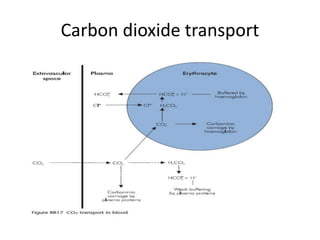
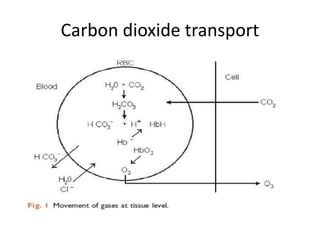
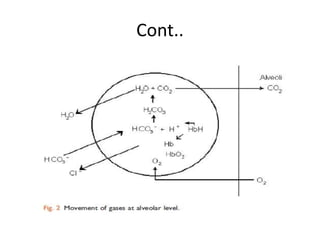
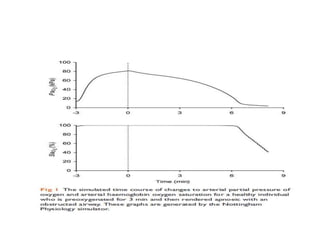
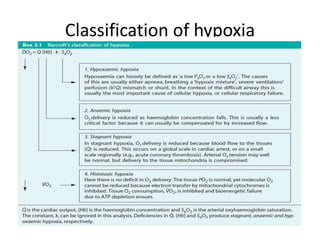
Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood in three ways: dissolved in solution, buffered with carbonic acid, and bound to hemoglobin. The Haldane effect refers to deoxygenated hemoglobin being more effective at carrying carbon dioxide, facilitating unloading in the lungs. During apnea, oxygen is removed from the lungs causing decreases in alveolar and arterial partial pressures of oxygen over time. Preoxygenation aims to maximize oxygen stores in the lungs and blood to delay the onset of critical hypoxia during periods of apnea.













![• The aim is to maximise O2 stores within the lung and the
blood.
• O2 content of blood
– O2 carried by Hb = [Hb] conc X saturation X 1.39 ml 100 ml1 blood
– O2 dissolved in plasma = O2 partial pressure (kPa) X 0.022 ml 100 ml1
plasma
• The major change during pre-oxygenation is in the amount of
O2 in the lungs.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbondioxidetransport-190215174359/85/Carbon-dioxide-transport-20-320.jpg)