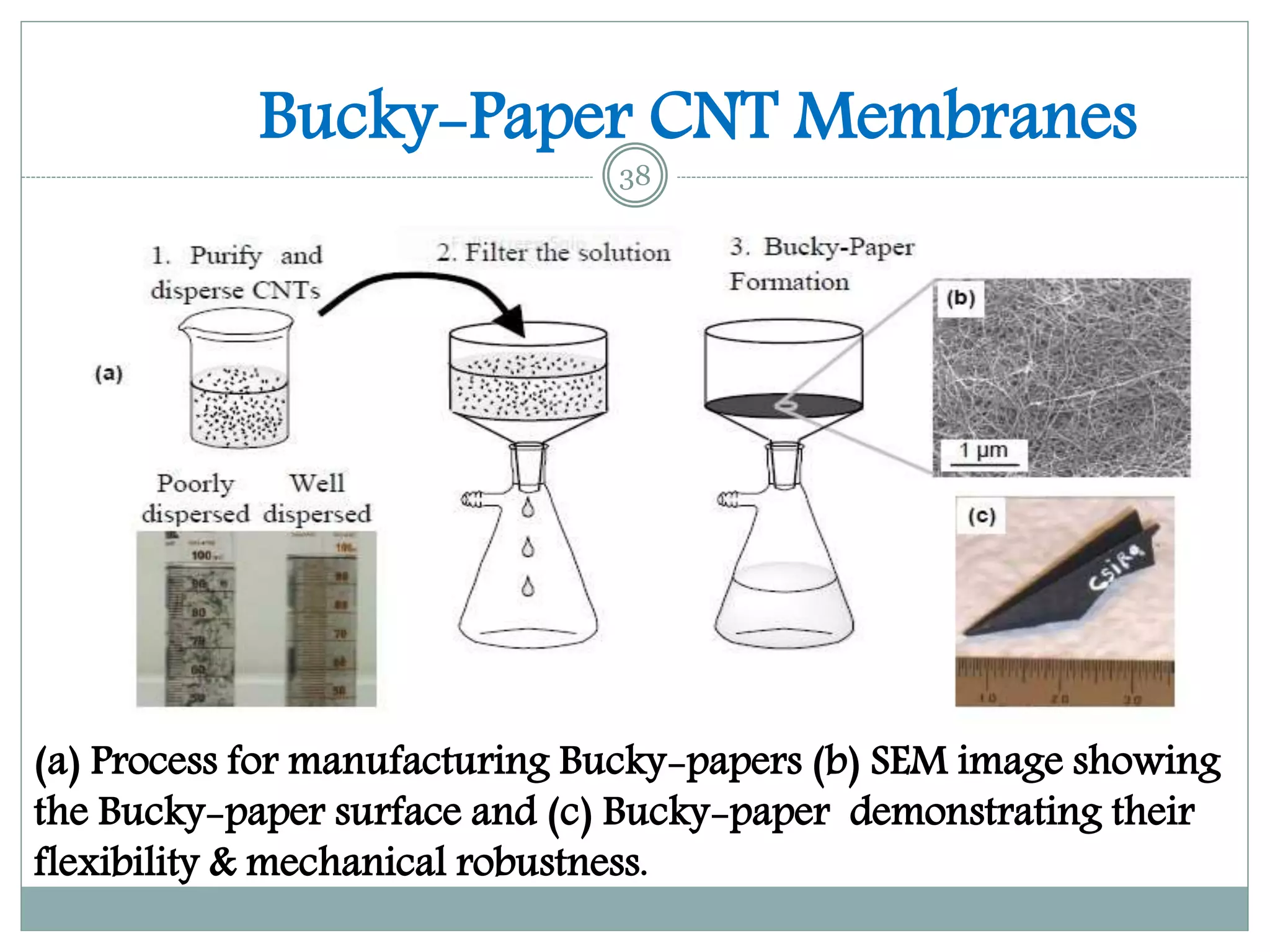
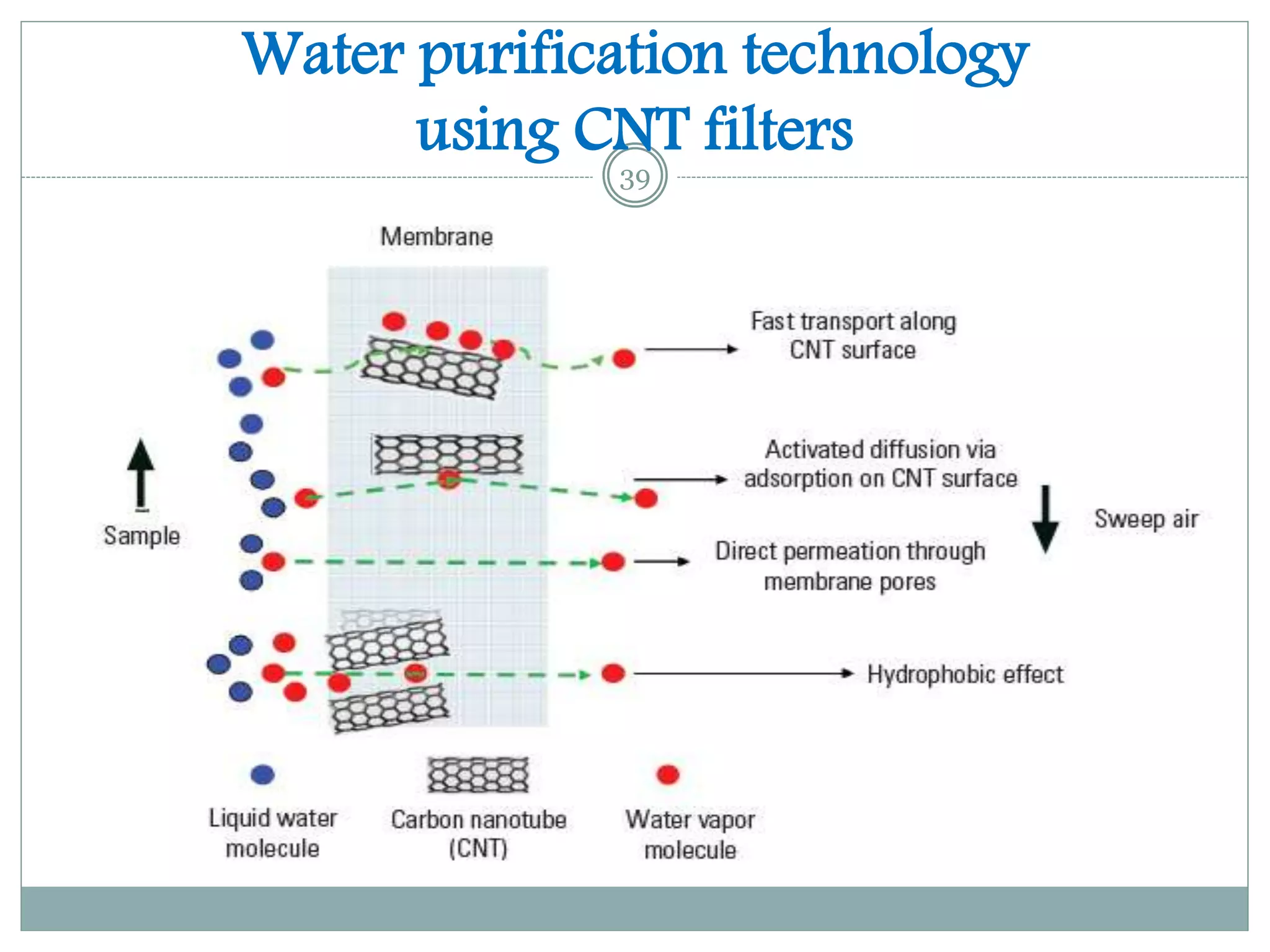
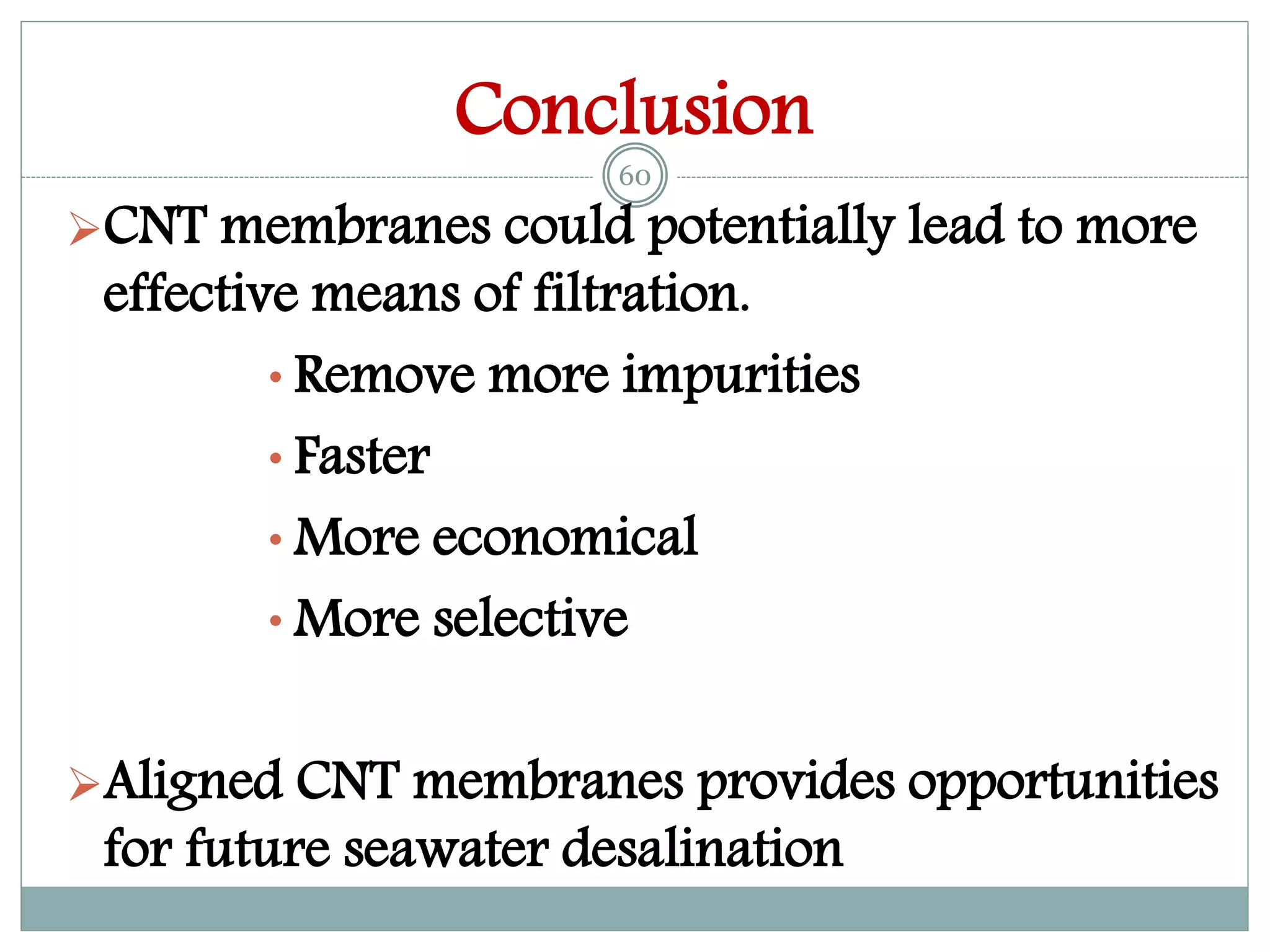
1) Carbon nanotube filters show potential for efficient and economical water purification by removing impurities faster than conventional methods at lower pressures and energy requirements.
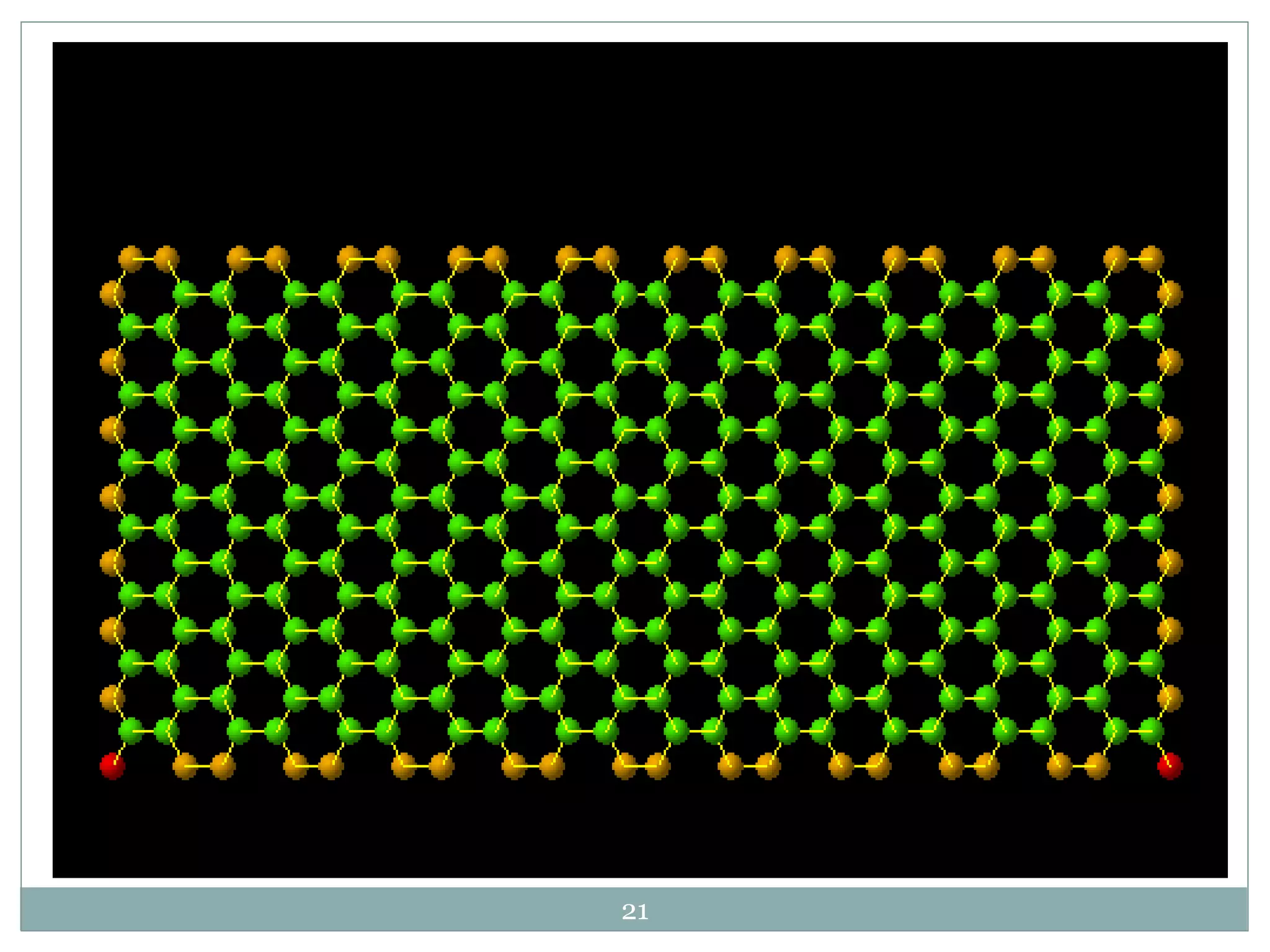
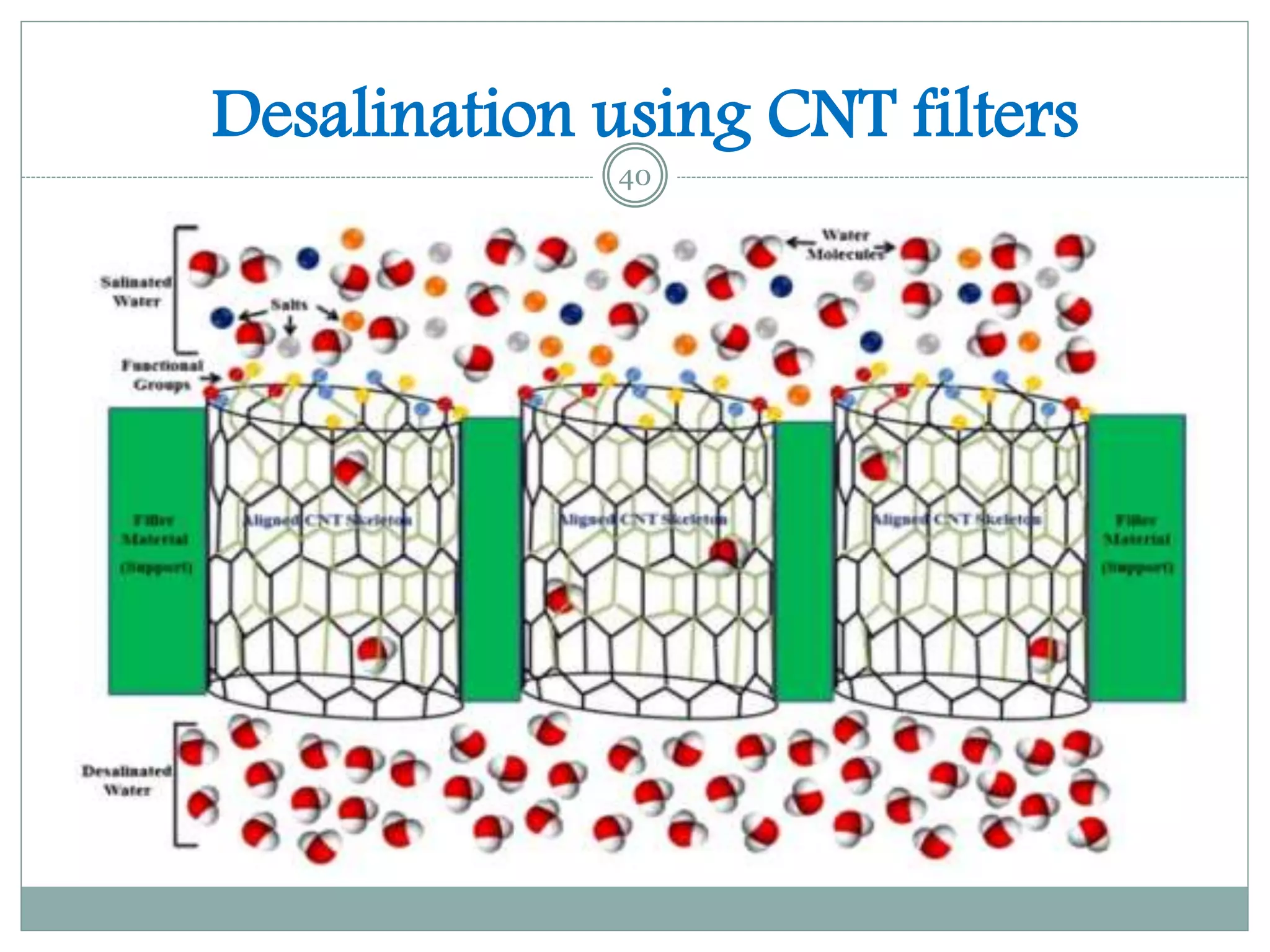
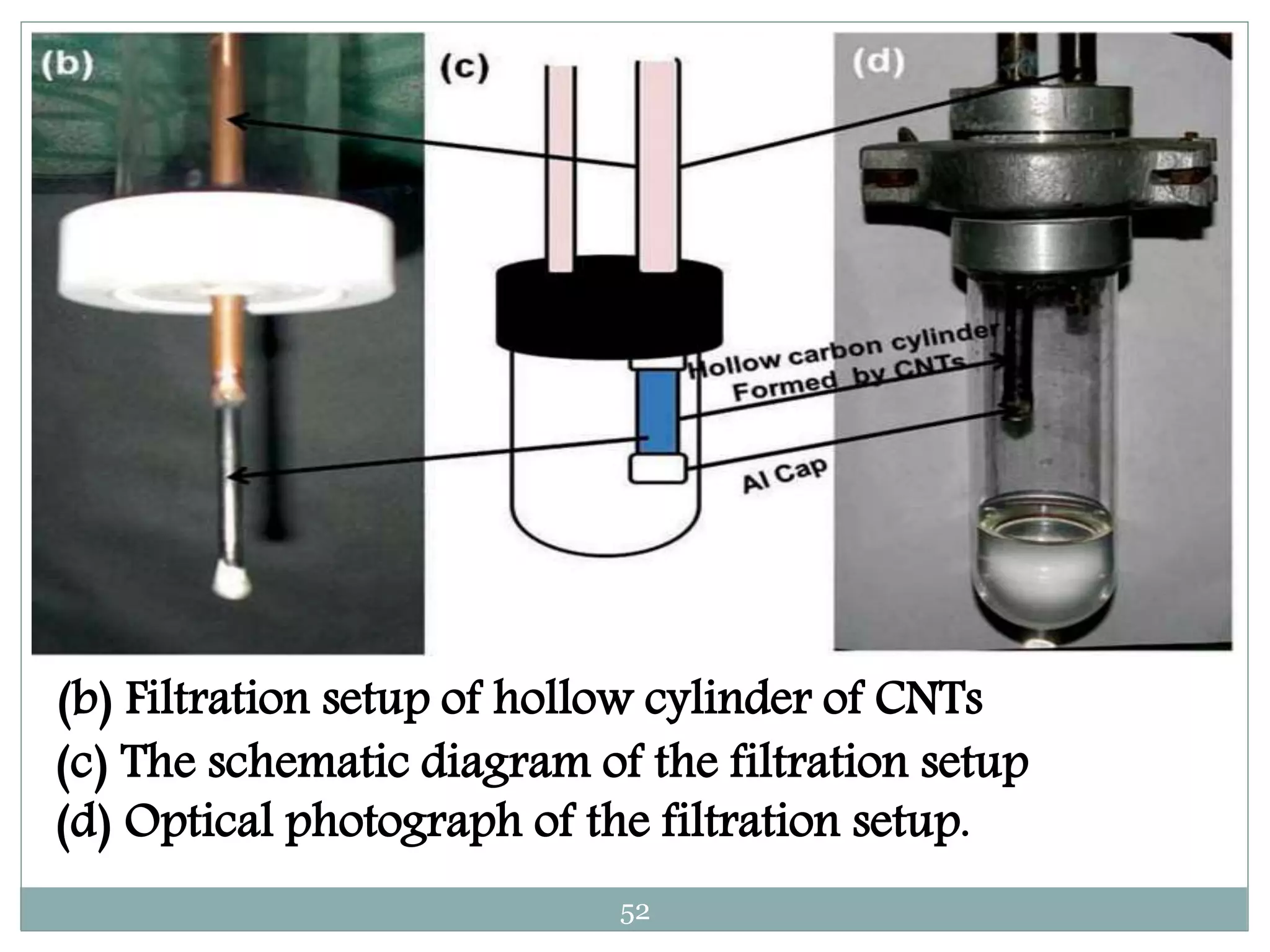
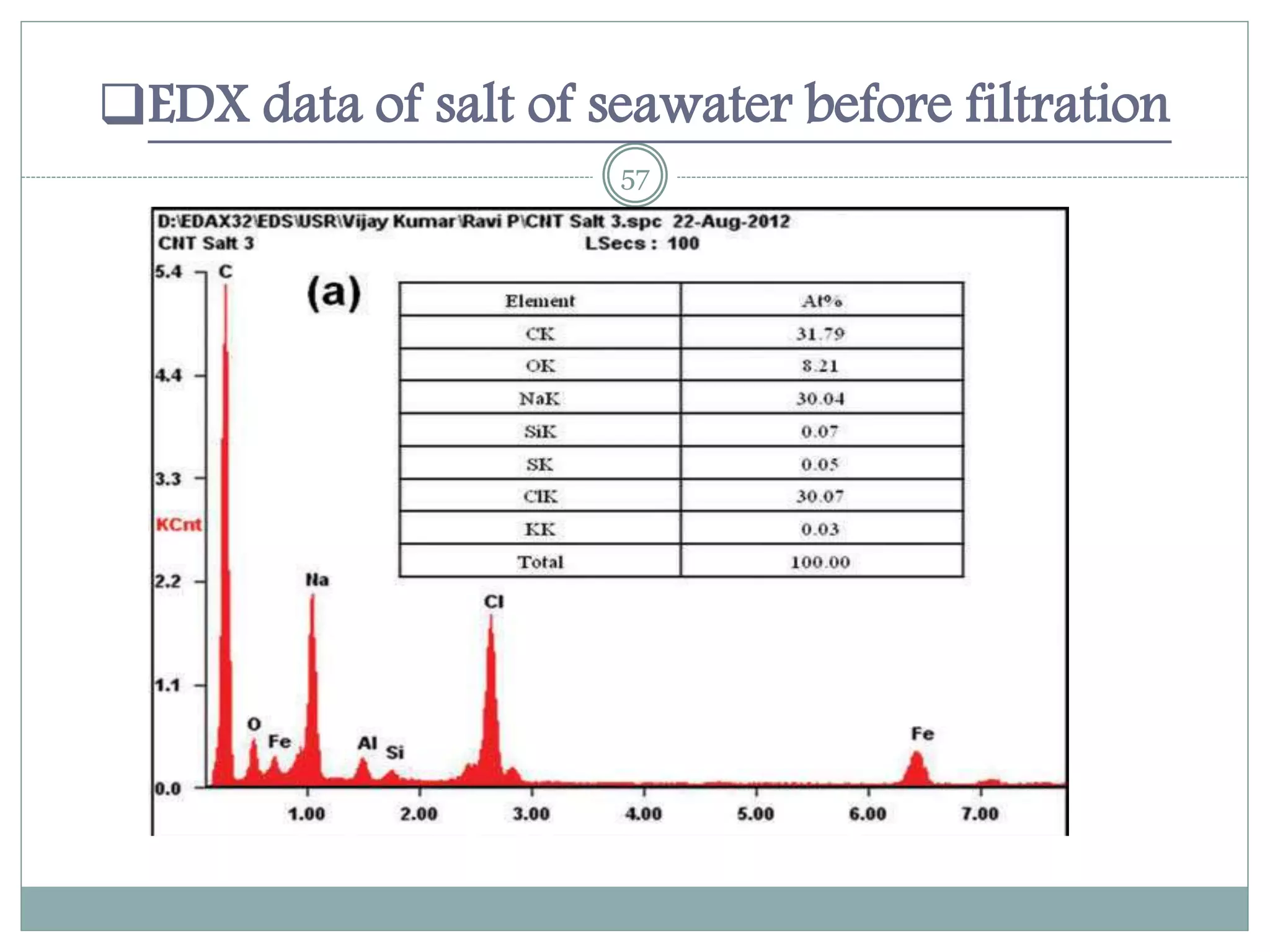
2) A case study demonstrated that a carbon hollow tube filter composed of radially aligned carbon nanotubes could filter sodium chloride from seawater, reducing sodium from 30.06% to 0.4% and chlorine from 11.44% to 0.17%.
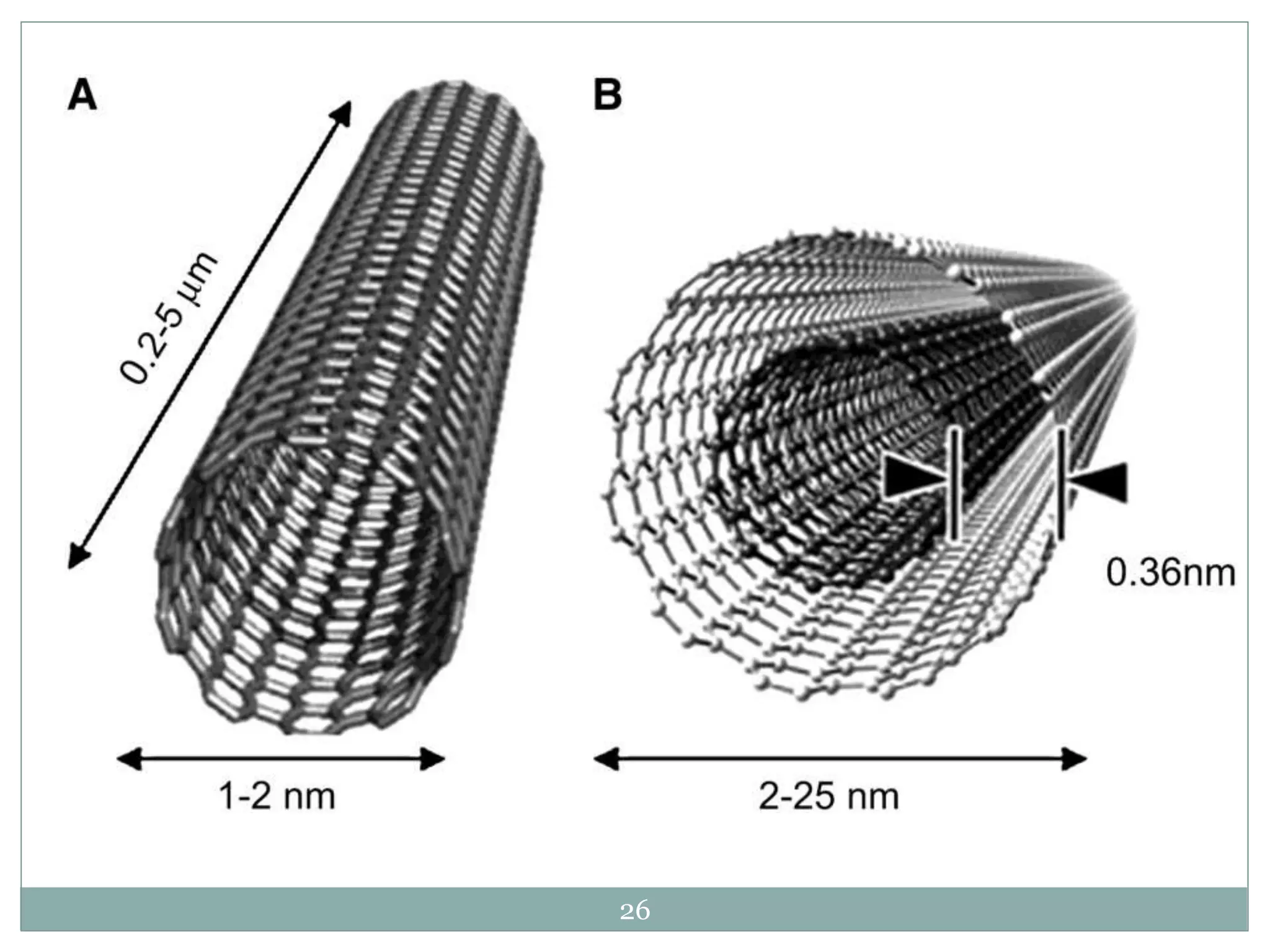
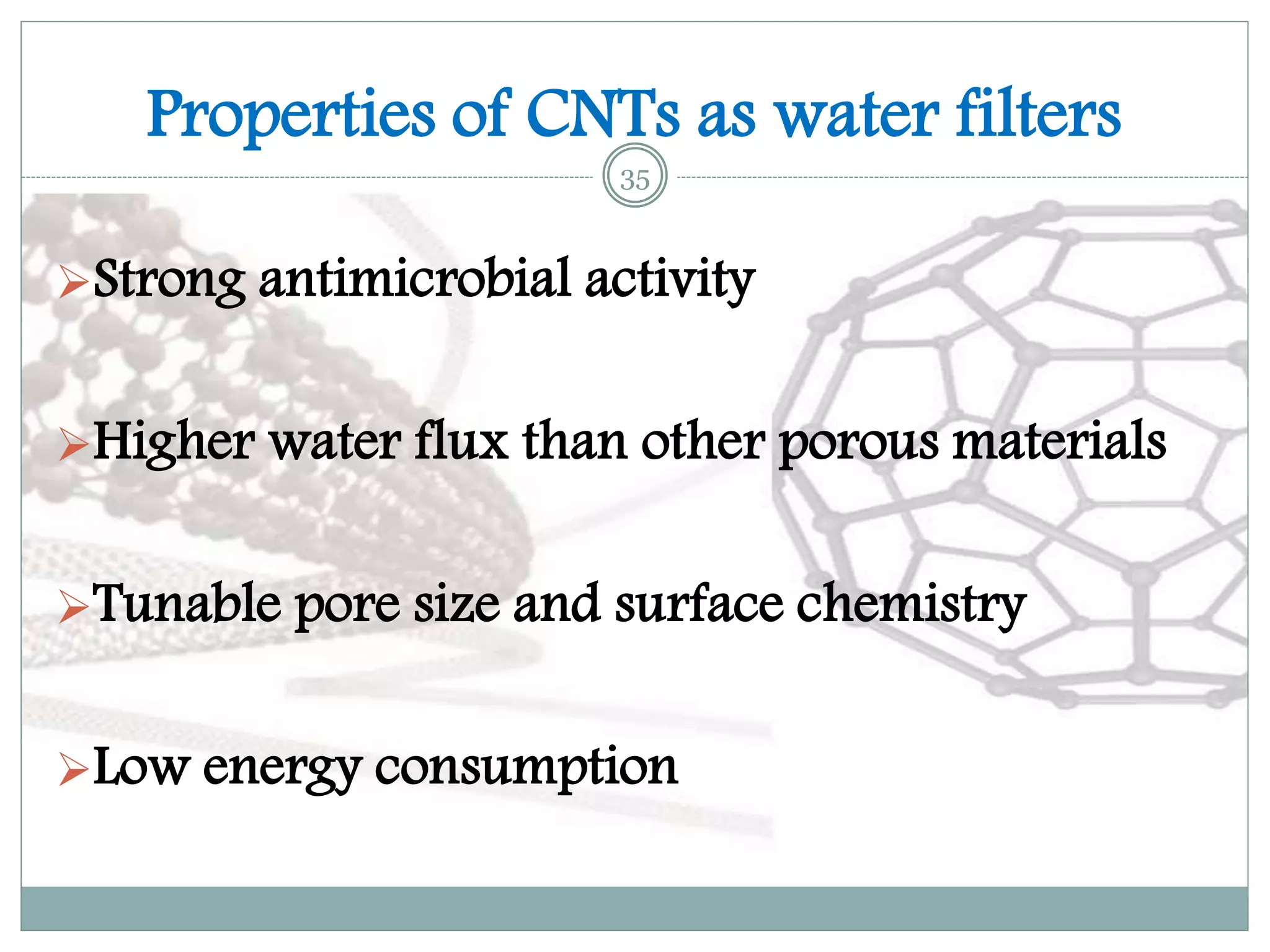
3) While carbon nanotube filters are still more expensive than other options, they provide very large surface areas, high water fluxes, tunable pore sizes, antibacterial properties, and the potential to scale up water purification technologies.














































![References
Harris, P. F. 1999. Carbon Nanotubes and Related
Structures .Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 123p.
Chaudhary Ravi Prakash Patel., Prashant Tripathi, O.N.,
Srivastava, O. N., and Yadav, T. P. 2013. Filtration of
sodium chloride from seawater using carbon hollow tube
composed of carbon nanotubes.Int. J. Smart and Nano
Materials. 5(3): 194-206. Available:
http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tsnm20 .pdf. [25
Nov.2014]
61](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbonnanotubefilterationforwaterpurification-150921054915-lva1-app6892/75/CARBON-NANOTUBE-FILTERATION-FOR-WATER-PURIFICATION-61-2048.jpg)

