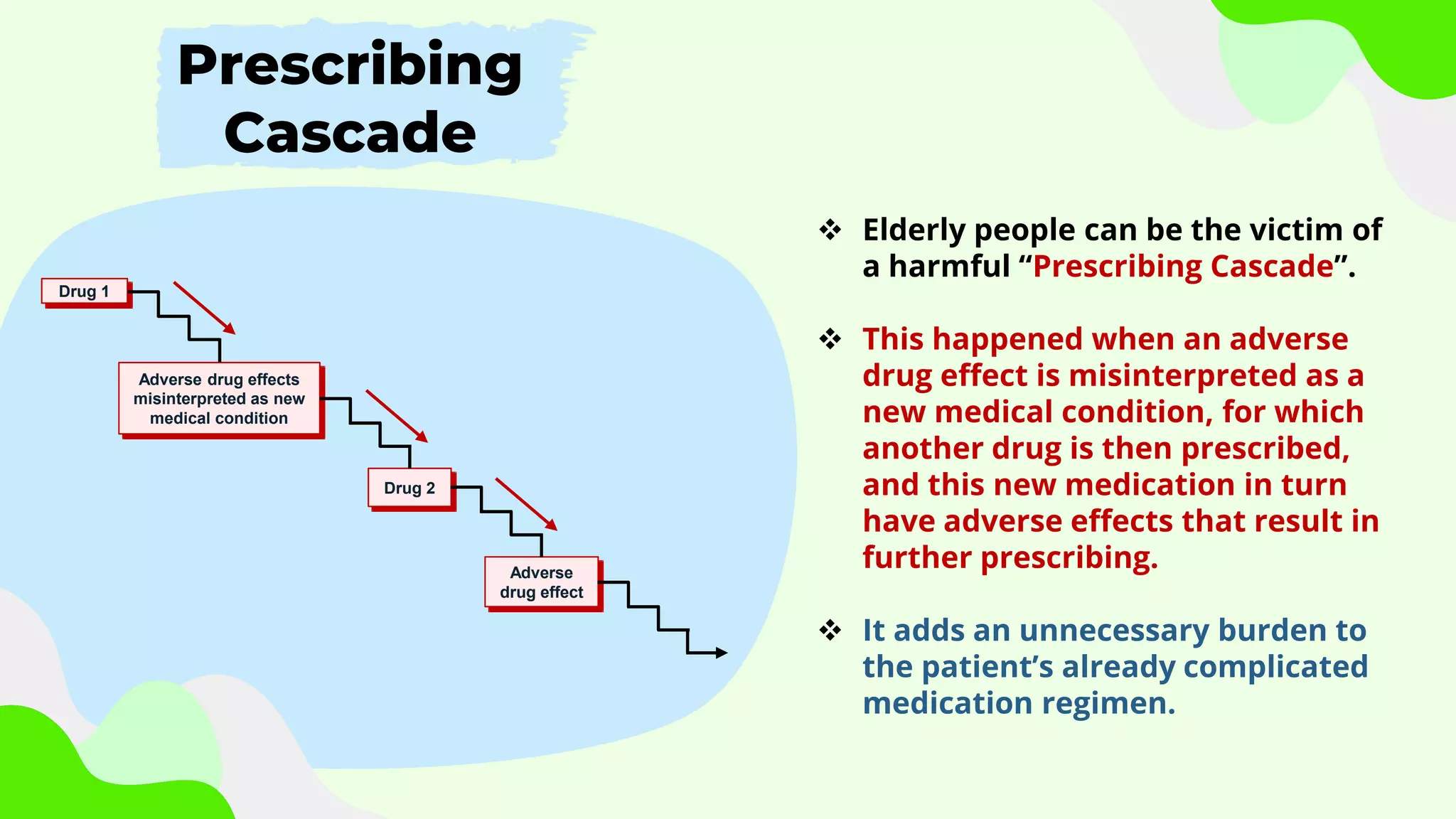
The document discusses the issue of polypharmacy in elderly patients, defining it as the use of five or more medications, and highlights its prevalence and significant consequences, such as adverse drug reactions and medication nonadherence. It emphasizes the importance of rational prescribing and deprescribing processes to improve medication management and reduce risks associated with polypharmacy. Tools like the Beers Criteria are recommended for healthcare providers to optimize medication use and enhance patient outcomes.