Embed presentation
Download to read offline





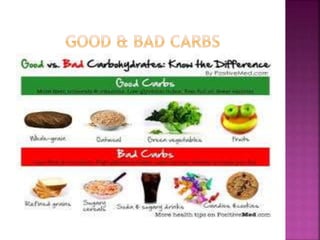




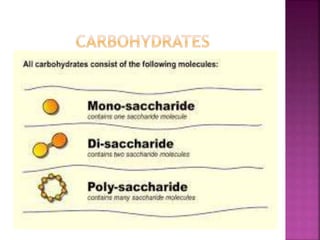
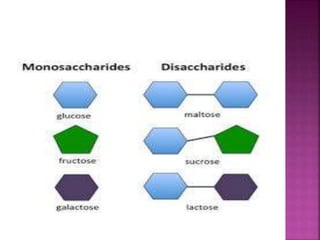
Carbohydrates are organic compounds made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 2:1 hydrogen to oxygen ratio. They provide the body's main source of fuel and energy for physical activity, brain function, and organ operation. Carbohydrates are classified as simple or complex, with simple carbohydrates like monosaccharides being the basic unit and complex carbohydrates like polysaccharides consisting of multiple sugar molecules bonded together. The main carbohydrates include glucose, fructose, lactose, sucrose, starch, cellulose, and glycogen.











