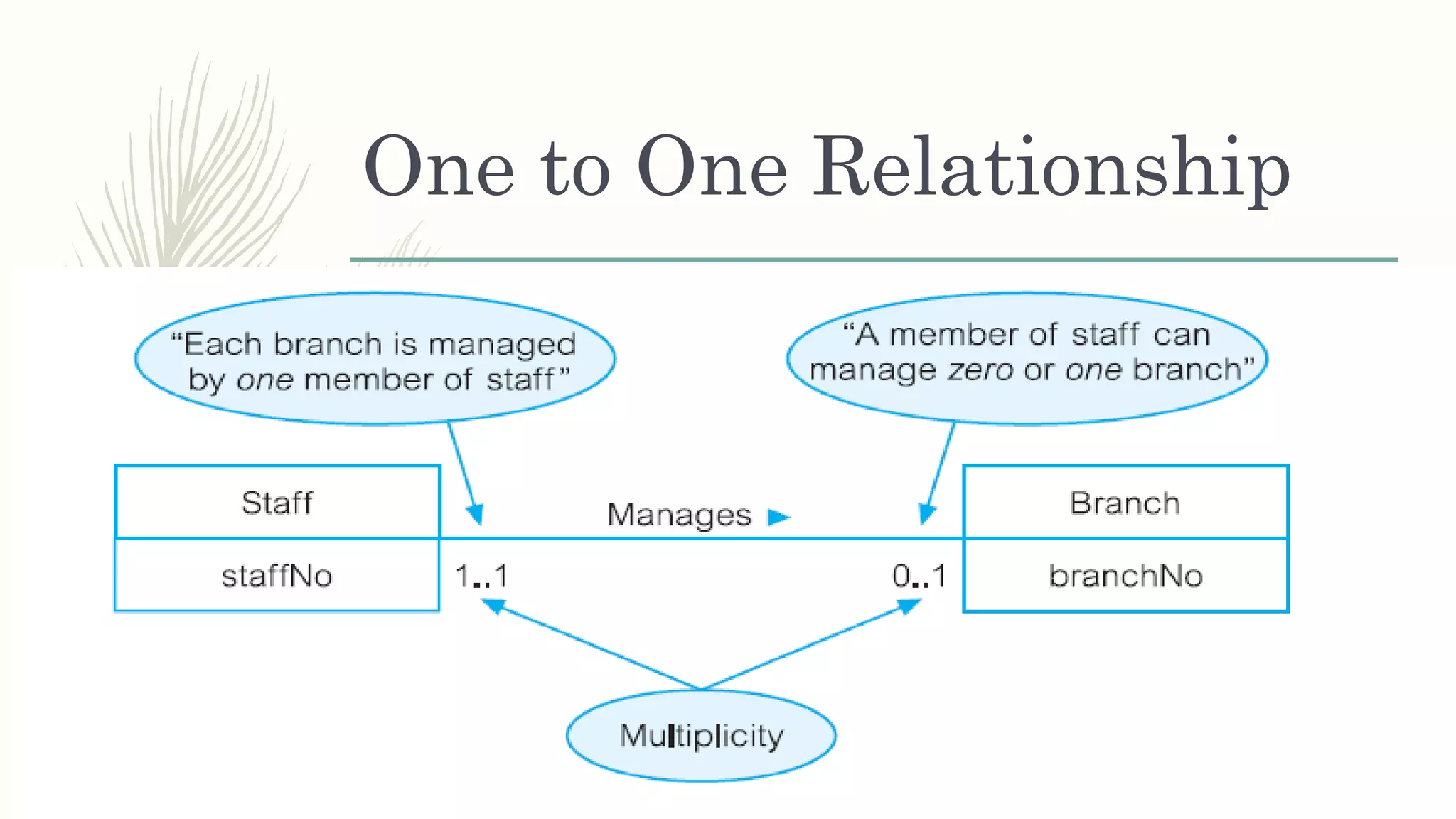
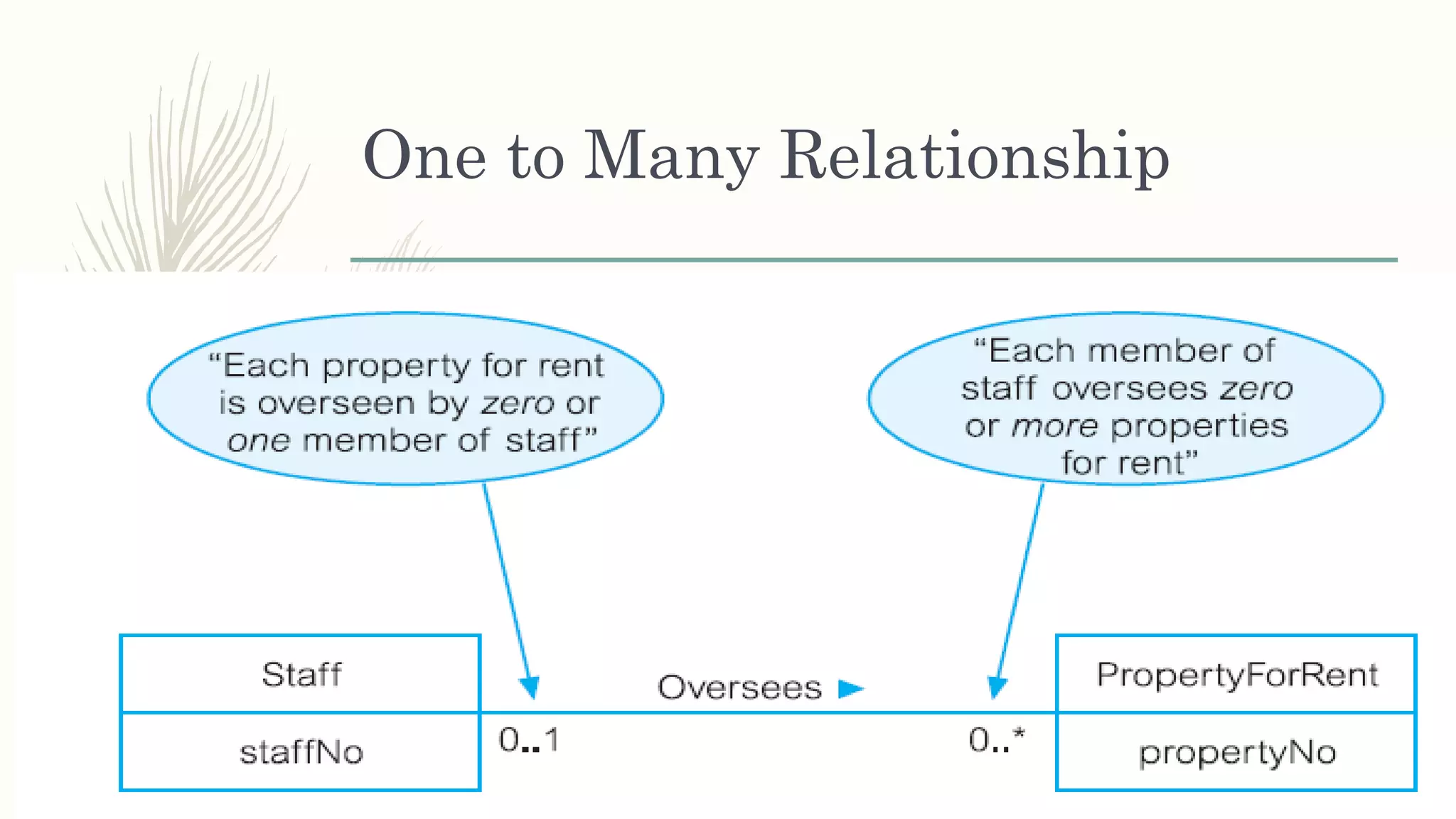
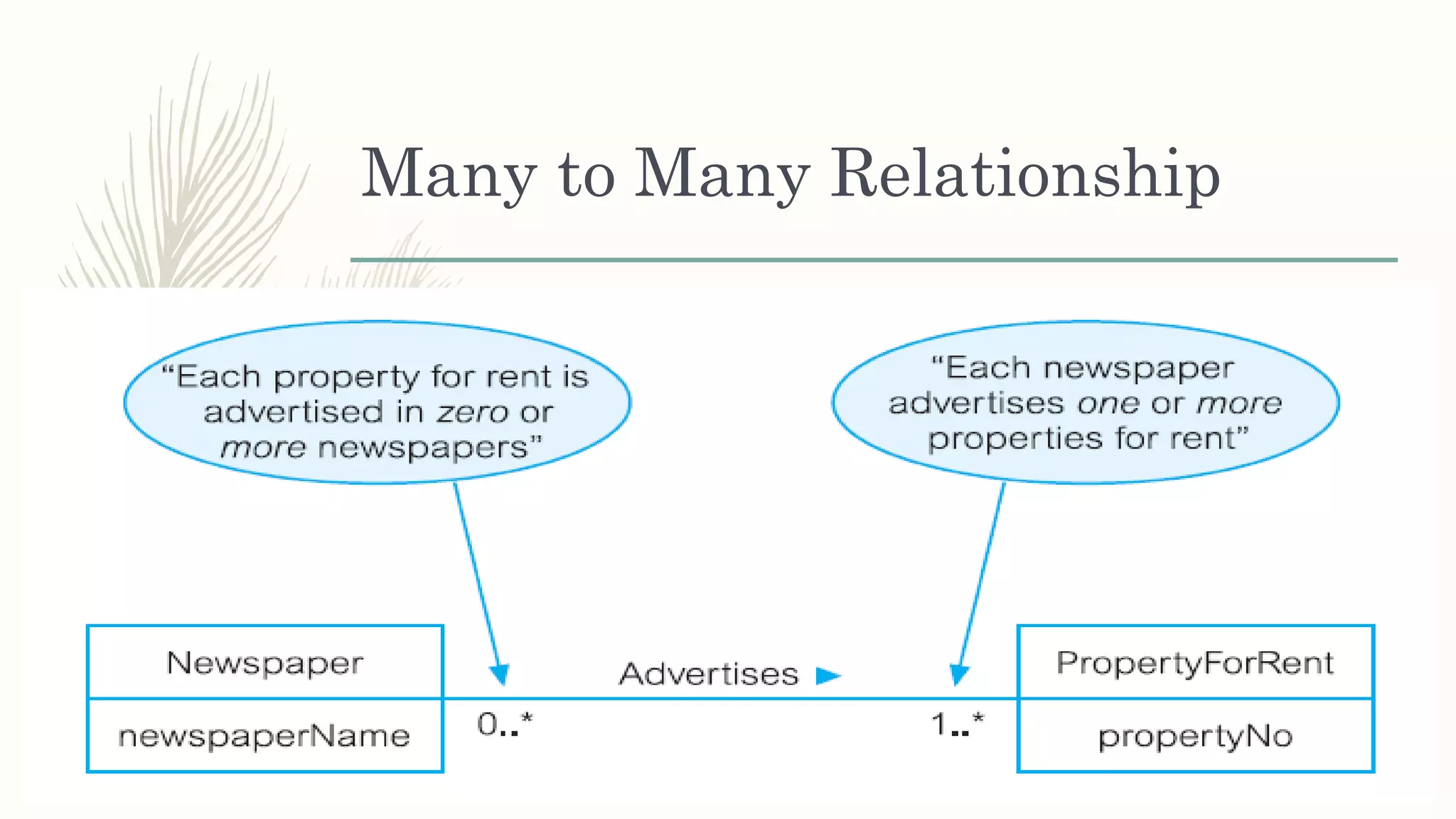
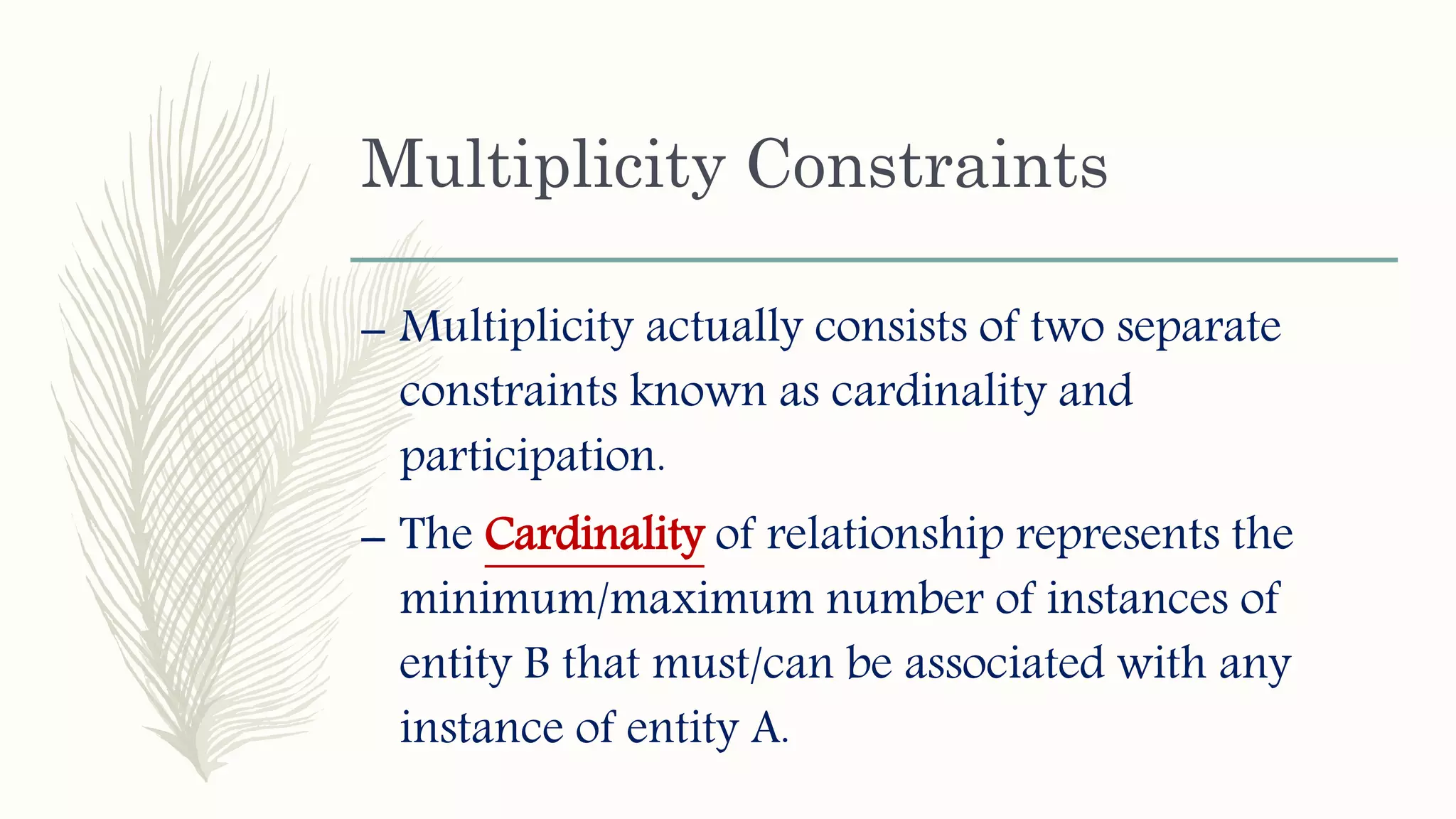
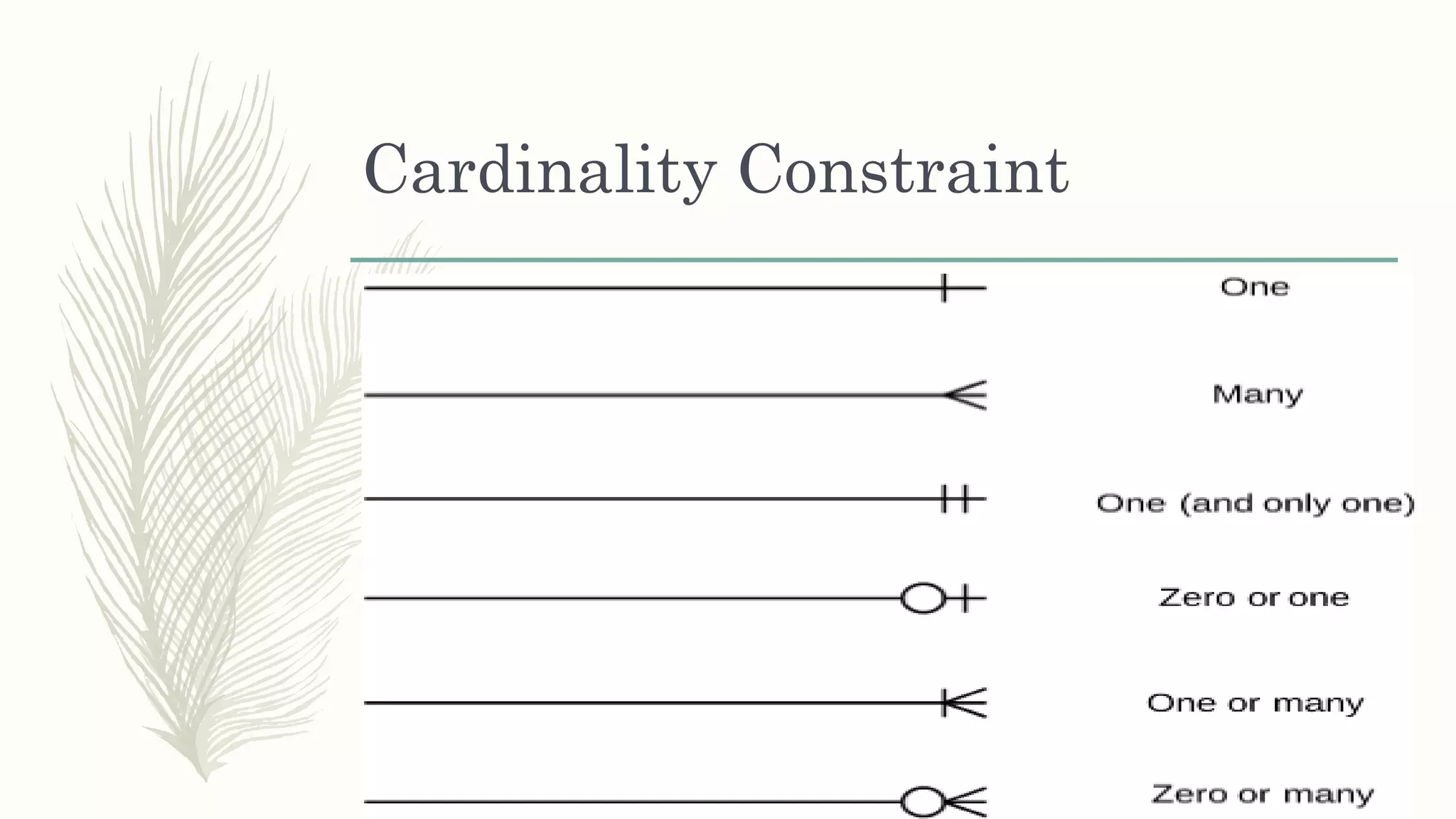
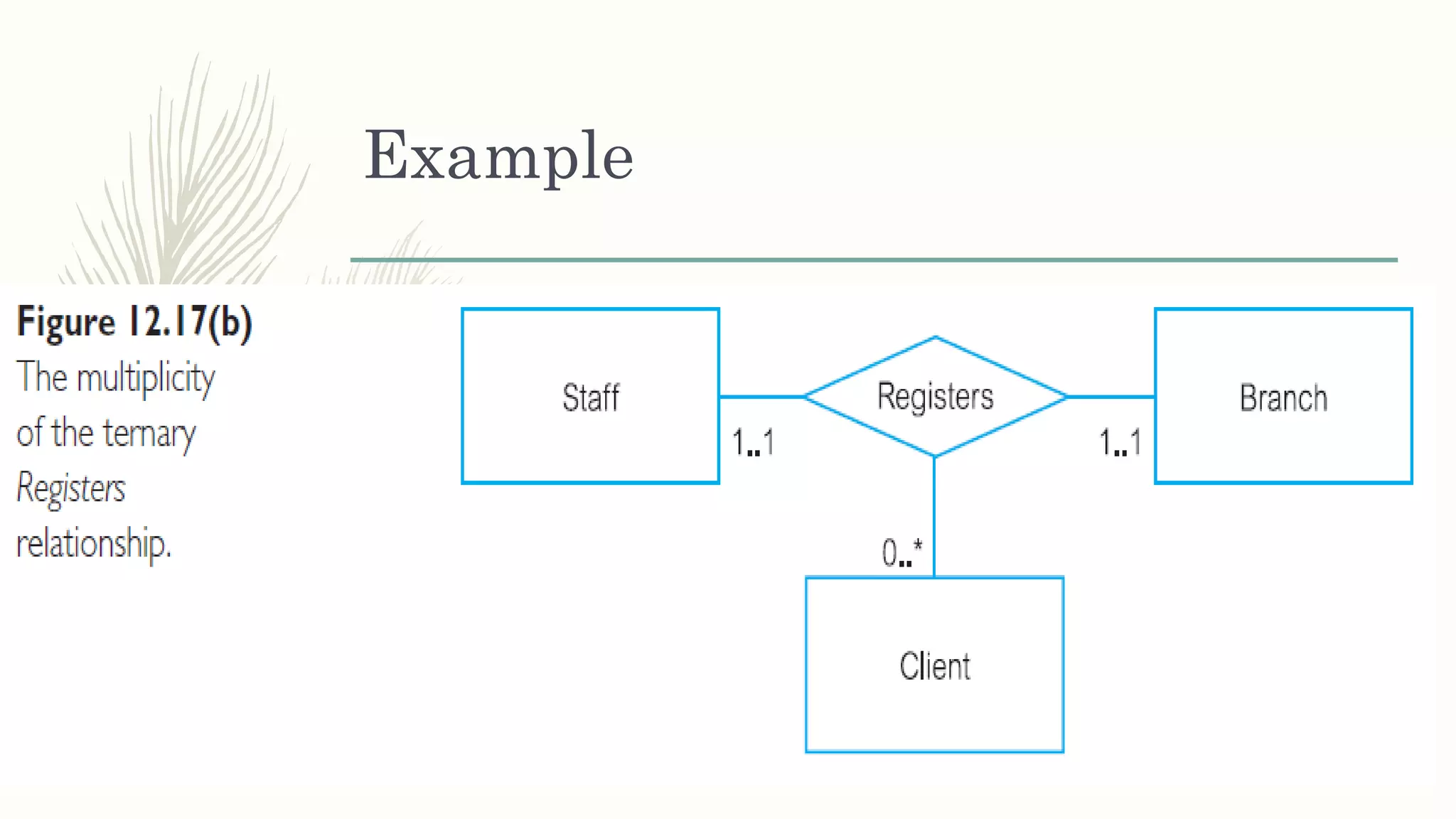
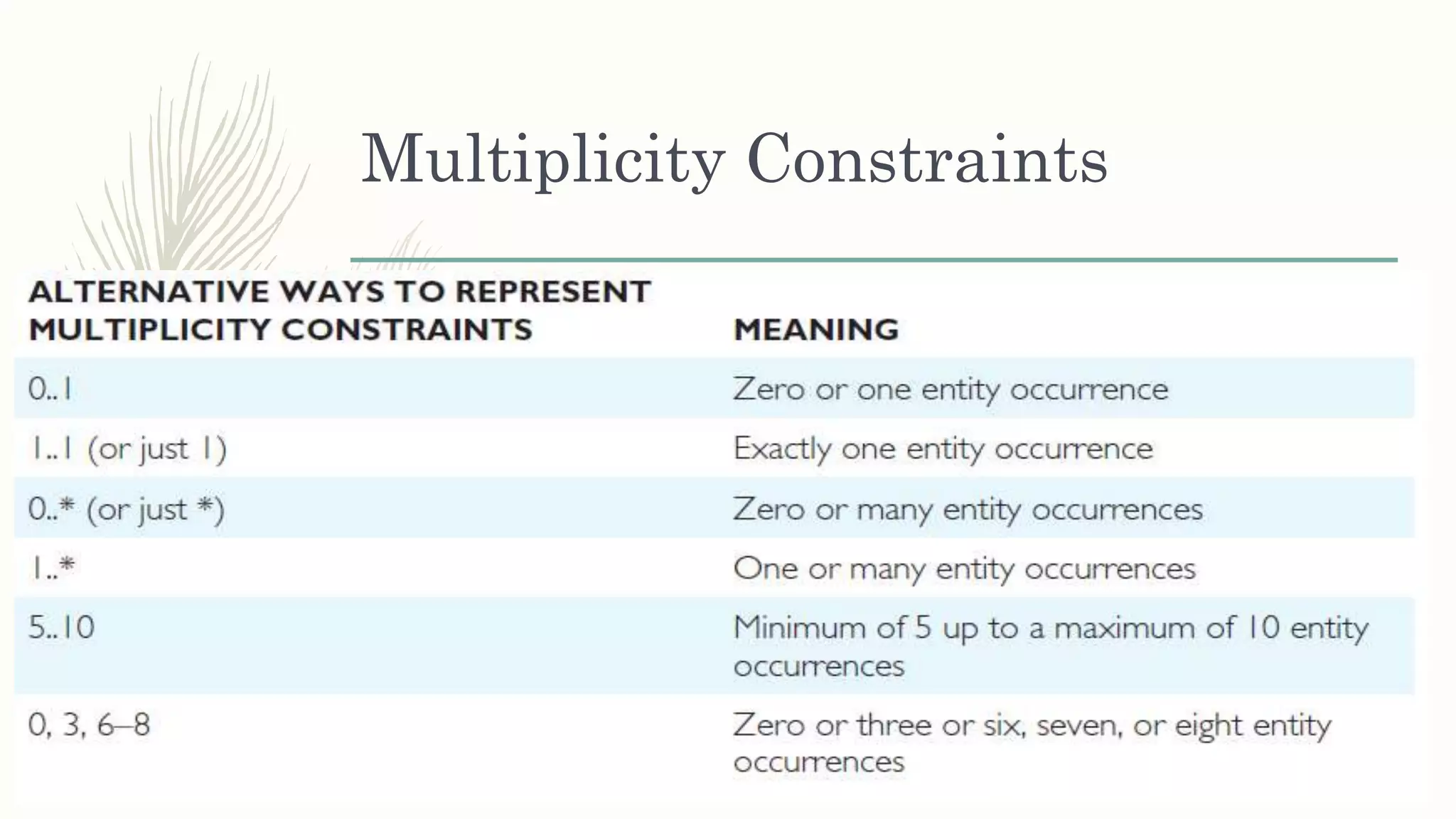
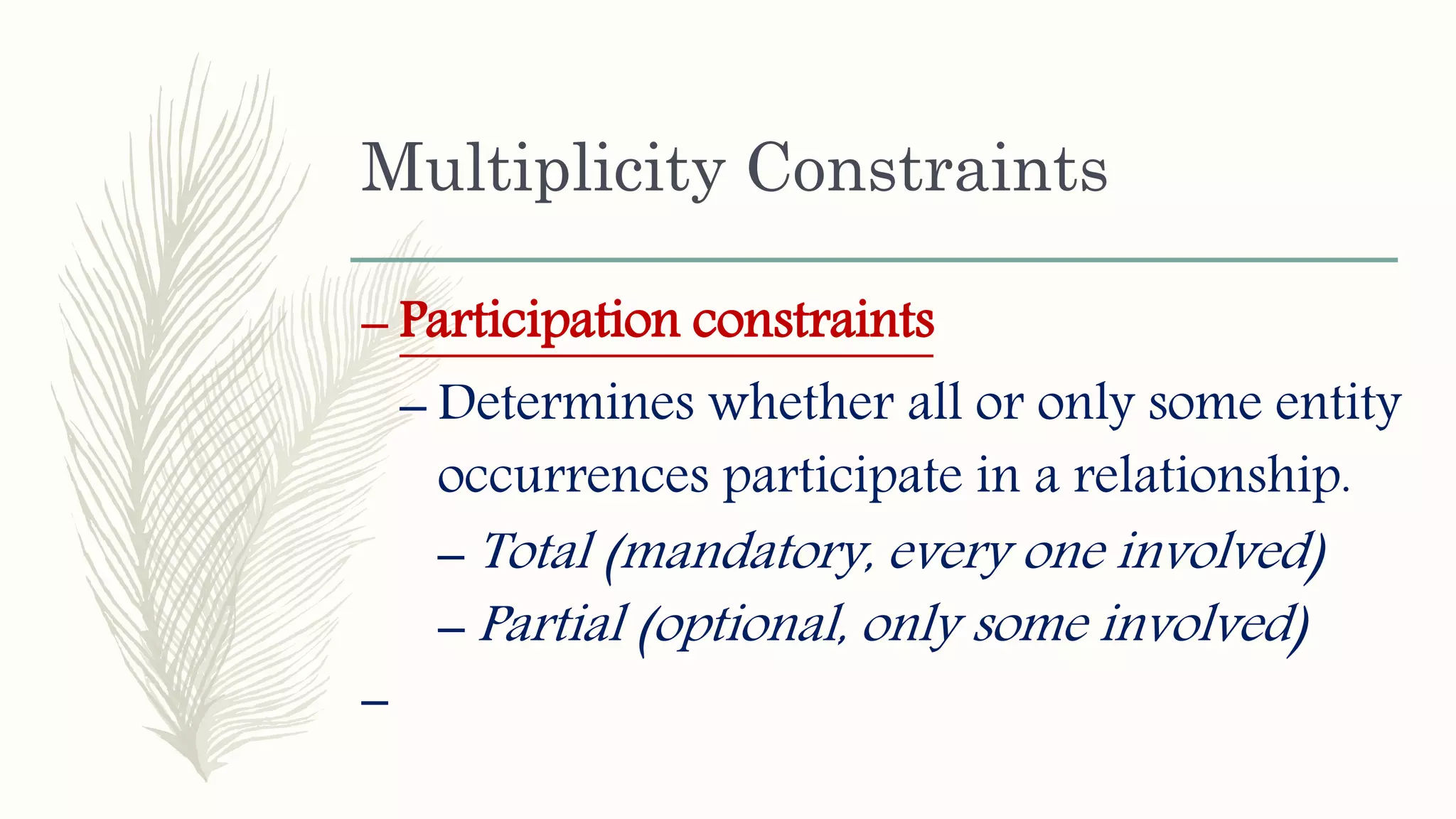
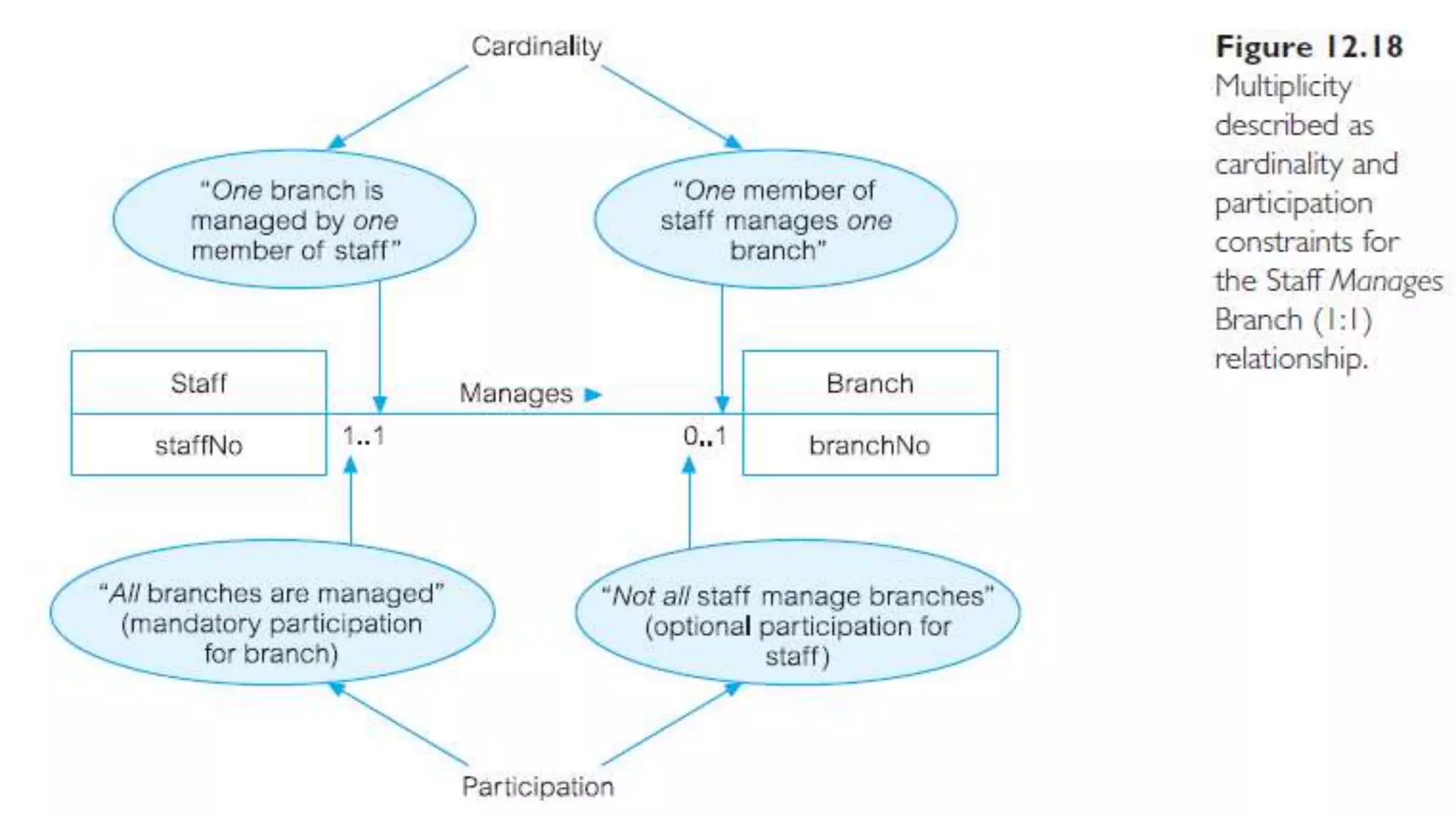
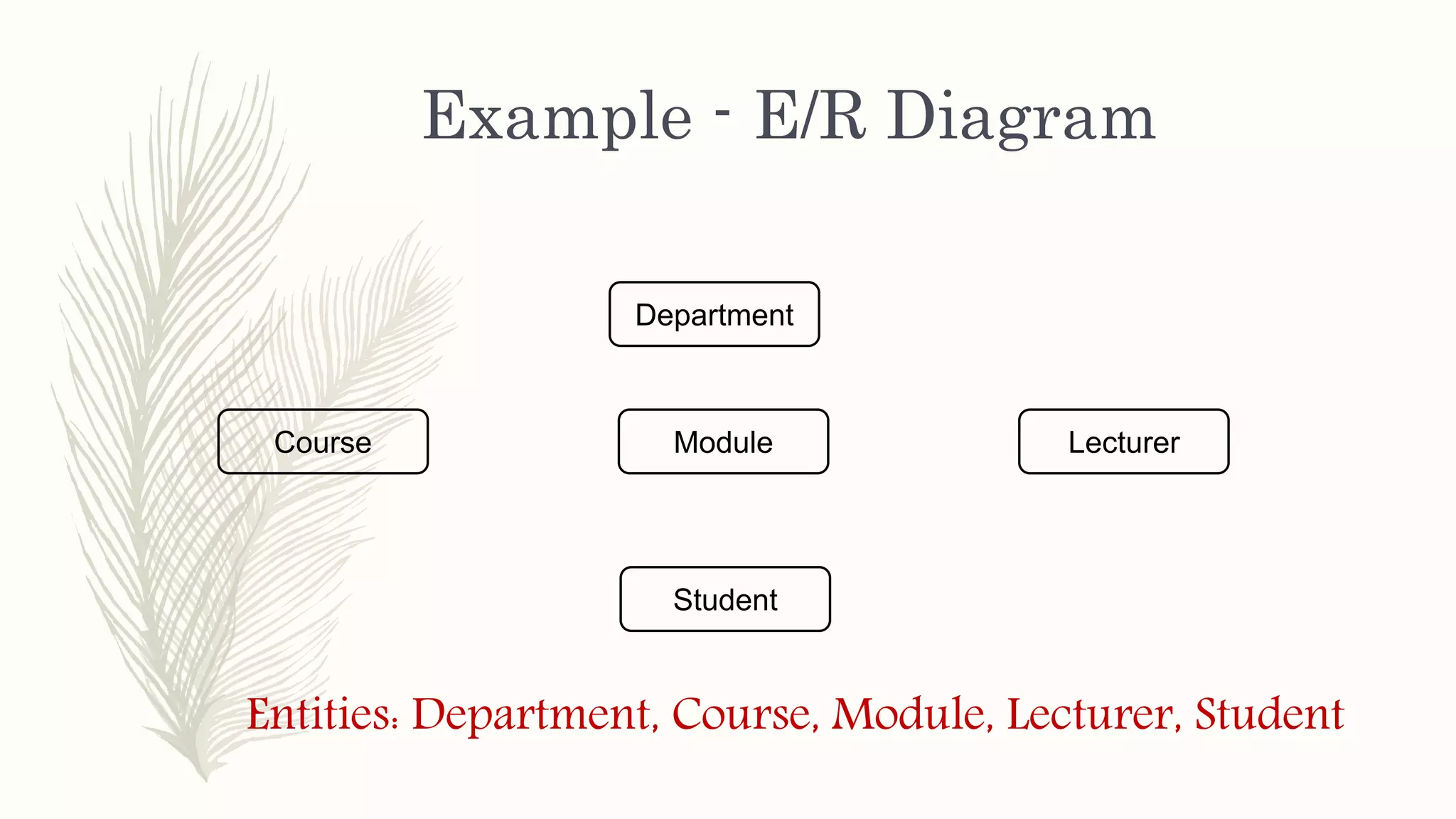
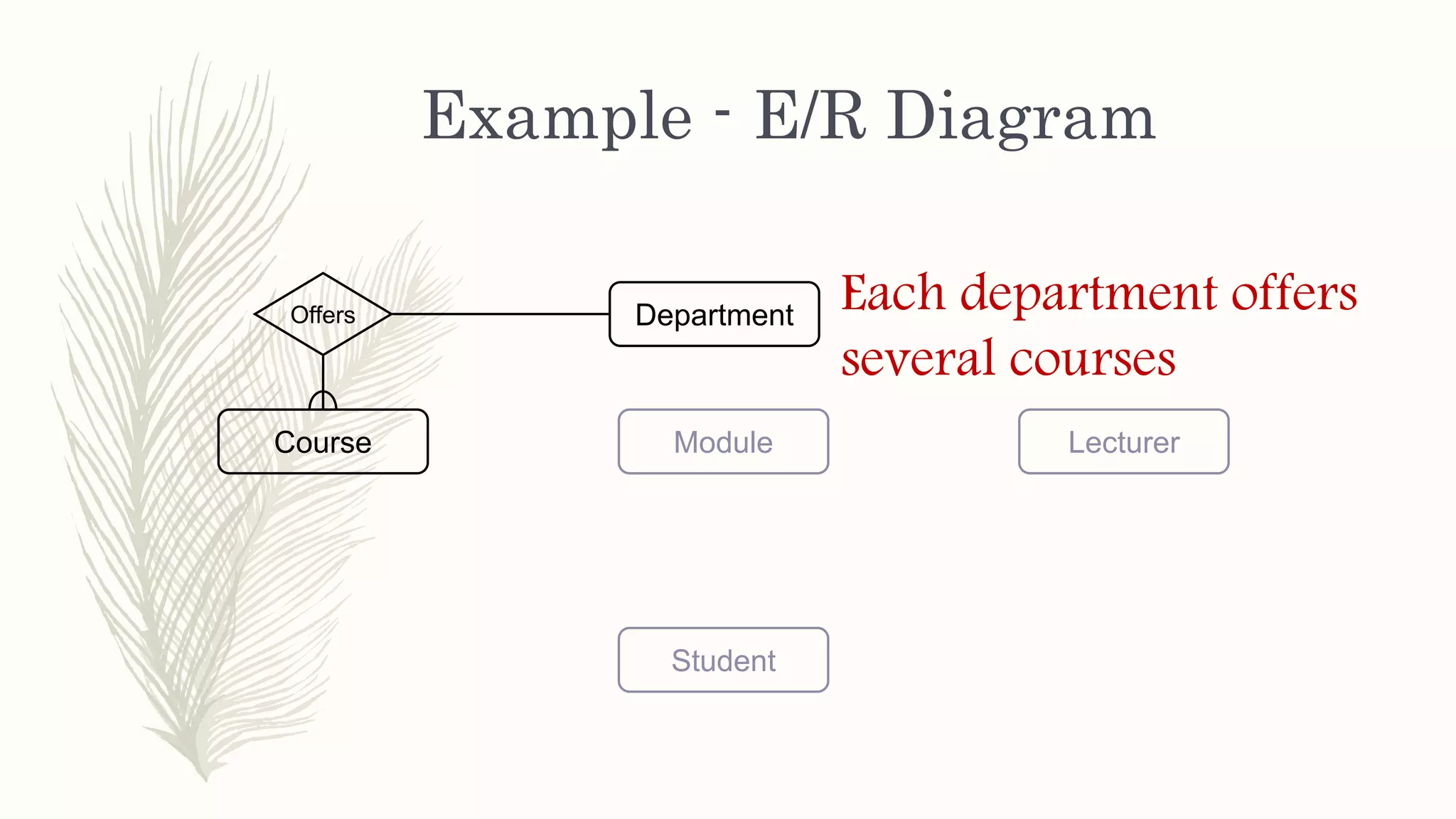
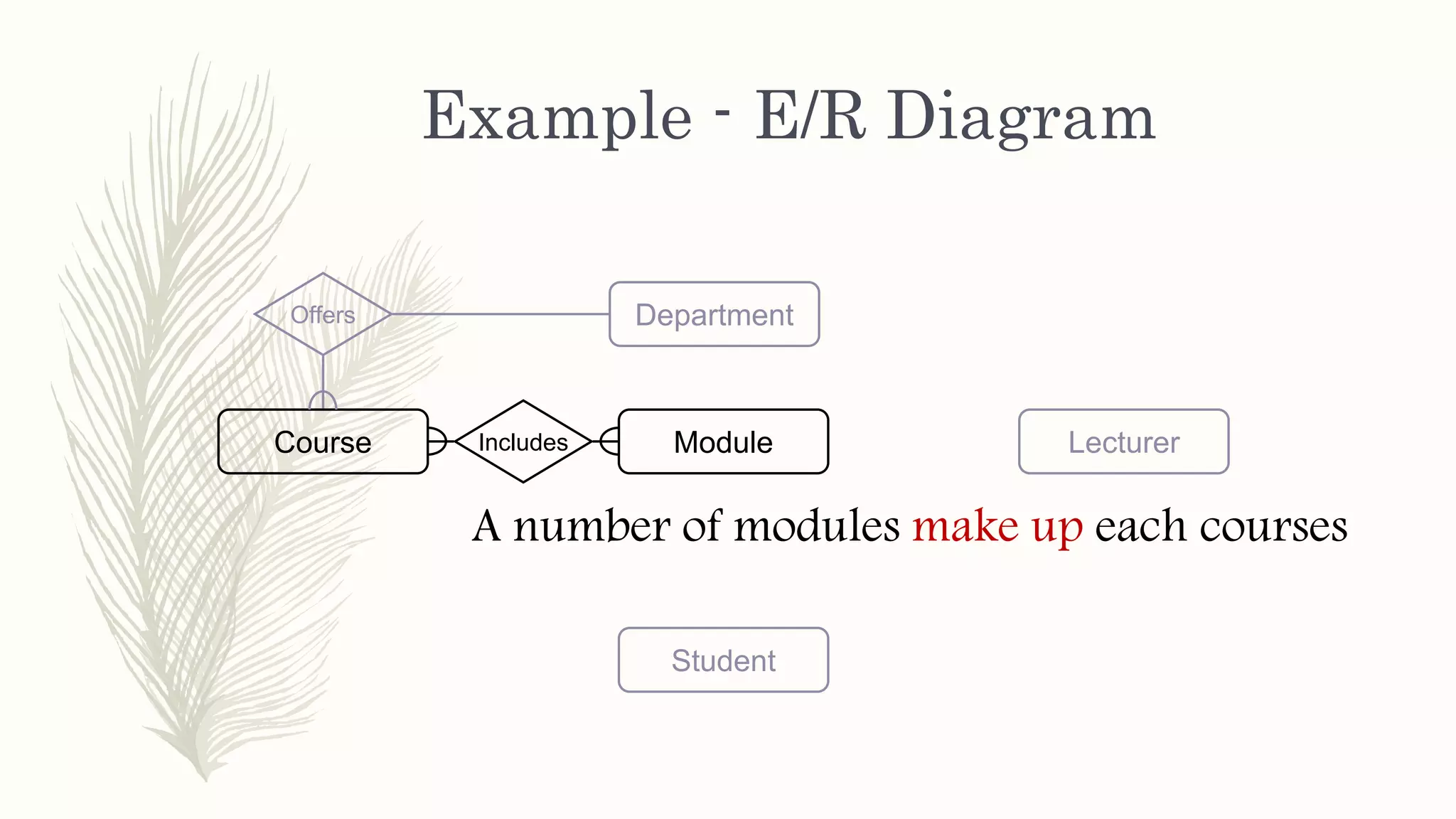
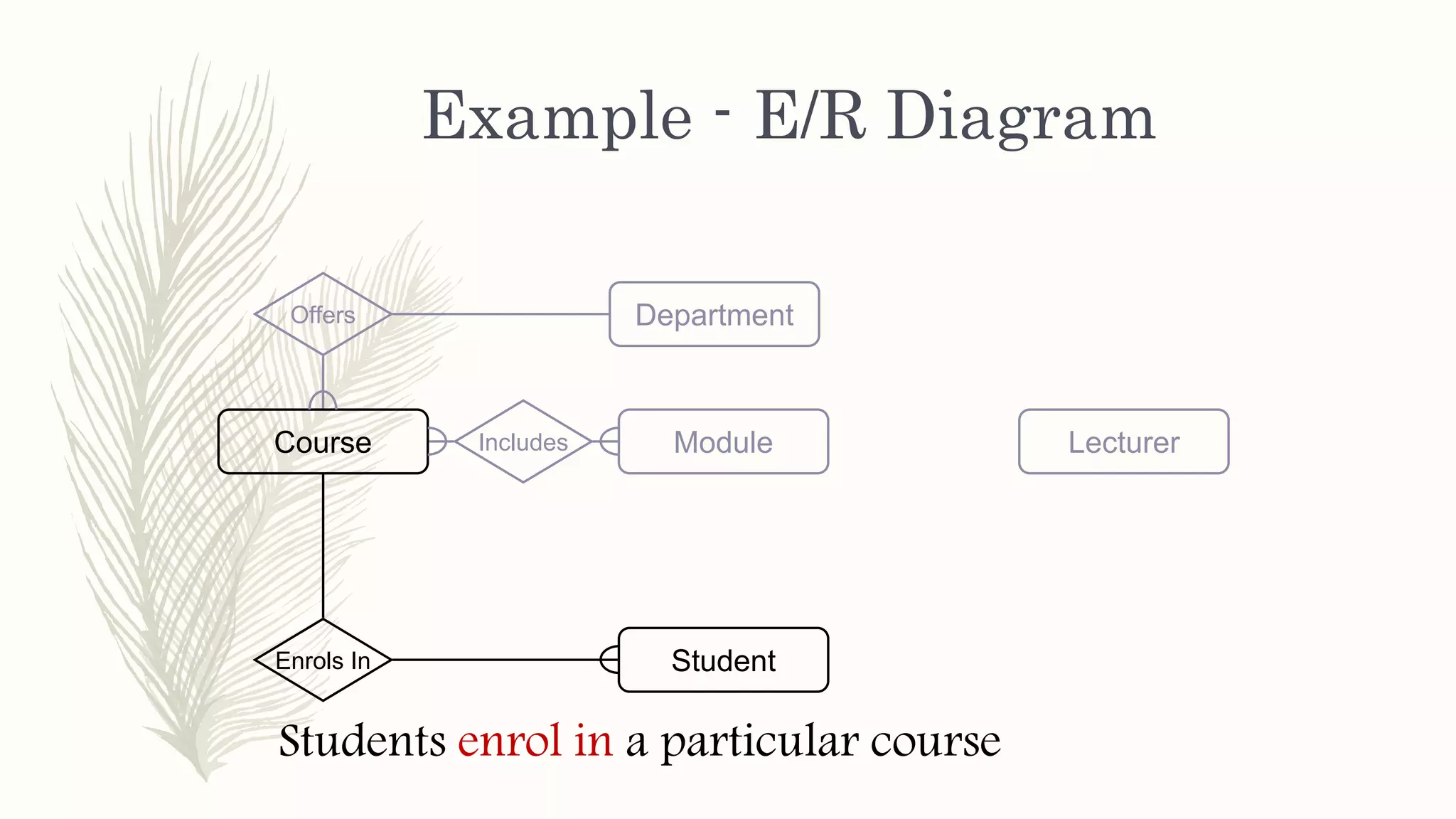
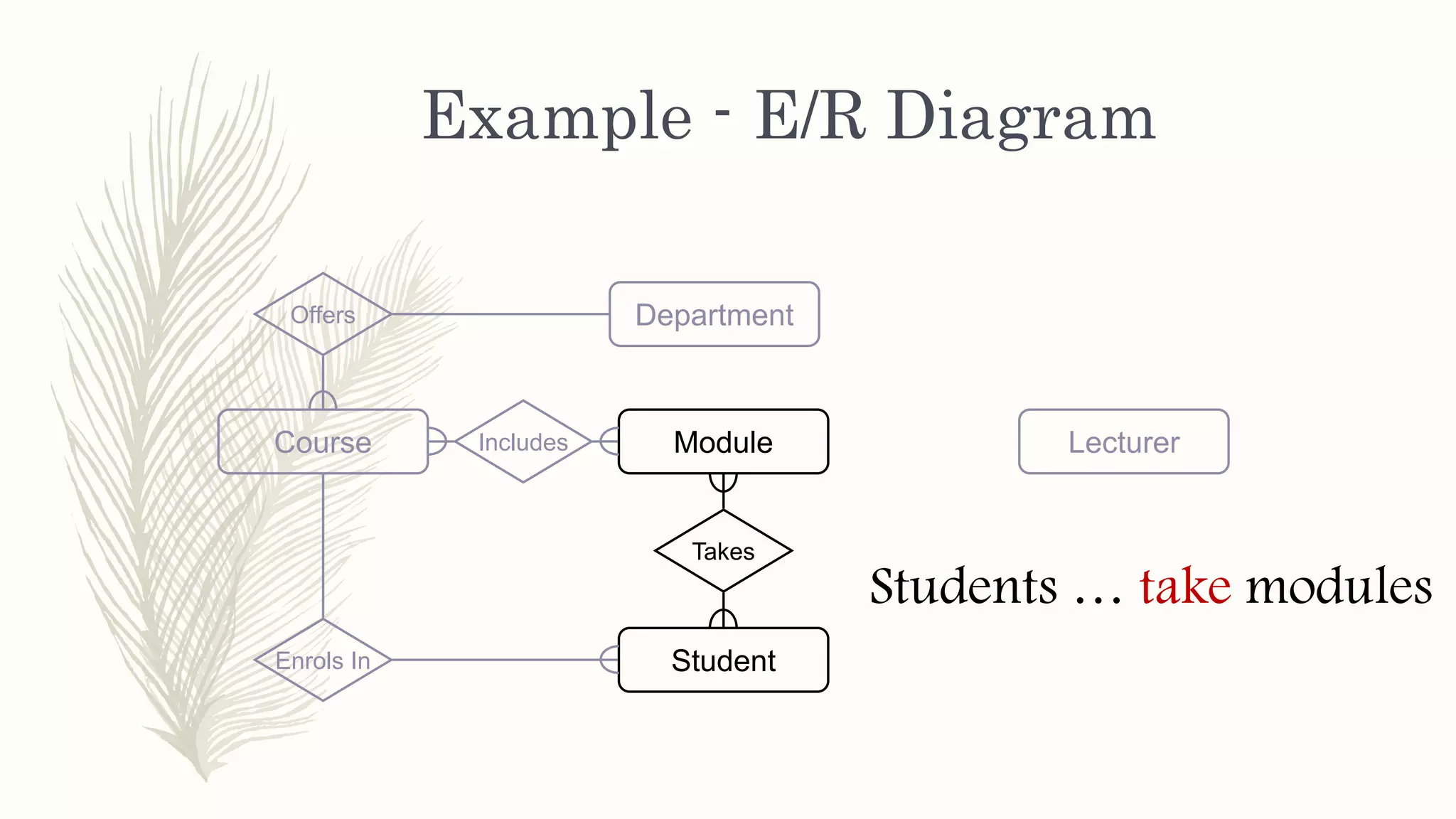
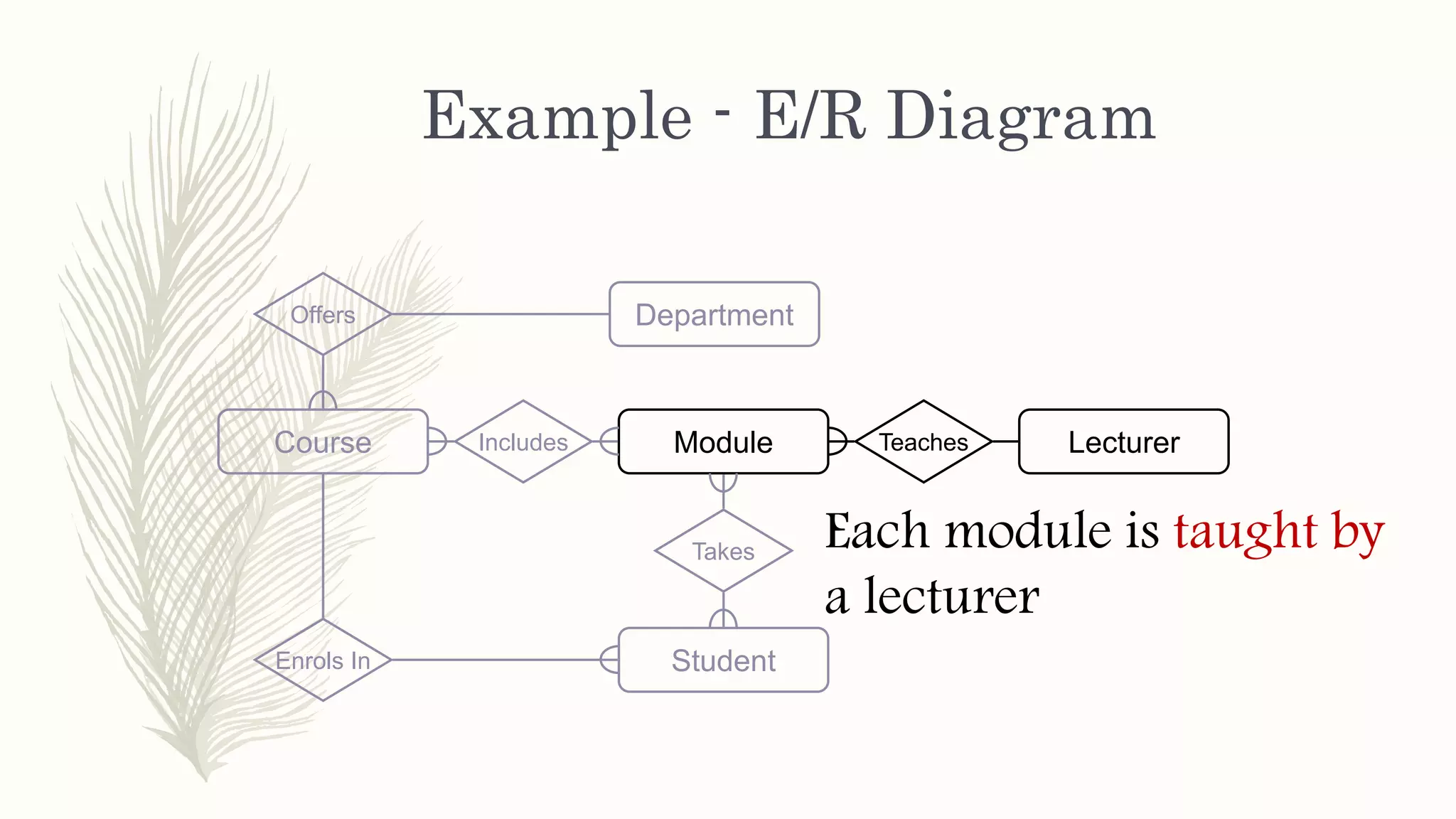
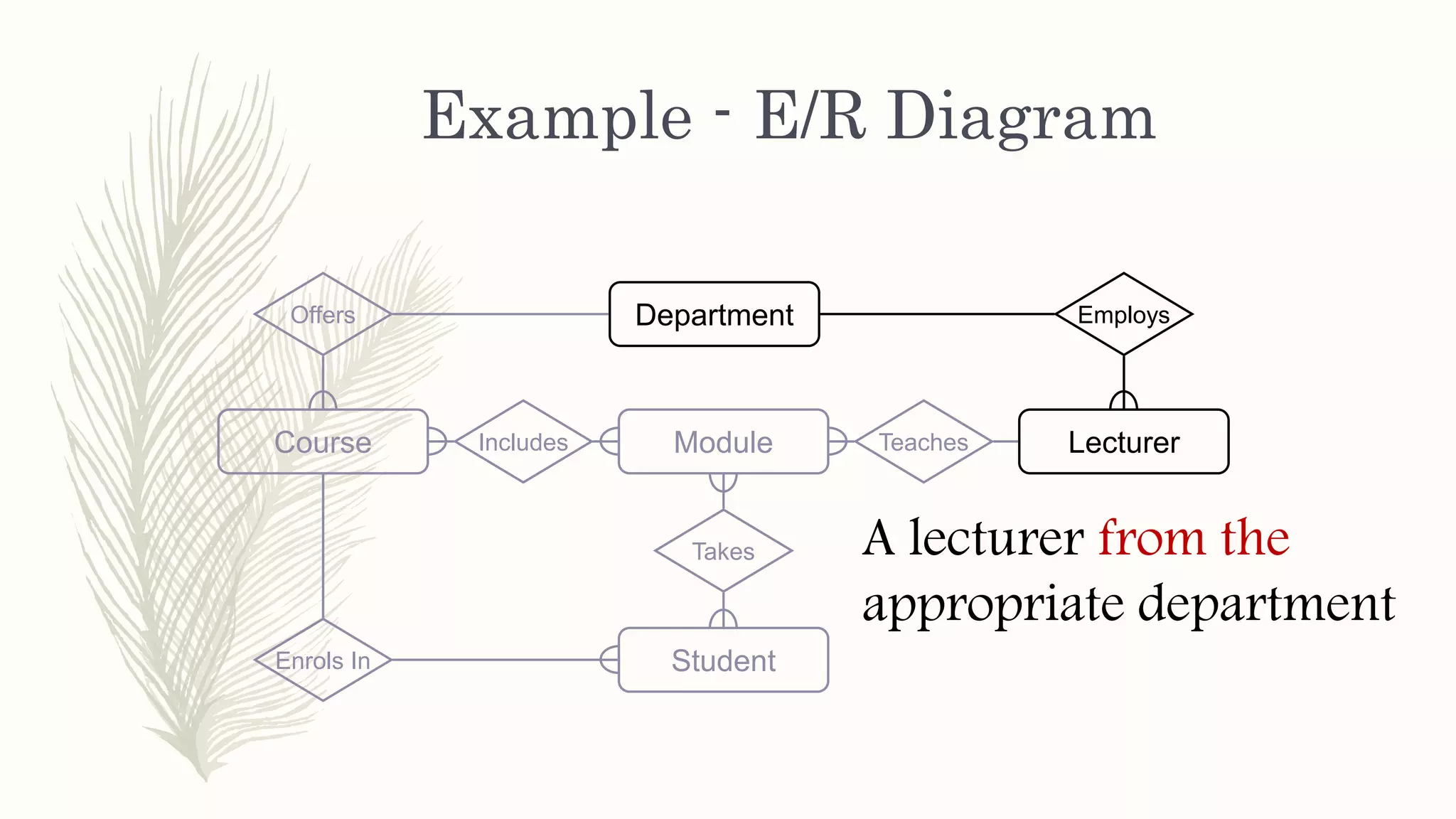
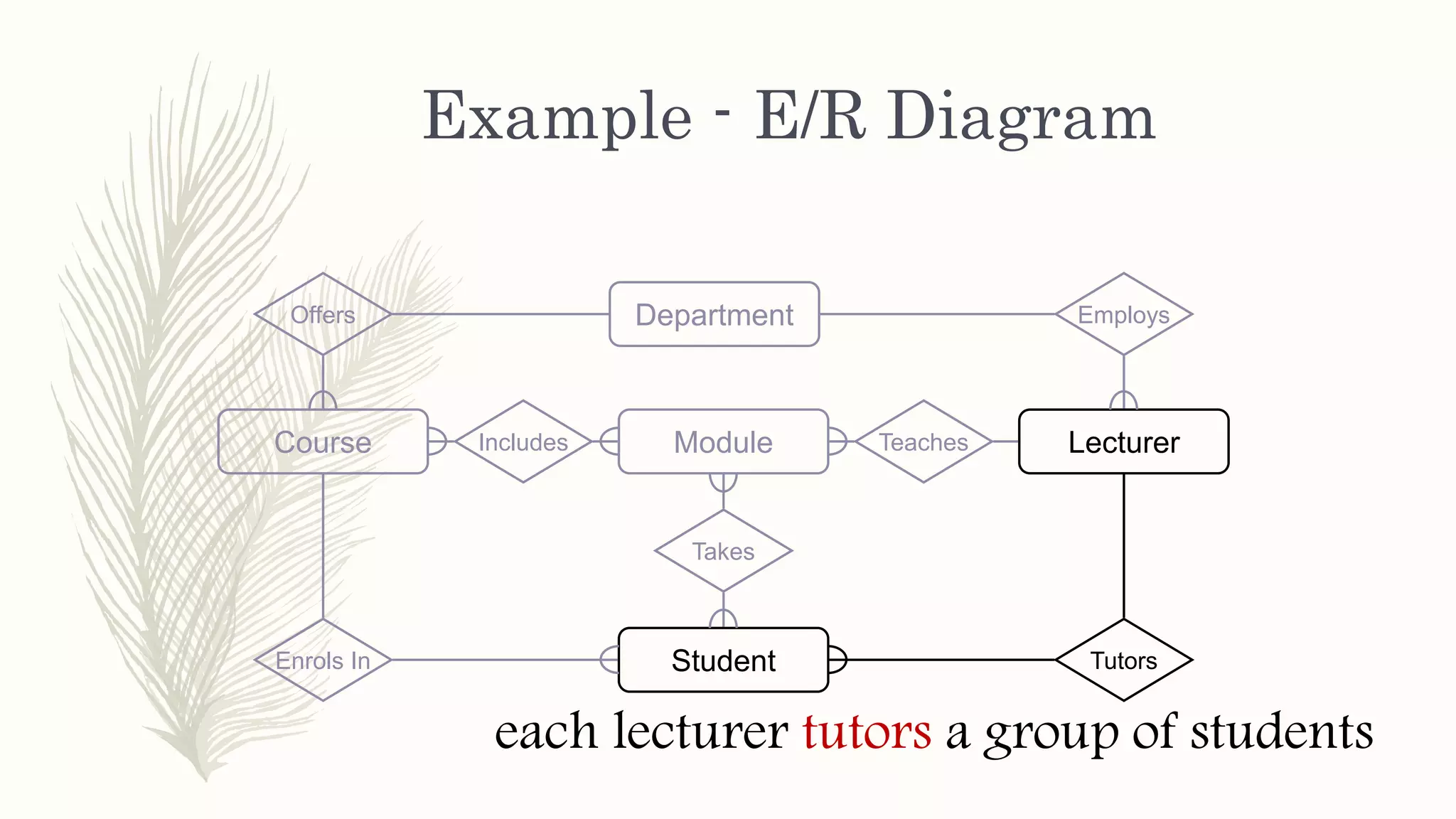
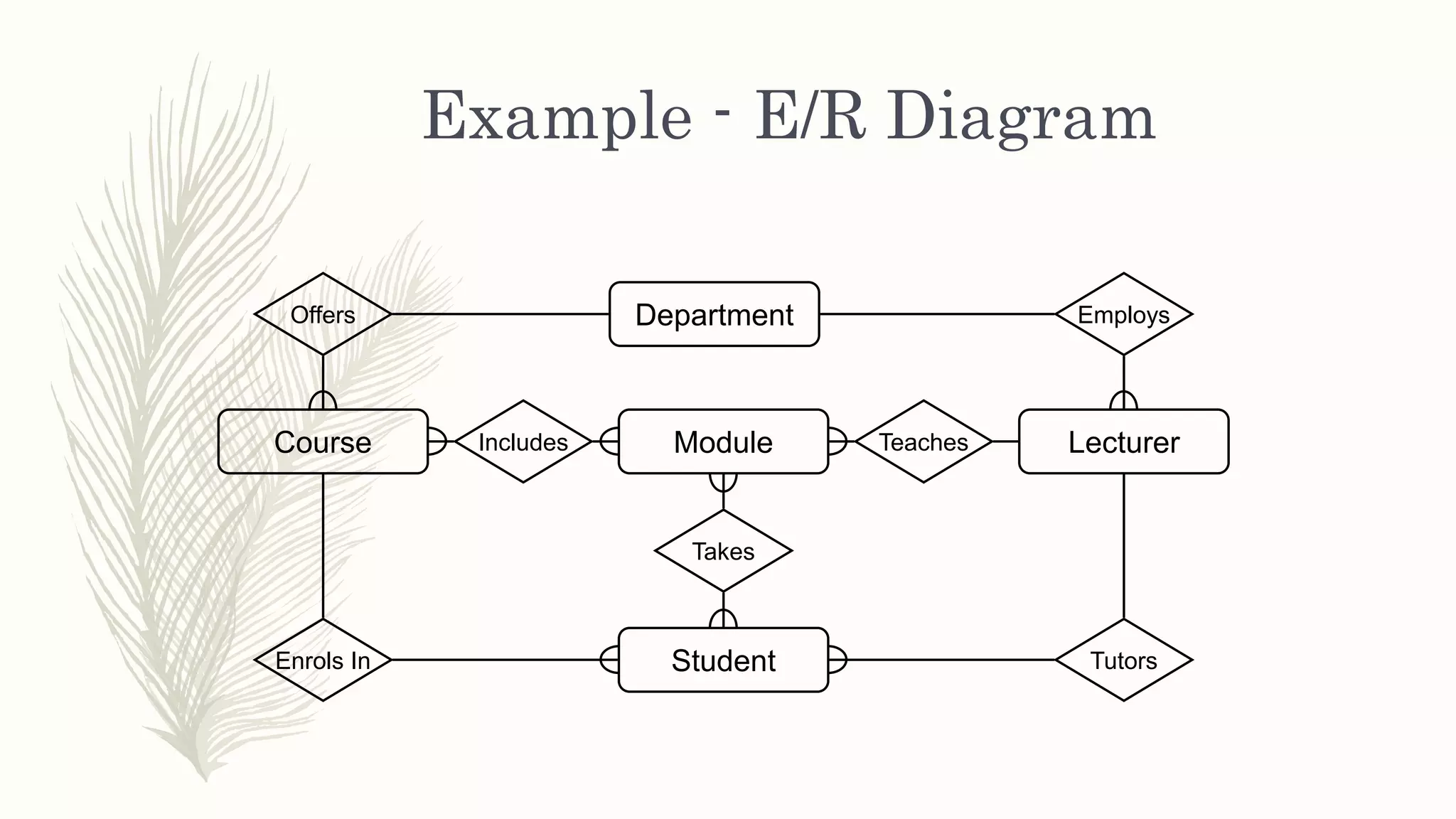
The document discusses entity relationship modeling. It defines key components of ER modeling including entities, attributes, relationships and constraints. Entities can be strong or weak. Relationships can be one to one, one to many, or many to many. Cardinality and participation constraints specify the minimum and maximum occurrences in a relationship. An example ER diagram is provided for a university system with entities for departments, courses, modules, students, and lecturers and the relationships between them.