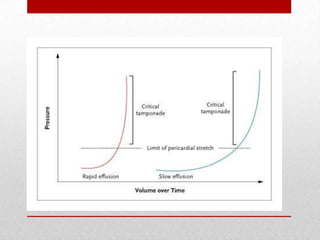
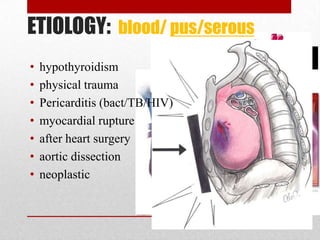
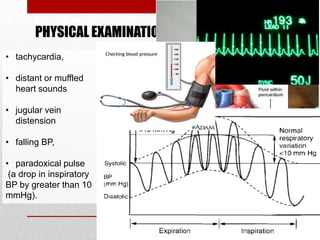
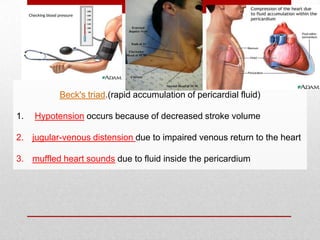
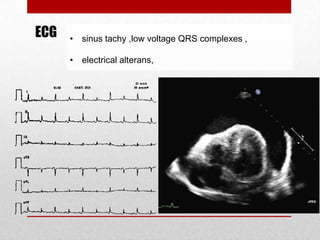
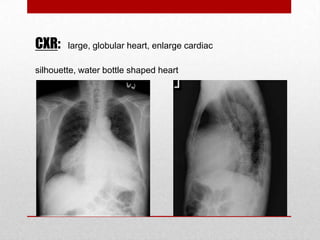
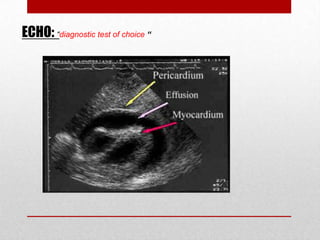
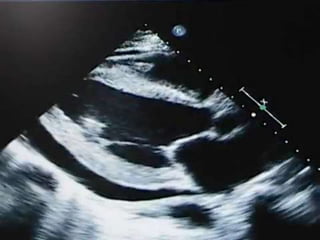
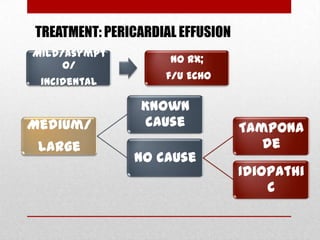
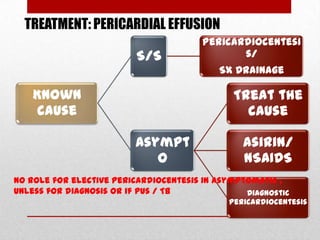
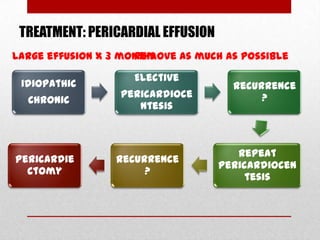
Pericardial effusion and cardiac tamponade are conditions caused by an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pericardial space. Cardiac tamponade occurs when excess fluid buildup leads to reduced ventricular filling and hemodynamic compromise. Symptoms include breathlessness, chest pain, and hypotension. Diagnosis is made through ECG, echocardiogram, and x-ray. Treatment depends on severity but may include medications, drainage of fluid via pericardiocentesis, or surgery. Cardiac tamponade requires urgent pericardiocentesis to drain fluid and prevent further hemodynamic compromise.